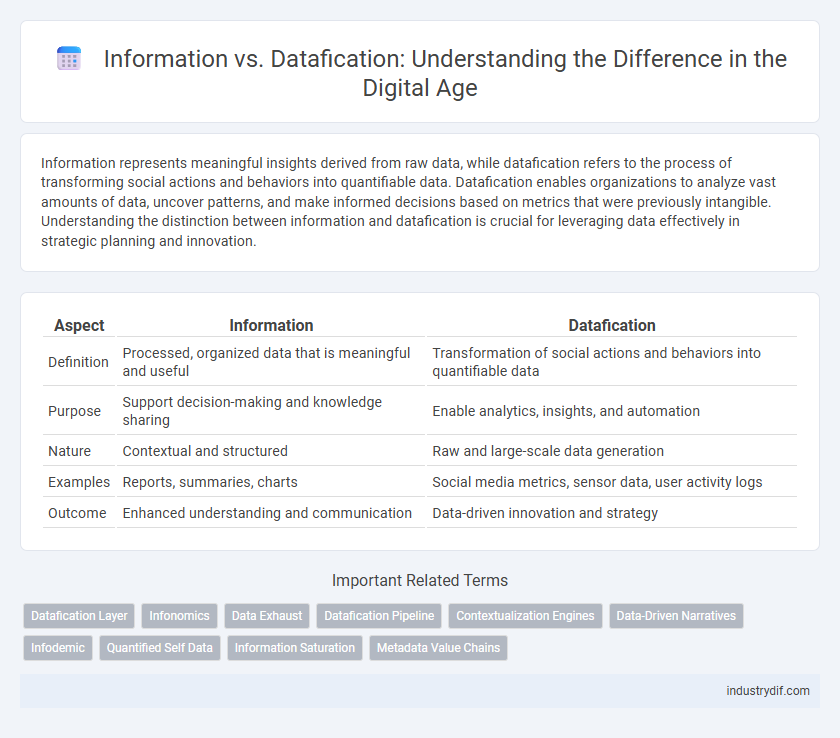
Information represents meaningful insights derived from raw data, while datafication refers to the process of transforming social actions and behaviors into quantifiable data. Datafication enables organizations to analyze vast amounts of data, uncover patterns, and make informed decisions based on metrics that were previously intangible. Understanding the distinction between information and datafication is crucial for leveraging data effectively in strategic planning and innovation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information | Datafication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processed, organized data that is meaningful and useful | Transformation of social actions and behaviors into quantifiable data |
| Purpose | Support decision-making and knowledge sharing | Enable analytics, insights, and automation |
| Nature | Contextual and structured | Raw and large-scale data generation |
| Examples | Reports, summaries, charts | Social media metrics, sensor data, user activity logs |
| Outcome | Enhanced understanding and communication | Data-driven innovation and strategy |
Understanding Information: Definition and Significance
Information represents processed and organized data that holds meaning and value for decision-making, communication, and knowledge creation. Understanding information involves recognizing its role in converting raw data into actionable insights, enhancing comprehension, and driving informed actions. The significance of information lies in its ability to reduce uncertainty, support problem-solving, and enable efficient management of resources across various domains.
What is Datafication? An Overview
Datafication refers to the process of transforming various aspects of life, activities, and behaviors into quantifiable data that can be analyzed and used for decision-making. Unlike raw data, which is unprocessed and contextless, datafication involves structuring and organizing information to reveal patterns, trends, and insights. This concept is fundamental in leveraging big data technologies and enabling more precise, data-driven strategies across industries.
Key Differences Between Information and Datafication
Information represents processed, organized, and meaningful data that provides context and understanding, whereas datafication involves transforming various aspects of life into quantifiable data streams. Key differences include information's interpretative nature versus datafication's emphasis on raw data collection and digitization. Information is context-dependent and used for decision-making, while datafication focuses on capturing continuous data points for analysis and automation.
The Role of Information in Modern Organizations
Information serves as a crucial asset in modern organizations by enabling informed decision-making, optimizing operational efficiency, and enhancing strategic planning. Unlike datafication, which converts complex human behaviors into quantifiable data, information provides meaningful context and insights essential for interpreting data effectively. Leveraging accurate and timely information fosters innovation, drives competitive advantage, and supports dynamic responses to market changes.
How Datafication Transforms Raw Data into Value
Datafication converts raw data into actionable insights by systematically capturing and analyzing vast datasets across various platforms. This transformation enables organizations to derive value through predictive analytics, enhanced decision-making, and personalized user experiences. Leveraging machine learning algorithms and big data technologies, datafication turns previously unstructured information into measurable metrics that drive innovation and efficiency.
Information Lifecycle vs. Datafication Process
The Information Lifecycle encompasses the phases of creation, storage, usage, sharing, archiving, and destruction of data-driven content, ensuring data integrity and relevance throughout its existence. Datafication Process transforms diverse human and organizational activities into quantifiable data, enabling advanced analytics and decision-making. Understanding the distinction between structured Information Lifecycle management and continuous Datafication is crucial for optimizing data governance and enhancing business intelligence.
Benefits and Challenges of Information Management
Effective information management enhances decision-making accuracy, streamlines organizational workflows, and supports regulatory compliance by converting raw data into actionable insights. Challenges include ensuring data quality, protecting sensitive information from breaches, and integrating diverse data sources for coherent analysis. Balancing the benefits of real-time datafication with privacy concerns requires robust governance frameworks and advanced analytics tools.
Datafication in Industry: Use Cases and Applications
Datafication in industry transforms raw information into structured, quantifiable data, enabling enhanced decision-making and operational efficiency. Key applications include predictive maintenance using sensor data, real-time supply chain optimization, and customer behavior analysis through data analytics platforms. These use cases drive automation, reduce costs, and foster innovation across manufacturing, logistics, and marketing sectors.
Impact of Datafication on Decision-Making
Datafication transforms raw information into quantifiable data, enabling organizations to leverage advanced analytics and machine learning for more precise decision-making. The impact of datafication on decision-making manifests in enhanced accuracy, real-time insights, and predictive capabilities that drive strategic business outcomes. By converting diverse information sources into structured datasets, datafication facilitates objective, data-driven decisions, reducing reliance on intuition and improving operational efficiency.
The Future: Balancing Information and Datafication
Balancing information and datafication is crucial for future digital strategies, as datafication transforms qualitative insights into quantifiable data streams that drive artificial intelligence and machine learning advancements. Emphasizing ethical data management, privacy regulations, and contextual understanding ensures that datafication enhances rather than diminishes the value of information. Organizations leveraging a synergistic approach to information and datafication will optimize decision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage in evolving digital ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Datafication Layer
Datafication transforms raw information into quantifiable data points through the datafication layer, enabling systematic analysis and actionable insights. This layer captures, processes, and standardizes diverse data types, turning experiential information into structured datasets for advanced analytics.
Infonomics
Infonomics explores the economic value of information, distinguishing it from datafication, which involves converting social action into quantifiable data. By assessing information as a valuable asset, Infonomics enables organizations to leverage data-driven insights for strategic decision-making and competitive advantage.
Data Exhaust
Data exhaust refers to the vast trails of digital footprints generated as byproducts of users' interactions with technology, which differ from raw information by being unstructured and often underutilized. While information is processed and meaningful data, datafication transforms these digital traces into data points for analysis, enabling insights but raising concerns about privacy and data management.
Datafication Pipeline
Datafication transforms raw information into structured data through a pipeline involving data collection, processing, and analysis to extract meaningful insights. The datafication pipeline enhances decision-making by converting diverse and unstructured information into actionable datasets.
Contextualization Engines
Contextualization engines enhance information by transforming raw data into meaningful insights through advanced algorithms that interpret context, relevance, and semantics. Unlike basic datafication, which converts activities into quantifiable data, these engines enable dynamic understanding, enabling smarter decision-making and personalized content delivery.
Data-Driven Narratives
Data-driven narratives transform raw data into meaningful stories by leveraging analytics and visualization tools that reveal patterns and insights. Unlike information, which is static and context-dependent, datafication converts diverse data sources into dynamic, actionable content that drives decision-making and innovation.
Infodemic
Information, when distorted or excessively amplified through datafication processes, can contribute to an infodemic--an overabundance of misleading or false content that hampers public understanding and decision-making. Effective management of accurate information is critical to counteract the negative impacts of infodemics on health communication and societal trust.
Quantified Self Data
Quantified Self data involves the systematic collection and analysis of personal information through wearable devices and apps, transforming raw data into meaningful insights about individual health and behavior. Unlike datafication, which converts various social actions into quantifiable data, Quantified Self emphasizes personal empowerment by enabling users to monitor and optimize their well-being through precise information metrics.
Information Saturation
Information saturation occurs when the volume of data exceeds an individual's or system's capacity to process it effectively, often resulting in diminished decision-making quality. Unlike datafication, which transforms social actions into quantifiable data, information saturation highlights the critical challenge of filtering and prioritizing relevant information amidst overwhelming data influx.
Metadata Value Chains
Metadata value chains transform raw data into structured information by enriching context, enabling efficient data integration, retrieval, and analysis across diverse systems. This process amplifies datafication benefits by creating interoperable, actionable insights that drive decision-making and innovation.
Information vs Datafication Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com