Diet plans provide general guidelines for pet feeding based on species and age, while personalized nutrition tailors meals to an individual pet's health conditions, activity level, and genetic factors. Personalized nutrition enhances overall well-being by addressing specific dietary needs, potentially improving immunity, digestion, and energy levels. This targeted approach helps prevent common health issues, promoting a longer, healthier life for pets.
Table of Comparison
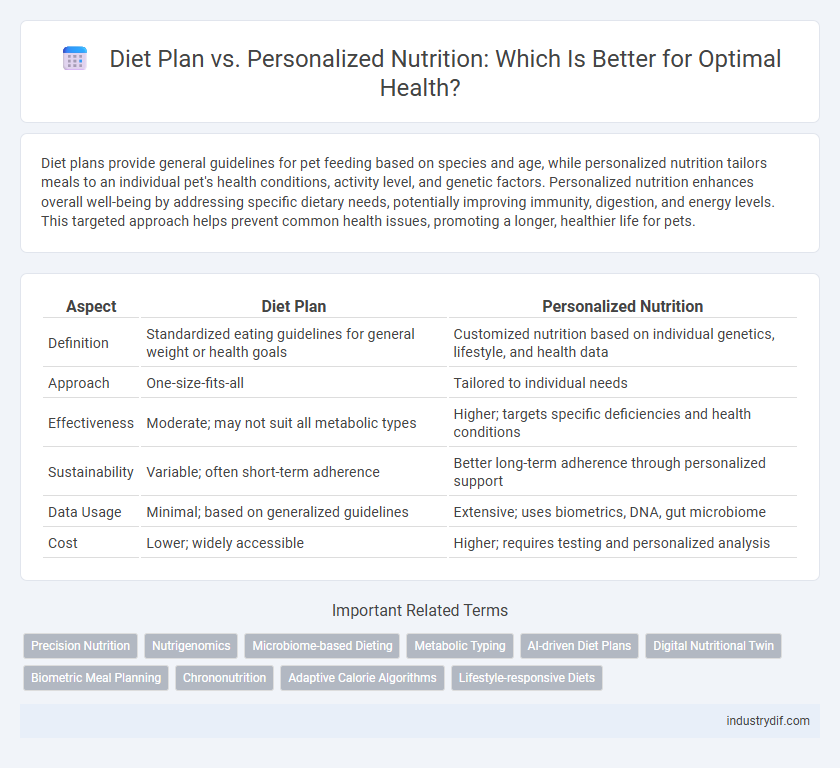
| Aspect | Diet Plan | Personalized Nutrition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardized eating guidelines for general weight or health goals | Customized nutrition based on individual genetics, lifestyle, and health data |
| Approach | One-size-fits-all | Tailored to individual needs |
| Effectiveness | Moderate; may not suit all metabolic types | Higher; targets specific deficiencies and health conditions |
| Sustainability | Variable; often short-term adherence | Better long-term adherence through personalized support |
| Data Usage | Minimal; based on generalized guidelines | Extensive; uses biometrics, DNA, gut microbiome |
| Cost | Lower; widely accessible | Higher; requires testing and personalized analysis |
Understanding Diet Plans: A Standardized Approach
Diet plans offer a standardized approach by providing general guidelines on calorie intake, macronutrient distribution, and meal timing to promote weight loss or maintenance. These plans are designed based on population averages and common dietary recommendations without tailoring to individual genetic, metabolic, or lifestyle factors. Understanding diet plans helps highlight the limitations of one-size-fits-all strategies compared to personalized nutrition, which customizes dietary choices to optimize health outcomes effectively.
What Is Personalized Nutrition?
Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations based on individual genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle factors, optimizing health outcomes and disease prevention. Unlike generic diet plans, it uses data from DNA analysis, microbiome profiles, and biometric measurements to create customized meal plans that meet unique nutritional needs. This approach enhances adherence and effectiveness by addressing specific biological differences and personal goals.
Key Differences Between Diet Plans and Personalized Nutrition
Diet plans typically offer generalized guidelines based on common nutritional needs and calorie intake, while personalized nutrition is tailored to an individual's genetics, lifestyle, and health conditions. Personalized nutrition leverages biomarkers, metabolic data, and food sensitivities to optimize dietary recommendations for better health outcomes. This approach enhances diet adherence and efficacy by addressing unique biological and environmental factors.
The Science Behind Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition leverages genetic, metabolic, and microbiome data to tailor diet plans specifically to an individual's unique biological makeup, optimizing health outcomes. Unlike generic diet plans, personalized approaches consider nutrient absorption rates, metabolic responses, and genetic predispositions, enhancing efficacy in disease prevention and weight management. Scientific studies highlight that integrating omics technologies and continuous health monitoring significantly improves adherence and long-term success in personalized nutrition interventions.
Benefits of Traditional Diet Plans
Traditional diet plans provide structured guidelines that simplify meal choices and promote balanced nutrient intake, aiding in consistent weight management and overall health improvement. These plans often emphasize portion control and calorie counting, which help users develop discipline and awareness of their eating habits. Their standardized nature makes them accessible and easy to follow, contributing to long-term adherence and measurable health benefits.
Limitations of Generic Diet Plans
Generic diet plans often fail to address individual metabolic differences, genetic factors, and personal health conditions, leading to suboptimal nutritional outcomes. Such one-size-fits-all approaches may overlook nutrient deficiencies or intolerances specific to an individual, reducing diet efficacy. Personalized nutrition, by contrast, tailors dietary recommendations based on unique biomarkers, lifestyle, and health goals, overcoming these limitations.
Advantages of Custom-Tailored Nutrition
Custom-tailored nutrition offers precise alignment with individual genetic profiles, metabolic rates, and health conditions, enhancing diet effectiveness and sustainability. Personalized nutrition improves nutrient absorption and supports specific health goals, such as weight management, chronic disease prevention, and improved energy levels. This approach reduces the risk of nutrient deficiencies and food intolerances by considering unique biochemical and lifestyle factors.
Technology’s Role in Personalized Nutrition
Advanced algorithms and AI-driven platforms analyze genetic, microbiome, and lifestyle data to craft highly precise personalized nutrition plans, outperforming generic diet plans in effectiveness. Wearable devices continuously monitor biometrics such as glucose levels, activity, and sleep patterns, feeding real-time data to adaptive nutrition applications. This seamless integration of technology empowers individuals with dynamic, customized dietary recommendations that evolve with their unique health profiles.
Diet Plan vs Personalized Nutrition: Health Outcomes
Diet plans often provide general guidelines based on population averages, which may lead to moderate health improvements but lack specificity for individual biological differences. Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations using genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle data, resulting in optimized health outcomes such as improved metabolic markers, weight management, and disease risk reduction. Studies demonstrate that personalized nutrition approaches yield superior adherence and more significant improvements in biomarkers compared to standard diet plans.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Health Goals
A diet plan offers structured guidelines based on general nutritional principles suited for weight loss or maintenance, while personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations to individual genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health conditions. Choosing the right approach depends on factors such as metabolic rate, chronic diseases, and specific health goals like improving cardiovascular health or managing diabetes. Leveraging technologies like nutrigenomics and continuous glucose monitoring enhances the precision of personalized nutrition, making it a superior choice for long-term health optimization.
Related Important Terms
Precision Nutrition
Precision Nutrition leverages genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle data to tailor diet plans that optimize individual health outcomes more effectively than generalized diet plans. Personalized nutrition enhances nutrient absorption and metabolic response, reducing chronic disease risk while maximizing energy and weight management benefits.
Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics explores how individual genetic makeup influences nutrient metabolism, making personalized nutrition more effective than generic diet plans by tailoring food choices to optimize health outcomes. Personalized nutrition leverages genetic data to identify specific dietary needs, enhancing disease prevention and improving metabolic responses compared to one-size-fits-all diet plans.
Microbiome-based Dieting
Microbiome-based dieting leverages individual gut flora composition to create diet plans tailored for enhanced digestion and metabolic health, surpassing generic diet plans in effectiveness. Personalized nutrition, grounded in microbiome analysis, optimizes nutrient absorption and supports immune function by targeting specific bacterial strains unique to each individual's digestive system.
Metabolic Typing
Metabolic typing categorizes individuals based on their unique biochemical makeup, allowing personalized nutrition plans to optimize metabolic efficiency and weight management more effectively than generic diet plans. Tailoring nutrient intake to metabolic types enhances energy levels, supports hormonal balance, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases through customized dietary strategies.
AI-driven Diet Plans
AI-driven diet plans leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze individual health data, dietary preferences, and lifestyle factors, creating tailored nutrition strategies that optimize wellness and prevent chronic diseases. Unlike generic diet plans, personalized nutrition powered by AI continuously adapts recommendations based on real-time feedback and biomarker monitoring, enhancing diet effectiveness and long-term adherence.
Digital Nutritional Twin
Diet plans provide general guidelines based on population averages, while personalized nutrition leverages digital nutritional twins to tailor dietary recommendations using real-time biometric data and metabolic profiling. Digital nutritional twins simulate individual responses to various foods, enhancing precision in managing health conditions and optimizing nutrient intake for improved wellness outcomes.
Biometric Meal Planning
Biometric meal planning leverages individual health data such as glucose levels, metabolic rate, and genetic markers to tailor diet plans that optimize nutrient intake and improve health outcomes. Unlike generic diet plans, personalized nutrition based on biometric analysis enhances weight management, metabolic efficiency, and chronic disease prevention by aligning food choices with precise biological needs.
Chrononutrition
Chrononutrition explores the timing of food intake to optimize metabolism and hormonal balance, offering advantages beyond traditional diet plans by aligning meals with the body's circadian rhythms. Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations based on individual genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle factors, enhancing the efficacy of chrononutrition strategies for improved weight management and overall health.
Adaptive Calorie Algorithms
Adaptive calorie algorithms enhance personalized nutrition by analyzing individual metabolic rates, activity levels, and dietary preferences to dynamically adjust caloric intake for optimal health outcomes. Unlike generic diet plans, these algorithms provide tailored calorie recommendations that evolve with changes in weight, lifestyle, and nutritional needs, maximizing effectiveness and sustainability.
Lifestyle-responsive Diets
Lifestyle-responsive diets integrate individual habits, activity levels, and health goals to create dynamic diet plans that adapt to changing lifestyle factors, optimizing nutritional intake and promoting sustained well-being. Personalized nutrition goes beyond generic diet plans by analyzing genetic, metabolic, and environmental data to tailor dietary recommendations that enhance metabolic efficiency and reduce chronic disease risks.
Diet Plan vs Personalized Nutrition Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com