Traditional surgery in pets involves manual techniques where veterinarians rely on direct visualization and conventional instruments, often resulting in longer recovery times and increased risk of infection. Robotic surgery offers enhanced precision through minimally invasive procedures, reducing trauma and promoting faster healing in animals. The use of robotic systems allows for improved accuracy, smaller incisions, and better outcomes compared to traditional surgical methods in veterinary care.
Table of Comparison
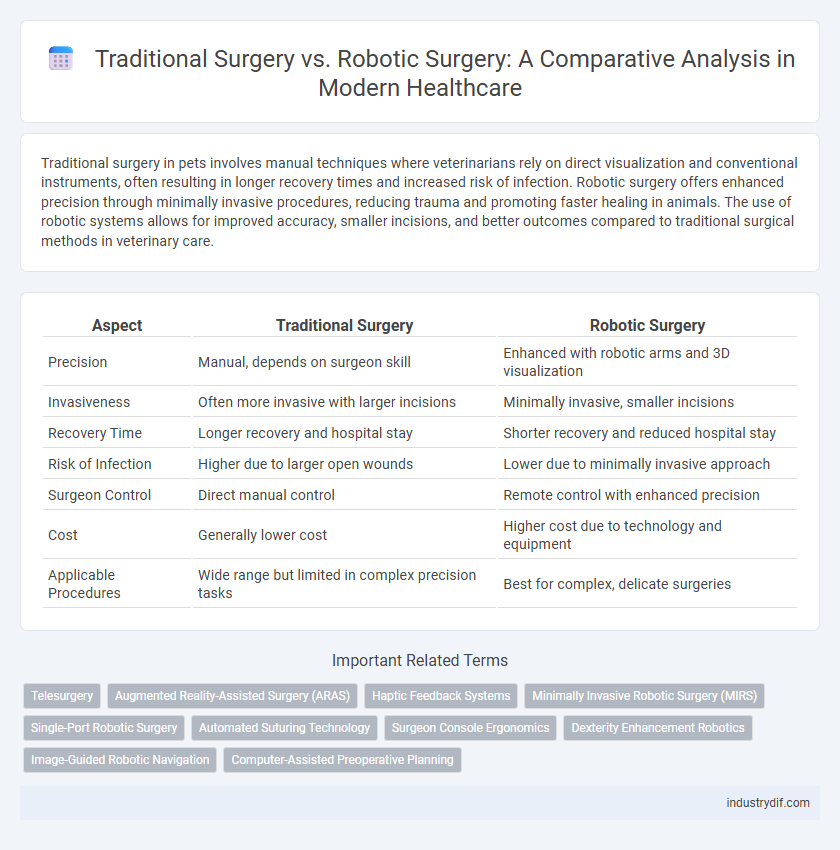
| Aspect | Traditional Surgery | Robotic Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Manual, depends on surgeon skill | Enhanced with robotic arms and 3D visualization |
| Invasiveness | Often more invasive with larger incisions | Minimally invasive, smaller incisions |
| Recovery Time | Longer recovery and hospital stay | Shorter recovery and reduced hospital stay |
| Risk of Infection | Higher due to larger open wounds | Lower due to minimally invasive approach |
| Surgeon Control | Direct manual control | Remote control with enhanced precision |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to technology and equipment |
| Applicable Procedures | Wide range but limited in complex precision tasks | Best for complex, delicate surgeries |
Overview of Traditional Surgery
Traditional surgery involves manual techniques where surgeons use scalpels, forceps, and other handheld instruments to perform procedures. It relies heavily on the surgeon's skill, experience, and direct visualization of the surgical site, often requiring larger incisions and longer recovery times. Despite advancements, traditional surgery remains widely used for complex cases where tactile feedback and surgeon judgment are critical.
Introduction to Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery utilizes advanced robotic systems to enhance the precision, control, and flexibility of surgical procedures compared to traditional surgery. Surgeons operate these robotic arms through a console, allowing for minimally invasive techniques that reduce patient recovery time, blood loss, and postoperative pain. The integration of 3D high-definition visualization and tremor filtration technology improves surgical accuracy, making robotic surgery a transformative approach in fields like urology, gynecology, and cardiothoracic surgery.
Key Technological Differences
Traditional surgery relies on the surgeon's direct hand movements and visibility through open or laparoscopic techniques, limiting precision in complex procedures. Robotic surgery uses advanced robotic arms controlled remotely by the surgeon, providing enhanced dexterity, 3D high-definition visualization, and greater precision in minimally invasive operations. The integration of computer-assisted technology in robotic systems allows real-time feedback and tremor filtration, reducing human error and improving surgical outcomes.
Patient Recovery and Outcomes
Robotic surgery offers enhanced precision and minimally invasive techniques, leading to reduced blood loss, smaller incisions, and lower infection risks compared to traditional surgery. Patients undergoing robotic-assisted procedures typically experience faster recovery times, less postoperative pain, and shorter hospital stays, improving overall outcomes. Studies indicate that robotic surgery can result in better functional recovery and fewer complications, particularly in complex surgeries such as prostatectomy and hysterectomy.
Surgeons’ Training and Expertise
Surgeons' training for traditional surgery emphasizes hands-on experience with manual techniques and direct tactile feedback, requiring extensive practice to master intricate skills. Robotic surgery demands proficiency in operating advanced robotic systems, which necessitates specialized training programs and simulation-based learning to develop precision and coordination. Surgeons skilled in robotic surgery often benefit from enhanced visualization and instrument control, contributing to improved patient outcomes in minimally invasive procedures.
Safety and Risk Assessment
Robotic surgery offers enhanced precision and reduced complication rates compared to traditional surgery, significantly lowering the risk of infection and blood loss during procedures. Safety assessments reveal that robotic systems provide superior visualization and dexterity, minimizing human error and improving patient outcomes. While traditional surgery carries higher risks of prolonged recovery and surgical trauma, robotic-assisted techniques promote faster healing and decreased postoperative pain.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
Robotic surgery often involves higher upfront costs than traditional surgery due to advanced technology and equipment expenses, impacting overall healthcare budgets. Traditional surgery remains more accessible, especially in rural or underfunded hospitals, since it requires less specialized infrastructure. Cost-effectiveness of each method varies depending on procedure complexity, hospital resources, and patient insurance coverage.
Procedure Precision and Accuracy
Robotic surgery offers enhanced precision and accuracy by utilizing advanced imaging and robotic arms capable of finer movements than the human hand, reducing tissue trauma and improving surgical outcomes. Traditional surgery relies heavily on the surgeon's manual skills, which can introduce variability and limit the ability to operate in confined or complex anatomical areas. Studies show robotic-assisted procedures often result in less blood loss, shorter recovery times, and lower complication rates due to superior control and visualization.
Postoperative Complications
Robotic surgery significantly reduces postoperative complications such as infections, bleeding, and pain compared to traditional surgery due to its precision and minimally invasive techniques. Studies indicate lower rates of wound infections and shorter hospital stays with robotic procedures. Enhanced visualization and dexterity in robotic surgery contribute to faster recovery and fewer postoperative risks.
Future Trends in Surgical Innovation
Robotic surgery is poised to revolutionize future surgical innovation by integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning for enhanced precision and real-time decision support, surpassing the limitations of traditional surgery. Advances in minimally invasive robotic systems are reducing patient recovery times, minimizing complications, and enabling complex procedures that were previously unfeasible with conventional surgical techniques. The continuous development of haptic feedback, augmented reality, and telesurgery is expected to democratize access to expert surgical care globally, shaping the next frontier in healthcare technology.
Related Important Terms
Telesurgery
Telesurgery leverages robotic systems to perform surgical procedures remotely, enhancing precision and reducing infection risks compared to traditional surgery. This technology enables expert surgeons to operate across distances, improving access to specialized care while minimizing patient recovery time and hospital stays.
Augmented Reality-Assisted Surgery (ARAS)
Augmented Reality-Assisted Surgery (ARAS) enhances precision in both traditional and robotic surgeries by providing real-time 3D visualization of anatomical structures, improving surgeon accuracy and patient outcomes. ARAS integrates imaging data with surgical instruments, reducing operative time and minimizing risks compared to conventional techniques.
Haptic Feedback Systems
Traditional surgery relies heavily on the surgeon's direct tactile sense to navigate tissues, whereas robotic surgery integrates advanced haptic feedback systems that simulate touch sensations through force feedback, enhancing precision and control. These haptic technologies improve surgical outcomes by providing real-time sensory information, reducing tissue damage, and allowing minimally invasive procedures with greater dexterity.
Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery (MIRS)
Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery (MIRS) offers enhanced precision, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. Utilizing advanced robotic systems, MIRS allows surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions, minimizing trauma and improving patient outcomes.
Single-Port Robotic Surgery
Single-port robotic surgery offers enhanced precision and minimal invasiveness compared to traditional surgery by utilizing a single incision site, reducing patient recovery time and postoperative complications. This advanced technique leverages robotic arms and high-definition 3D visualization to improve surgical accuracy while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
Automated Suturing Technology
Automated suturing technology in robotic surgery enhances precision and consistency, reducing human error and minimizing tissue trauma compared to traditional surgery. This advancement leads to faster recovery times, lower infection rates, and improved surgical outcomes in complex procedures.
Surgeon Console Ergonomics
Robotic surgery enhances surgeon console ergonomics by offering adjustable seating, intuitive hand controls, and 3D high-definition visualization, reducing physical strain and fatigue during lengthy procedures. In contrast, traditional surgery often requires awkward postures and repetitive motions, increasing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders among surgeons.
Dexterity Enhancement Robotics
Robotic surgery enhances dexterity by providing surgeons with precise, tremor-free movements and improved access to hard-to-reach anatomical areas through articulated robotic arms. This technology enables minimally invasive procedures with greater accuracy and reduced tissue damage compared to traditional surgery.
Image-Guided Robotic Navigation
Image-Guided Robotic Navigation enhances traditional surgery by providing high-precision, real-time 3D imaging, allowing surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with improved accuracy and reduced risk. This technology integrates advanced robotic systems with intraoperative imaging modalities such as MRI and CT scans, optimizing surgical outcomes through precise targeting and reduced tissue damage.
Computer-Assisted Preoperative Planning
Computer-assisted preoperative planning in robotic surgery leverages advanced imaging and 3D modeling to enhance surgical precision, reduce human error, and improve patient outcomes. Traditional surgery often relies on manual planning and surgeon experience, which may result in less accurate incisions and longer recovery times.
Traditional Surgery vs Robotic Surgery Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com