Retaining walls provide essential structural support by holding back soil and preventing erosion, making them crucial in landscaping and construction projects where terrain stabilization is required. Living walls incorporate vegetation into vertical structures, enhancing aesthetic appeal and improving air quality while offering natural insulation. Both solutions address environmental challenges, but retaining walls prioritize durability and stability, whereas living walls emphasize sustainability and visual integration with the surrounding landscape.
Table of Comparison
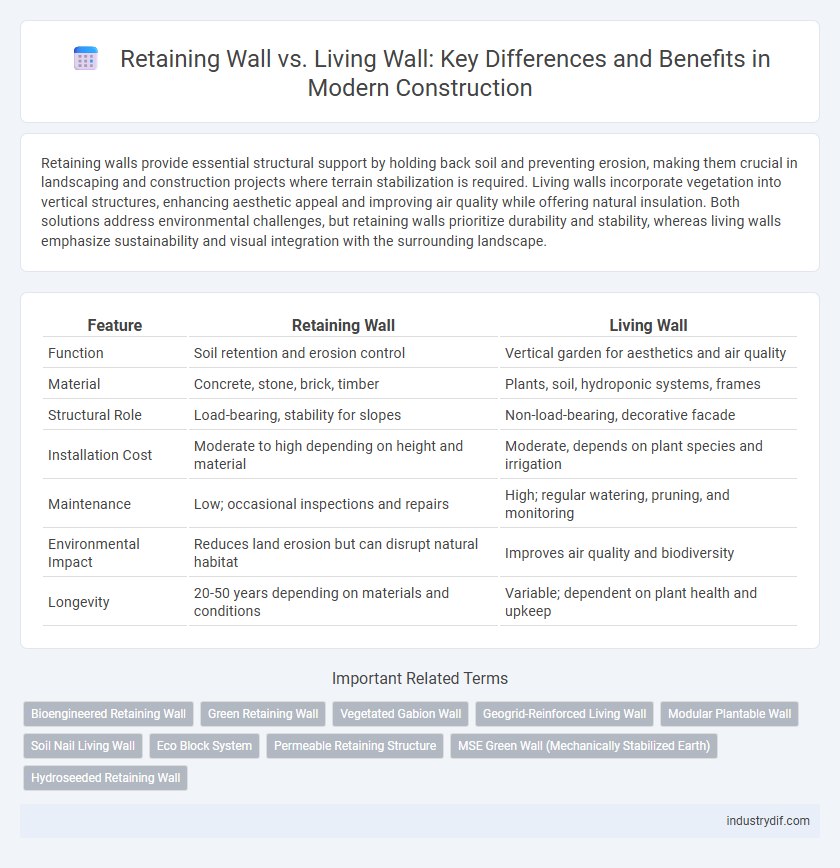
| Feature | Retaining Wall | Living Wall |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Soil retention and erosion control | Vertical garden for aesthetics and air quality |
| Material | Concrete, stone, brick, timber | Plants, soil, hydroponic systems, frames |
| Structural Role | Load-bearing, stability for slopes | Non-load-bearing, decorative facade |
| Installation Cost | Moderate to high depending on height and material | Moderate, depends on plant species and irrigation |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional inspections and repairs | High; regular watering, pruning, and monitoring |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces land erosion but can disrupt natural habitat | Improves air quality and biodiversity |
| Longevity | 20-50 years depending on materials and conditions | Variable; dependent on plant health and upkeep |
Understanding Retaining Walls: Function and Purpose
Retaining walls are engineered structures designed to hold back soil and prevent erosion, ensuring slope stability and protecting built environments. They are crucial in managing elevation changes and supplying lateral support to vertical or near-vertical grade changes in construction projects. These walls are typically constructed from concrete, stone, or timber, prioritizing durability and load-bearing capacity for effective soil retention.
What Is a Living Wall? Definition and Applications
A living wall, also known as a green wall or vertical garden, is a structure covered with vegetation that is rooted in a growing medium attached to a wall. These walls provide benefits such as improving air quality, reducing noise pollution, and enhancing building insulation, making them ideal for urban environments and sustainable construction projects. Common applications of living walls include commercial building facades, interior office spaces, and public installations aimed at promoting biophilic design and environmental well-being.
Key Differences Between Retaining Walls and Living Walls
Retaining walls are engineered structures designed to hold back soil and prevent erosion, typically constructed using concrete, stone, or timber to provide stability on sloped terrain. Living walls, also known as green walls, integrate vegetation into vertical surfaces, enhancing environmental benefits such as air purification and insulation while improving aesthetic appeal. Unlike retaining walls, living walls prioritize ecological functions and biodiversity, often requiring irrigation and maintenance to sustain plant life.
Structural Benefits of Retaining Walls in Construction
Retaining walls provide crucial structural support by stabilizing soil and preventing erosion on sloped terrains, which safeguards foundations and infrastructure. Engineered with materials like concrete, stone, or reinforced earth, retaining walls effectively manage lateral earth pressures and water drainage. Unlike living walls, which primarily offer aesthetic and environmental benefits, retaining walls are essential for enhancing site stability and ensuring long-term structural integrity in construction projects.
Environmental Impact: Living Wall Advantages
Living walls significantly improve air quality by filtering pollutants and increasing oxygen levels, promoting healthier urban environments. Their natural insulation properties reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling, lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike traditional retaining walls, living walls support biodiversity by providing habitats for insects and birds, enhancing local ecosystems.
Cost Considerations: Retaining Wall vs Living Wall
Retaining walls typically involve higher upfront costs due to materials like concrete, stone, or brick and labor-intensive construction, while living walls often require investment in irrigation systems and ongoing plant maintenance. Long-term expenses for retaining walls include potential repairs from soil pressure or water damage, whereas living walls demand consistent upkeep such as watering, fertilizing, and plant replacement. Budget planning must consider initial installation costs and lifecycle maintenance to determine the most cost-effective solution for site-specific needs.
Material Options for Retaining and Living Walls
Retaining walls commonly utilize concrete, stone, and timber for durability and structural support, effectively handling soil pressure and erosion control. Living walls incorporate materials such as modular panels, felt, or metal frames combined with soil substrates to support plant growth and ensure proper drainage. Both wall types require tailored material selections that balance functionality, aesthetic appeal, and environmental considerations in construction projects.
Maintenance Requirements for Both Wall Types
Retaining walls require regular inspections for structural integrity, prompt repairs for cracks or erosion, and occasional cleaning to prevent buildup of debris. Living walls demand consistent irrigation, pruning, and nutrient management to maintain plant health and prevent overgrowth or pest infestations. Both wall types benefit from tailored maintenance plans to ensure long-term durability and aesthetic appeal.
Common Mistakes in Wall Selection and Installation
Common mistakes in retaining wall and living wall selection include underestimating soil pressure for retaining walls, leading to structural failure, and ignoring proper drainage systems, causing water buildup and wall instability. For living walls, improper plant selection incompatible with local climate and insufficient irrigation planning result in poor plant health and wall degradation. Both wall types require thorough site analysis and adherence to engineering standards to ensure durability and functionality.
Choosing the Right Wall Solution for Your Project
Retaining walls provide essential structural support by holding back soil and preventing erosion, ideal for sloped sites and heavy load conditions. Living walls enhance aesthetic appeal and environmental benefits, offering natural insulation, air purification, and improved biodiversity, suitable for urban and green building projects. Selecting the right wall solution depends on site conditions, project goals, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Related Important Terms
Bioengineered Retaining Wall
Bioengineered retaining walls integrate living vegetation with structural materials, enhancing soil stabilization and erosion control while promoting ecological benefits compared to traditional retaining walls. These hybrid systems utilize root reinforcement and natural materials to increase wall durability, reduce maintenance costs, and support biodiversity within construction projects.
Green Retaining Wall
Green retaining walls combine structural support with environmental benefits by integrating vegetation, effectively preventing soil erosion while enhancing aesthetics and improving air quality. Unlike traditional retaining walls that solely focus on stability, green retaining walls contribute to urban biodiversity and reduce heat island effects through their living plant layers.
Vegetated Gabion Wall
Vegetated gabion walls combine the structural strength of wire mesh cages filled with rocks and soil with live plant growth, offering enhanced erosion control and aesthetic appeal compared to traditional retaining walls. These living walls improve slope stability by integrating vegetation that promotes soil retention and biodiversity, making them an eco-friendly alternative in sustainable construction projects.
Geogrid-Reinforced Living Wall
Geogrid-reinforced living walls integrate engineered synthetic grids that stabilize soil while supporting vegetation growth, enhancing erosion control and structural durability compared to traditional retaining walls. This technique combines biomechanical reinforcement with ecological benefits, reducing runoff and improving slope stability in construction projects.
Modular Plantable Wall
Modular plantable walls offer a sustainable alternative to traditional retaining walls by integrating vegetation systems into durable, prefabricated panels that stabilize soil while enhancing urban green spaces. These systems improve erosion control, promote biodiversity, and reduce heat island effects, making them an innovative solution in modern construction and landscape design.
Soil Nail Living Wall
Soil nail living walls combine reinforced soil nails with vegetation layers, offering enhanced structural stability and environmental benefits compared to traditional retaining walls. These walls improve erosion control, promote biodiversity, and provide superior load-bearing capacity through the integration of geotechnical engineering and sustainable landscaping.
Eco Block System
Eco Block System offers superior environmental benefits by combining the structural integrity of retaining walls with the sustainable, natural filtration properties of living walls, promoting soil stabilization and biodiversity. This innovative approach enhances erosion control while reducing the urban heat island effect, making it an ideal solution for eco-friendly construction projects.
Permeable Retaining Structure
Permeable retaining structures like living walls enhance soil stability while promoting natural water drainage and reducing hydrostatic pressure, unlike traditional retaining walls that primarily focus on load-bearing and may require extensive drainage systems. Integrating vegetation in living walls improves environmental benefits by filtering pollutants and supporting biodiversity, offering sustainable solutions in modern construction projects.
MSE Green Wall (Mechanically Stabilized Earth)
MSE Green Walls utilize layered soil reinforcement combined with vegetation to provide enhanced structural stability and eco-friendly erosion control compared to traditional retaining walls, which rely primarily on concrete or masonry. These mechanically stabilized earth systems improve slope durability while promoting biodiversity and natural aesthetics in construction projects.
Hydroseeded Retaining Wall
A hydroseeded retaining wall integrates erosion control with vegetation growth by applying a slurry of seeds, mulch, and water to stabilize soil while promoting natural plant coverage. This method contrasts with traditional retaining walls that rely solely on concrete or stone for soil retention, offering enhanced environmental benefits and improved slope stability.
Retaining Wall vs Living Wall Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com