LEED Certification emphasizes sustainable building practices, energy efficiency, and environmental impact reduction to create eco-friendly structures. WELL Certification prioritizes occupant health and well-being by focusing on indoor air quality, natural lighting, and ergonomic design. Both certifications enhance building value but address distinct aspects of sustainability and human health.
Table of Comparison
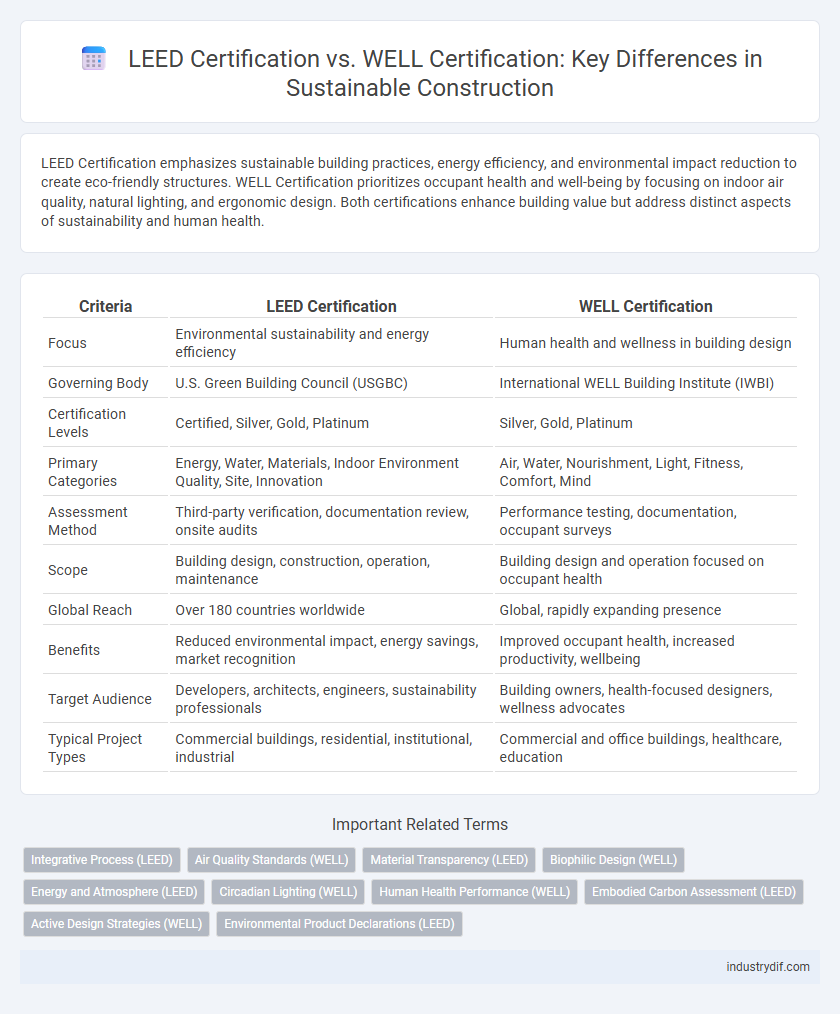
| Criteria | LEED Certification | WELL Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Environmental sustainability and energy efficiency | Human health and wellness in building design |
| Governing Body | U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) | International WELL Building Institute (IWBI) |
| Certification Levels | Certified, Silver, Gold, Platinum | Silver, Gold, Platinum |
| Primary Categories | Energy, Water, Materials, Indoor Environment Quality, Site, Innovation | Air, Water, Nourishment, Light, Fitness, Comfort, Mind |
| Assessment Method | Third-party verification, documentation review, onsite audits | Performance testing, documentation, occupant surveys |
| Scope | Building design, construction, operation, maintenance | Building design and operation focused on occupant health |
| Global Reach | Over 180 countries worldwide | Global, rapidly expanding presence |
| Benefits | Reduced environmental impact, energy savings, market recognition | Improved occupant health, increased productivity, wellbeing |
| Target Audience | Developers, architects, engineers, sustainability professionals | Building owners, health-focused designers, wellness advocates |
| Typical Project Types | Commercial buildings, residential, institutional, industrial | Commercial and office buildings, healthcare, education |
Introduction to LEED and WELL Certification
LEED Certification, developed by the U.S. Green Building Council, focuses on sustainable building design, construction, and operation, promoting energy efficiency, water savings, and reduced carbon emissions. WELL Certification, managed by the International WELL Building Institute, emphasizes the health and wellness of building occupants by addressing air quality, lighting, fitness, comfort, and mental well-being. Both certifications set global standards but target different priorities in the construction industry for creating healthier and more sustainable built environments.
Core Principles of LEED Certification
LEED Certification centers on sustainability principles including energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of renewable materials to minimize environmental impact within construction projects. It emphasizes site selection, indoor environmental quality, and innovation in design to enhance overall building performance and occupant health. LEED's core principles guide architects and builders to create eco-friendly, cost-effective structures that meet rigorous environmental standards.
Foundational Elements of WELL Certification
WELL Certification emphasizes health and wellness in building design through foundational elements such as air quality, water quality, nourishment, light, fitness, comfort, and mind. Its foundational features prioritize occupant wellbeing by promoting clean indoor environments, access to natural light, ergonomic comfort, and healthy lifestyle support. These elements differentiate WELL from LEED Certification, which primarily focuses on environmental sustainability and resource efficiency in construction practices.
Key Differences Between LEED and WELL
LEED Certification emphasizes sustainable building practices by focusing on energy efficiency, water conservation, and reduced environmental impact, whereas WELL Certification prioritizes occupant health and wellness through air quality, lighting, and ergonomic design. LEED evaluates a building's overall environmental performance, while WELL assesses how the built environment influences human health. Both certifications leverage rigorous standards, but LEED targets ecological sustainability and WELL enhances indoor environmental quality for user well-being.
Certification Process Comparison
LEED Certification requires a comprehensive evaluation of sustainable site development, water savings, energy efficiency, materials selection, and indoor environmental quality through a point-based system, assessed by the U.S. Green Building Council. WELL Certification emphasizes occupant health and wellness, assessing factors like air, water, nourishment, light, fitness, comfort, and mind, with performance verified by the International WELL Building Institute. The LEED process typically involves design submission, performance documentation, and third-party review, whereas WELL Certification mandates on-site performance testing and ongoing monitoring to ensure continuous compliance.
Cost Implications and ROI Analysis
LEED certification typically involves higher upfront costs due to stringent energy efficiency and sustainable material requirements, but offers long-term savings through reduced operational expenses and increased building value. WELL certification focuses on occupant health and wellness features, which can lead to higher tenant satisfaction and productivity, potentially increasing rental income and retention rates. An ROI analysis shows LEED often delivers cost benefits through utility savings, while WELL certification's financial returns hinge on improved occupant well-being and its impact on workforce performance.
Impact on Occupant Health and Wellbeing
LEED Certification emphasizes sustainable building practices that reduce environmental impact and improve indoor air quality, contributing to occupant health. WELL Certification directly targets occupant wellbeing through standards addressing air, water, lighting, fitness, comfort, and mental health. Projects combining LEED and WELL certifications maximize both environmental sustainability and comprehensive occupant health benefits.
Environmental Sustainability Focus
LEED Certification emphasizes energy efficiency, water conservation, and reduced carbon footprint through sustainable site development and materials selection in construction projects. WELL Certification prioritizes occupant health and well-being by improving indoor air quality, lighting, and thermal comfort while supporting environmental sustainability. Both certifications promote sustainable building practices but with LEED focusing more on environmental impact and WELL targeting human health within environmentally responsible frameworks.
Market Demand and Industry Trends
LEED Certification remains a dominant standard in the construction industry, driven by strong market demand for energy efficiency and sustainable building practices, with over 100,000 registered projects globally. WELL Certification is rapidly gaining traction by prioritizing occupant health and well-being, reflecting emerging industry trends focused on indoor environmental quality and human-centric design. Market analysis shows a growing integration of both certifications in commercial real estate, responding to increasing tenant and investor preferences for spaces that optimize sustainability and occupant wellness.
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Project
Selecting the ideal certification--LEED or WELL--depends on project goals, with LEED emphasizing sustainable building performance and energy efficiency, while WELL prioritizes occupant health and wellness features. LEED certification focuses on site sustainability, water efficiency, energy optimization, and materials selection, whereas WELL addresses air quality, lighting, fitness, and mental health aspects in built environments. Evaluating project priorities, budget, and desired impact on environmental or human health ensures the most appropriate rating system aligns with construction objectives.
Related Important Terms
Integrative Process (LEED)
The Integrative Process in LEED Certification emphasizes early-stage collaboration among design, construction, and operations teams to optimize building performance and sustainability outcomes. This approach contrasts with WELL Certification's focus on occupant health and wellness by prioritizing energy efficiency, resource management, and environmental impact reduction from project inception.
Air Quality Standards (WELL)
WELL Certification emphasizes rigorous air quality standards by promoting enhanced ventilation, pollutant reduction, and real-time air monitoring to improve occupant health and comfort within buildings. LEED Certification addresses indoor air quality primarily through sustainable design and materials but does not focus as intensively on continuous air performance metrics as WELL does.
Material Transparency (LEED)
LEED Certification emphasizes Material Transparency by requiring detailed disclosure of product ingredients and environmental impacts, fostering sustainability through reduced toxicity and enhanced indoor environmental quality. This focus ensures that construction materials meet rigorous standards for health and ecological responsibility, supporting green building initiatives.
Biophilic Design (WELL)
LEED Certification emphasizes energy efficiency and sustainable site development, while WELL Certification focuses on occupant health and wellness through biophilic design elements such as natural lighting, indoor plants, and improved air quality. Incorporating biophilic design in WELL-certified buildings enhances occupant cognitive function and emotional well-being, distinguishing it from LEED's broader environmental sustainability goals.
Energy and Atmosphere (LEED)
LEED Certification's Energy and Atmosphere category prioritizes reducing energy consumption through optimized building systems, enhanced insulation, and efficient HVAC technologies, driving significant carbon emission reductions in construction projects. WELL Certification concentrates on occupant health and comfort but incorporates fewer direct energy performance requirements compared to LEED's rigorous standards for sustainable energy management and renewable energy integration.
Circadian Lighting (WELL)
LEED Certification emphasizes energy efficiency and sustainable building practices, while WELL Certification prioritizes occupant health and wellness, with Circadian Lighting specifically designed to support natural sleep-wake cycles by mimicking natural daylight patterns. Circadian Lighting under WELL standards enhances indoor environmental quality by regulating melatonin production, improving occupant productivity and overall well-being.
Human Health Performance (WELL)
WELL Certification emphasizes human health performance by prioritizing air quality, water quality, lighting, and ergonomic design to enhance occupant wellness and productivity in buildings. LEED Certification primarily focuses on environmental sustainability, energy efficiency, and resource conservation, with less direct emphasis on occupant health metrics compared to WELL's holistic approach to human-centric building performance.
Embodied Carbon Assessment (LEED)
LEED Certification incorporates Embodied Carbon Assessment to measure and reduce the carbon footprint of building materials throughout a project's lifecycle, promoting sustainable construction practices. WELL Certification primarily focuses on occupant health and wellness, making embodied carbon less central to its criteria compared to LEED's emphasis on environmental impact.
Active Design Strategies (WELL)
LEED Certification emphasizes sustainable building practices such as energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact, while WELL Certification prioritizes human health and well-being by integrating Active Design Strategies that promote physical activity through features like accessible staircases, ergonomic workspaces, and optimized natural lighting. These strategies not only enhance occupant health but also improve productivity and overall indoor environmental quality, aligning with WELL's goal of creating healthier built environments.
Environmental Product Declarations (LEED)
Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) are a cornerstone of LEED Certification, providing transparent, third-party verified data on the environmental impact of building materials throughout their lifecycle. Unlike WELL Certification, which centers on human health and wellness within indoor environments, LEED emphasizes sustainability and resource efficiency, using EPDs to guide environmentally responsible material selection and reduce the building's carbon footprint.
LEED Certification vs WELL Certification Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com