Information represents processed and meaningful data that provides context and insights, while data provenance refers to the origin and history of that data, tracking its lifecycle from creation to modification. Understanding data provenance ensures the reliability, authenticity, and traceability of information, which is crucial for accurate decision-making and compliance. Proper management of data provenance enhances transparency and supports data governance frameworks in various industries.
Table of Comparison
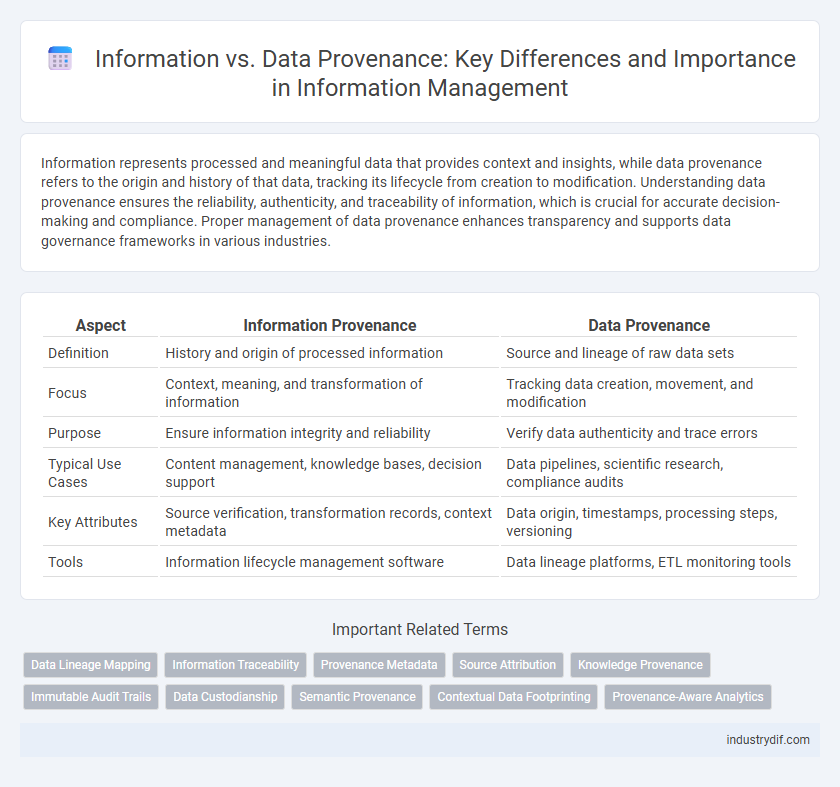
| Aspect | Information Provenance | Data Provenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | History and origin of processed information | Source and lineage of raw data sets |
| Focus | Context, meaning, and transformation of information | Tracking data creation, movement, and modification |
| Purpose | Ensure information integrity and reliability | Verify data authenticity and trace errors |
| Typical Use Cases | Content management, knowledge bases, decision support | Data pipelines, scientific research, compliance audits |
| Key Attributes | Source verification, transformation records, context metadata | Data origin, timestamps, processing steps, versioning |
| Tools | Information lifecycle management software | Data lineage platforms, ETL monitoring tools |
Understanding Information and Data Provenance
Information provenance refers to the origin and history of information as it is processed and transformed, highlighting its authenticity and reliability. Data provenance focuses on tracking the lifecycle and lineage of raw data elements, ensuring accurate documentation of data sources and transformations. Understanding both concepts is essential for data integrity, enabling transparency in data-driven decision-making and effective management of information assets.
Key Differences Between Information and Data Provenance
Information provenance traces the origin, context, and processing of information, emphasizing the transformation of raw data into meaningful insights. Data provenance specifically tracks the lineage, source, and changes made to raw data sets, focusing on authenticity, accuracy, and integrity. Key differences lie in scope and purpose: information provenance encompasses the entire lifecycle and interpretation of data, while data provenance targets the detailed history and manipulation of data elements.
The Role of Data Provenance in Information Management
Data provenance plays a crucial role in information management by tracing the origin, history, and transformations of data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring accuracy and reliability. It enhances data governance by enabling transparency, accountability, and compliance with regulatory standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. Effective data provenance integration facilitates better decision-making and risk management by providing a verifiable audit trail for information usage and modifications.
Importance of Data Lineage for Information Integrity
Data lineage traces the origin and transformations of data, ensuring transparency and accountability in data management processes. Maintaining accurate data lineage is crucial for verifying information integrity by enabling precise auditing and error detection. Organizations rely on data provenance to enhance trustworthiness, regulatory compliance, and informed decision-making.
How Information Context Relies on Provenance Tracking
Information context critically depends on provenance tracking to verify the origin, accuracy, and reliability of data sources. Provenance metadata captures the history and transformation processes of information, enabling contextual understanding and trustworthiness assessment. Effective provenance tracking supports data integrity and enhances decision-making by providing transparent evidence of information lineage.
Applications of Information and Data Provenance in Industry
Information and data provenance enable traceability and accountability in industries such as healthcare, finance, and supply chain management by providing detailed records of data origin and transformation. Provenance applications improve data quality, enhance regulatory compliance, and support forensic analysis by ensuring the authenticity and integrity of critical information. Advanced provenance tracking also facilitates secure data sharing and auditing, which are essential for maintaining trust and transparency in industrial processes.
Data Provenance Tools vs Information Management Systems
Data provenance tools specialize in tracking the origin, movement, and transformations of data across systems, ensuring data integrity and transparency throughout its lifecycle. Information management systems focus on organizing, storing, and retrieving information effectively to support decision-making and operational processes. While data provenance tools provide detailed metadata and lineage tracking critical for compliance and audit purposes, information management systems offer broader capabilities for content management, workflow automation, and user collaboration.
Security and Compliance: Information vs Data Provenance
Information provenance ensures the authenticity and integrity of data by tracking its origin, transformations, and access history, which is crucial for maintaining security and regulatory compliance. Data provenance provides detailed metadata for audit trails, enabling organizations to detect unauthorized modifications and ensure accountability in data handling. Robust provenance mechanisms support compliance frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA by proving traceability and safeguarding sensitive information throughout its lifecycle.
Best Practices for Managing Information and Data Provenance
Effective management of information and data provenance requires implementing robust tracking systems that capture origins, transformations, and access histories to ensure data integrity and accountability. Utilizing metadata standards and automated provenance tools enhances traceability and supports compliance with regulatory requirements. Regular audits and validation processes help maintain the accuracy and reliability of provenance records throughout the data lifecycle.
Future Trends in Information and Data Provenance
Future trends in information and data provenance emphasize enhanced integration of blockchain technology to ensure immutable and transparent lineage tracking. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning will enable automated provenance extraction and real-time validation, improving data reliability and auditability across complex systems. The growing adoption of standardized provenance models like W3C PROV will facilitate interoperability and seamless data sharing in distributed environments.
Related Important Terms
Data Lineage Mapping
Data lineage mapping visualizes the flow of data through various systems, capturing origins, transformations, and destinations to ensure data provenance accuracy. By tracing data movement across databases and processes, organizations enhance transparency, maintain data integrity, and support compliance with regulatory standards.
Information Traceability
Information traceability involves tracking the origin, movement, and transformations of information throughout its lifecycle, ensuring transparency and accountability in data usage. Unlike data provenance, which focuses on raw data lineage, information traceability emphasizes contextual metadata and the semantic relationships that preserve the integrity and reliability of processed information.
Provenance Metadata
Provenance metadata captures the origin, history, and modifications of data, enabling traceability and authenticity verification in information systems. Unlike raw data, provenance metadata provides essential context about data creation processes, sources, and ownership, supporting data integrity and accountability.
Source Attribution
Information provenance emphasizes the accurate attribution of sources to verify authenticity and establish trustworthiness, whereas data provenance primarily tracks the origin and history of datasets for reproducibility and accountability. Source attribution in information provenance enables users to assess credibility by linking content to its original creator or publisher, enhancing transparency and reliability in information management.
Knowledge Provenance
Knowledge provenance traces the origin and transformation of knowledge by capturing context, sources, and validation processes, distinguishing it from data provenance which records the history of raw data. This approach enhances trustworthiness and accountability in information management by emphasizing the lineage of interpreted knowledge rather than just data.
Immutable Audit Trails
Immutable audit trails provide a secure and unalterable record of data provenance, ensuring transparency and trust in the origin and history of information. By maintaining a fixed sequence of changes, these trails prevent tampering and support compliance with regulatory standards in data management.
Data Custodianship
Data custodianship involves the responsible management, storage, and protection of data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring data integrity and security. Unlike data provenance, which tracks the origin and transformations of data, custodianship focuses on controlled access and compliance with organizational policies and regulations.
Semantic Provenance
Semantic provenance captures the context, meaning, and relationships within information, enabling more accurate traceability and trust compared to basic data provenance that tracks only the origin and history of raw data. This enhanced semantic metadata facilitates richer data integration, interpretation, and verification across complex systems such as knowledge graphs and linked data environments.
Contextual Data Footprinting
Information provenance captures the origins and transformations of information within a system, emphasizing the contextual data footprinting that traces data lineage and usage patterns. Contextual data footprinting enhances data provenance by linking metadata to specific environmental, temporal, and procedural contexts, ensuring accurate tracking of information flow and integrity.
Provenance-Aware Analytics
Provenance-aware analytics enhances data provenance by tracking the origin, lineage, and transformations of data to ensure accuracy and trustworthiness in analytical results. Integrating provenance information enables organizations to validate data quality, support compliance, and optimize decision-making processes through transparent and verifiable data histories.
Information vs Data Provenance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com