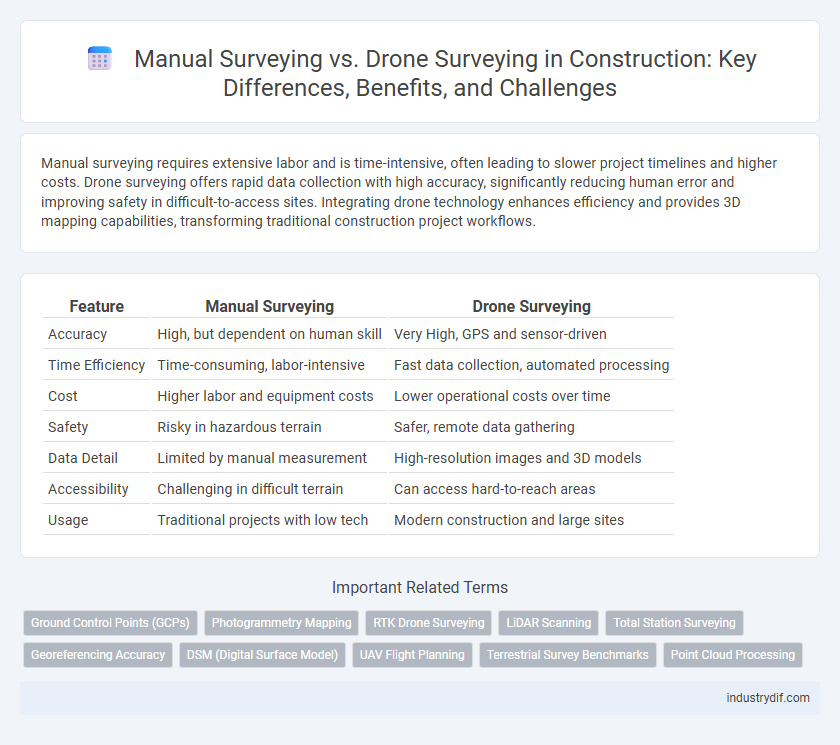
Manual surveying requires extensive labor and is time-intensive, often leading to slower project timelines and higher costs. Drone surveying offers rapid data collection with high accuracy, significantly reducing human error and improving safety in difficult-to-access sites. Integrating drone technology enhances efficiency and provides 3D mapping capabilities, transforming traditional construction project workflows.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Surveying | Drone Surveying |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High, but dependent on human skill | Very High, GPS and sensor-driven |
| Time Efficiency | Time-consuming, labor-intensive | Fast data collection, automated processing |
| Cost | Higher labor and equipment costs | Lower operational costs over time |
| Safety | Risky in hazardous terrain | Safer, remote data gathering |
| Data Detail | Limited by manual measurement | High-resolution images and 3D models |
| Accessibility | Challenging in difficult terrain | Can access hard-to-reach areas |
| Usage | Traditional projects with low tech | Modern construction and large sites |
Introduction to Surveying Methods in Construction
Manual surveying in construction relies on traditional tools like total stations, theodolites, and measuring tapes to collect precise land and site data through physical measurements. Drone surveying employs unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-resolution cameras and LiDAR sensors for rapid, extensive mapping and topographic data collection over large construction sites. Choosing between these methods depends on project scale, accuracy requirements, and time constraints, with drone surveying offering enhanced efficiency and data richness for complex or expansive projects.
Overview of Manual Surveying Techniques
Manual surveying techniques in construction rely on traditional tools such as theodolites, total stations, and measuring tapes to capture precise land measurements and topographical data. Surveyors use methods like triangulation, leveling, and traversing to establish accurate control points and map site contours, ensuring detailed ground verification. These proven techniques offer high accuracy for small to medium-scale projects but demand significant time, labor, and physical access to survey areas.
Evolution and Adoption of Drone Surveying
Drone surveying has revolutionized construction site mapping by offering rapid data acquisition and high-resolution aerial imagery, significantly reducing manual labor and human error compared to traditional manual surveying methods. The adoption of drone surveying is accelerating due to advancements in GPS technology, improved drone endurance, and integrated photogrammetry software that enables precise 3D modeling and real-time data analysis. Construction firms benefit from enhanced project accuracy, faster decision-making, and cost efficiency as drone surveying continues to evolve and replace conventional manual techniques.
Accuracy and Precision: Manual vs Drone Surveying
Manual surveying relies on traditional tools like total stations and theodolites, offering high accuracy but is time-consuming and prone to human error in complex terrains. Drone surveying utilizes advanced GPS and photogrammetry technologies, delivering high precision with rapid data collection and the ability to cover large areas efficiently. Studies reveal drone surveys can achieve accuracy within a few centimeters, often surpassing manual methods in both consistency and detail resolution for construction site mapping.
Time Efficiency Comparison
Manual surveying in construction is significantly more time-consuming, often requiring days or weeks to complete large site measurements due to physical constraints and equipment setup. Drone surveying dramatically reduces data collection time, capturing high-resolution imagery and topographic data within hours and enabling faster processing through advanced software. This enhanced time efficiency accelerates project timelines and improves decision-making accuracy on-site.
Cost Implications in Surveying Methods
Manual surveying typically involves higher labor costs and longer project durations due to intensive fieldwork and the need for specialized personnel. Drone surveying significantly reduces expenses by minimizing manpower, accelerating data collection, and lowering equipment costs through advanced aerial technology. The integration of drones in construction projects leads to improved budget efficiency and faster decision-making processes.
Safety Considerations in Surveying Practices
Manual surveying in construction poses higher safety risks due to physical exposure to hazardous environments, uneven terrains, and heavy machinery, increasing potential for accidents and injuries. Drone surveying minimizes these dangers by allowing remote data collection, reducing on-site personnel exposure to risky conditions such as unstable structures or high traffic zones. Integrating drone technology enhances overall site safety protocols, while ensuring accurate topographic and structural analysis without compromising worker well-being.
Accessibility to Challenging Survey Sites
Manual surveying often faces significant limitations in accessing challenging survey sites due to difficult terrain, hazards, and time constraints, requiring extensive manpower and specialized equipment. Drone surveying enhances site accessibility by capturing high-resolution aerial data remotely, allowing rapid, safe assessment of areas such as steep slopes, dense vegetation, and hazardous zones. This technological advancement reduces project timelines and improves data accuracy in construction site surveys, particularly in environments previously considered inaccessible.
Data Integration and Digital Output
Manual surveying relies on traditional tools such as total stations and GPS to collect spatial data, requiring extensive post-processing to integrate information into CAD or GIS platforms. Drone surveying captures high-resolution aerial imagery and LiDAR data that can be rapidly processed into digital 3D models and orthomosaic maps, enabling seamless integration with BIM systems for real-time analysis. Digital output from drones enhances accuracy and efficiency in construction projects by providing comprehensive data sets that improve decision-making and reduce errors during the planning and execution phases.
Future Trends in Construction Surveying
Future trends in construction surveying emphasize integration of drone surveying technologies with AI-powered data analytics, enhancing precision and efficiency on sites. Manual surveying remains vital for intricate or inaccessible areas, but drones enable rapid, high-resolution topographic mapping and real-time progress monitoring. Advancements in automated image processing and 3D modeling from drone-captured data are set to revolutionize project management and reduce overall surveying costs.
Related Important Terms
Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Ground Control Points (GCPs) serve critical roles in both manual surveying and drone surveying for ensuring spatial accuracy and georeferencing precision in construction projects. Drone surveying often leverages GCPs for high-resolution mapping and 3D modeling, enabling faster data acquisition compared to labor-intensive manual surveying methods that rely on traditional total stations and GPS equipment for precise point measurements.
Photogrammetry Mapping
Manual surveying relies on traditional techniques such as total stations and GPS, offering high accuracy but requiring extensive time and labor for photogrammetry mapping. Drone surveying captures high-resolution aerial images quickly, enabling efficient photogrammetry mapping with advanced software that generates detailed 3D models and orthomosaics, significantly enhancing data collection speed and site analysis accuracy.
RTK Drone Surveying
RTK drone surveying enhances construction site accuracy by providing real-time kinematic positioning with centimeter-level precision, significantly reducing errors compared to traditional manual surveying methods. This technology accelerates data collection and processing, enabling efficient topographic mapping and earthwork calculations that improve project timelines and cost management.
LiDAR Scanning
Manual surveying relies on traditional tools like total stations and GPS receivers to collect precise ground measurements, but it is time-consuming and limited by terrain accessibility. Drone surveying equipped with LiDAR scanning captures high-density, three-dimensional point clouds rapidly over large or complex construction sites, enhancing accuracy and enabling detailed topographic mapping.
Total Station Surveying
Total Station Surveying offers high precision and real-time data integration essential for construction site measurements, outperforming manual surveying techniques in accuracy and efficiency. Unlike drone surveying, which provides broad aerial perspectives, Total Station enables detailed ground-level measurements critical for complex structural layouts and boundary determinations.
Georeferencing Accuracy
Manual surveying achieves georeferencing accuracy through precise instrument calibration and skilled operator measurements, but is often limited by physical access and environmental conditions. Drone surveying leverages high-resolution GPS and advanced photogrammetry, providing rapid, consistent georeferencing with centimeter-level accuracy across large or difficult terrains.
DSM (Digital Surface Model)
Manual surveying produces accurate Digital Surface Models (DSM) through ground measurements but is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Drone surveying rapidly captures high-resolution DSM data over large construction sites with enhanced detail and efficiency, improving project timelines and cost-effectiveness.
UAV Flight Planning
UAV flight planning enhances drone surveying precision by optimizing flight paths, altitude, and sensor settings, enabling efficient data capture over large construction sites compared to manual surveying. Accurate UAV flight planning reduces human error and accelerates topographical data collection, improving project timelines and cost-effectiveness in construction management.
Terrestrial Survey Benchmarks
Manual surveying of terrestrial survey benchmarks relies on handheld instruments and physical measurements, offering high accuracy but requiring significant time and labor. Drone surveying automates data collection with aerial imaging and GPS technology, enhancing speed and coverage while maintaining reliable accuracy for benchmark verification.
Point Cloud Processing
Manual surveying in construction relies on traditional measurements that can be time-consuming and prone to human error, resulting in less dense and lower accuracy point cloud data. Drone surveying generates high-resolution, precise point clouds quickly using LiDAR or photogrammetry, significantly enhancing construction site mapping, monitoring, and progress tracking efficiency.
Manual Surveying vs Drone Surveying Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com