Site surveys involve traditional ground-based inspections to assess terrain, identify obstacles, and collect accurate measurements crucial for construction planning. Drone surveys utilize aerial technology to quickly capture high-resolution images and topographic data, enabling detailed site analysis and monitoring with enhanced safety and efficiency. Combining both methods optimizes project accuracy by balancing thorough ground verification with expansive aerial perspectives.
Table of Comparison
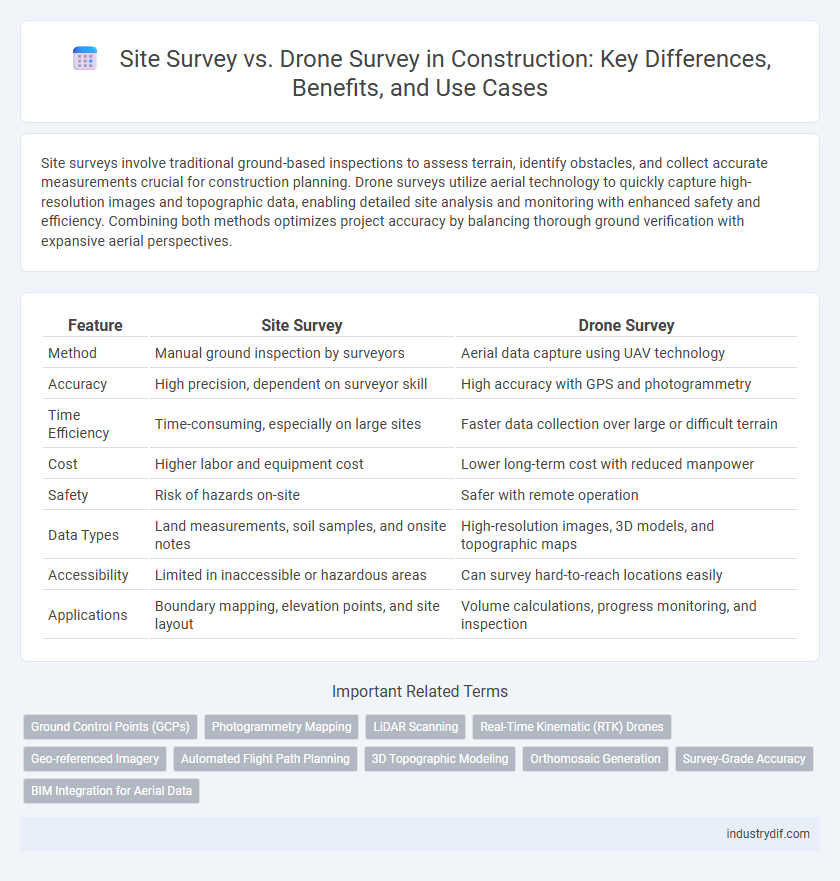
| Feature | Site Survey | Drone Survey |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Manual ground inspection by surveyors | Aerial data capture using UAV technology |
| Accuracy | High precision, dependent on surveyor skill | High accuracy with GPS and photogrammetry |
| Time Efficiency | Time-consuming, especially on large sites | Faster data collection over large or difficult terrain |
| Cost | Higher labor and equipment cost | Lower long-term cost with reduced manpower |
| Safety | Risk of hazards on-site | Safer with remote operation |
| Data Types | Land measurements, soil samples, and onsite notes | High-resolution images, 3D models, and topographic maps |
| Accessibility | Limited in inaccessible or hazardous areas | Can survey hard-to-reach locations easily |
| Applications | Boundary mapping, elevation points, and site layout | Volume calculations, progress monitoring, and inspection |
Introduction to Site Survey and Drone Survey
Site surveys involve manual measurement and assessment of construction sites to gather precise data on topography, boundaries, and existing conditions, crucial for project planning and design. Drone surveys utilize unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors to rapidly capture detailed site imagery and generate accurate 3D models and maps. Both methods enhance site analysis, with drones providing increased efficiency and broader coverage compared to traditional manual site surveys.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Drone Surveys
Traditional site surveys require manual measurements with tools such as total stations and GPS, often consuming significant time and labor, while drone surveys collect high-resolution aerial data rapidly with advanced imaging sensors. Drone surveys offer enhanced accuracy through real-time data processing and 3D mapping, reducing human error and improving site monitoring efficiency. Unlike traditional methods, drones can access hard-to-reach areas and provide comprehensive visual documentation, streamlining project planning and risk assessment.
Technology Used in Site and Drone Surveys
Site surveys traditionally rely on total stations, GPS equipment, and laser scanning technology to capture accurate measurements of terrain and structures, enabling precise planning and design. Drone surveys leverage advanced UAVs equipped with high-resolution cameras, LiDAR sensors, and photogrammetry software to rapidly collect detailed aerial data and generate 3D models and orthomosaic maps. The integration of GNSS technology enhances location accuracy in both methods, but drone surveys offer higher efficiency and the ability to access hard-to-reach areas without physical entry.
Accuracy and Precision: Site Survey vs Drone Survey
Site surveys provide high accuracy through direct measurements and detailed topographic data, essential for precise construction planning. Drone surveys deliver rapid data collection with impressive precision using advanced sensors and photogrammetry, but may face limitations in complex terrains or obstructed sites. Combining both methods enhances accuracy and precision, optimizing site analysis and project execution in construction.
Efficiency and Time Considerations
Site surveys traditionally require manual measurements and physical inspections, often consuming several days depending on project scale and terrain complexity. Drone surveys dramatically reduce time by capturing high-resolution aerial data within hours, enabling rapid analysis and decision-making. Efficiency increases as drones provide accurate topographic maps and 3D models, minimizing on-site labor and accelerating project timelines in construction planning.
Cost Implications: Manual vs Drone Surveys
Manual site surveys typically involve higher labor costs and extended project timelines due to the need for extensive human resources and equipment setup. Drone surveys reduce overall expenses by providing rapid data collection, minimizing the number of personnel required, and decreasing onsite risks, which translates to lower insurance premiums. Investment in drone technology offers long-term savings through enhanced accuracy, faster reporting, and reduced rework costs in construction project management.
Data Collection and Processing Methods
Site surveys rely on manual measurements and visual inspections using traditional tools like total stations and GPS equipment, providing detailed ground-level data but often requiring more time and labor. Drone surveys utilize high-resolution aerial imagery and LiDAR sensors to capture comprehensive site data quickly, enabling rapid processing through photogrammetry software and 3D modeling technology. While site surveys excel in accuracy for complex terrain and small details, drone surveys offer efficient data collection over large areas with advanced processing methods for generating orthomosaics and digital elevation models.
Safety Protocols in Both Survey Techniques
Site surveys require ground personnel to follow strict safety protocols such as wearing protective gear, maintaining clear communication, and monitoring environmental hazards to prevent accidents. Drone surveys, while reducing human exposure to dangerous areas, must comply with aviation safety regulations, including no-fly zones, operator certification, and pre-flight equipment checks. Both techniques prioritize safety by mitigating risks through tailored protocols suited to their operational environments.
Applications in Modern Construction Projects
Site surveys provide precise ground-level measurements essential for initial project planning, foundation layout, and utility mapping, ensuring accuracy in complex terrains. Drone surveys accelerate data collection through high-resolution aerial imagery and 3D mapping, enabling efficient monitoring of large-scale construction sites, progress tracking, and safety inspections. Integrating both methods enhances decision-making, reduces errors, and optimizes resource allocation in modern construction management.
Future Trends in Construction Surveying
Site surveys remain essential for precise ground-level measurements and detailed analysis, while drone surveys offer rapid aerial data collection and real-time monitoring capabilities. Future trends in construction surveying emphasize integrating drone technology with AI-powered data processing to enhance accuracy, reduce human error, and accelerate project timelines. Advanced photogrammetry and 3D modeling derived from drone surveys are set to revolutionize site planning and progress tracking in the construction industry.
Related Important Terms
Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Site surveys rely heavily on Ground Control Points (GCPs) to ensure precise spatial accuracy by physically marking reference locations on the terrain, which is essential for traditional leveling and alignment tasks. Drone surveys integrate GCPs to enhance georeferencing accuracy, but their main advantage lies in capturing high-resolution aerial imagery quickly, reducing the time and labor needed compared to conventional site survey methods.
Photogrammetry Mapping
Site surveys and drone surveys both enable photogrammetry mapping, but drone surveys offer higher accuracy and faster data collection over large construction sites through aerial imagery. Photogrammetry mapping with drones provides detailed 3D models and topographic data, improving project planning and reducing manual survey labor.
LiDAR Scanning
LiDAR scanning enhances both site surveys and drone surveys by capturing precise 3D data of construction areas, enabling accurate topographic mapping and volumetric calculations. While traditional site surveys rely on ground-based measurements, drone-based LiDAR surveys offer rapid data collection over difficult terrain, improving project efficiency and reducing safety risks.
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Drones
Site surveys traditionally rely on manual measurements and total stations, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error, whereas RTK drones offer centimeter-level accuracy by integrating GPS with real-time corrections. RTK drones enhance construction site surveying efficiency by providing rapid geospatial data collection, enabling precise mapping and reducing project timelines.
Geo-referenced Imagery
Site surveys provide accurate ground-level measurements essential for construction planning, while drone surveys generate high-resolution geo-referenced imagery that enhances topographic data and site visualization. Integrating drone survey data with GIS platforms improves precision in mapping, reduces survey time, and supports real-time decision-making on construction projects.
Automated Flight Path Planning
Automated flight path planning in drone surveys enhances site survey accuracy by optimizing aerial data collection with precise, pre-programmed routes, significantly reducing manual errors and survey time compared to traditional ground-based site surveys. This technology provides high-resolution, georeferenced imagery and real-time data, enabling efficient monitoring and analysis for construction project management.
3D Topographic Modeling
Site surveys traditionally rely on manual measurements and ground-based equipment to create 3D topographic models, often requiring more time and labor for accurate data collection. Drone surveys leverage aerial imagery and LiDAR technology to rapidly generate high-resolution 3D topographic models, enhancing precision and efficiency in construction planning and site analysis.
Orthomosaic Generation
Orthomosaic generation in construction leverages drone surveys to produce high-resolution, georeferenced aerial maps that accurately represent site conditions, offering greater detail and efficiency compared to traditional site surveys. Drone-based orthomosaics enable precise volume calculations, progress monitoring, and site planning by integrating multispectral imaging and automated data processing technologies.
Survey-Grade Accuracy
Survey-grade accuracy in construction site assessments is critical, with traditional site surveys providing centimeter-level precision through established GPS and total station methods. Drone surveys, enhanced by RTK and PPK technologies, increasingly deliver comparable accuracy but require careful calibration and controlled flight conditions to ensure reliable data for precise mapping and measurement.
BIM Integration for Aerial Data
Site surveys provide ground-level accuracy for BIM integration, enabling detailed structural assessments and precise topographical mapping, while drone surveys capture high-resolution aerial imagery and 3D data rapidly, enhancing BIM workflows with extensive site coverage and real-time updates. Combining drone surveys with traditional site data accelerates model accuracy, supports clash detection, and improves project coordination within BIM environments.
Site Survey vs Drone Survey Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com