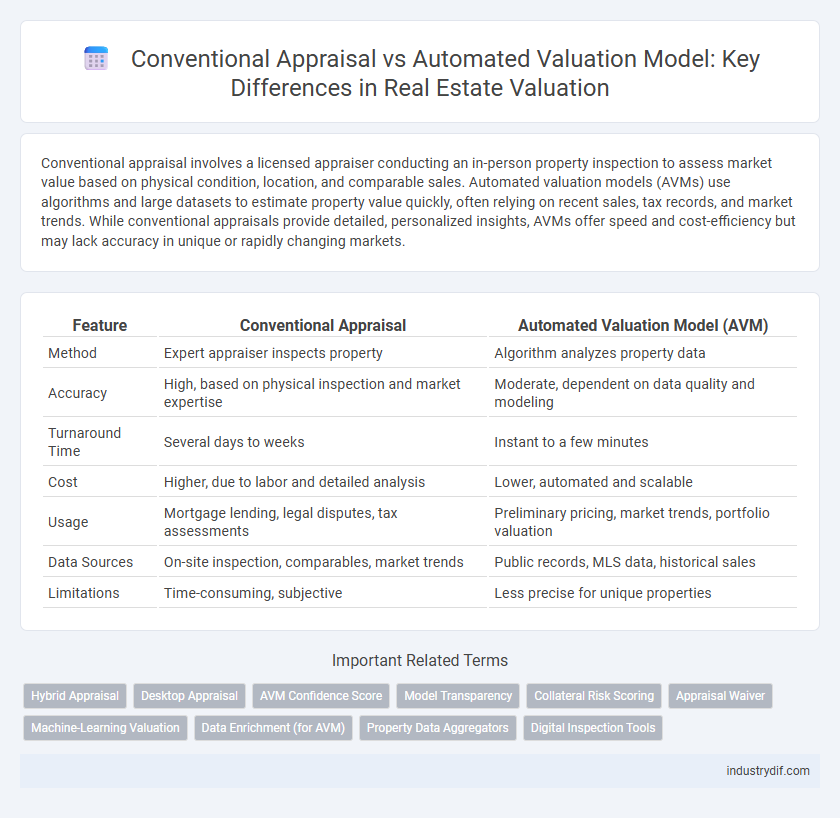
Conventional appraisal involves a licensed appraiser conducting an in-person property inspection to assess market value based on physical condition, location, and comparable sales. Automated valuation models (AVMs) use algorithms and large datasets to estimate property value quickly, often relying on recent sales, tax records, and market trends. While conventional appraisals provide detailed, personalized insights, AVMs offer speed and cost-efficiency but may lack accuracy in unique or rapidly changing markets.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Conventional Appraisal | Automated Valuation Model (AVM) |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Expert appraiser inspects property | Algorithm analyzes property data |
| Accuracy | High, based on physical inspection and market expertise | Moderate, dependent on data quality and modeling |
| Turnaround Time | Several days to weeks | Instant to a few minutes |
| Cost | Higher, due to labor and detailed analysis | Lower, automated and scalable |
| Usage | Mortgage lending, legal disputes, tax assessments | Preliminary pricing, market trends, portfolio valuation |
| Data Sources | On-site inspection, comparables, market trends | Public records, MLS data, historical sales |
| Limitations | Time-consuming, subjective | Less precise for unique properties |
Introduction to Real Estate Valuation Methods
Conventional appraisal involves a licensed appraiser conducting a comprehensive property inspection, analyzing comparable sales, and considering market conditions to determine accurate real estate value. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) utilize algorithms and large databases of recent sales, tax assessments, and property characteristics to provide rapid estimates. Both methods are essential in real estate, with appraisals offering detailed, personalized assessments and AVMs providing efficient, data-driven valuations.
Defining Conventional Appraisal
Conventional appraisal in real estate involves a licensed appraiser conducting a thorough property inspection and analysis using comparable sales, market trends, and physical property conditions to determine accurate market value. This method relies on expert judgment and detailed, on-site evaluation, ensuring a comprehensive assessment tailored to the unique characteristics of the property. Conventional appraisals are essential for securing mortgages, refinancing, and legal matters due to their high level of accuracy and regulatory acceptance.
Understanding Automated Valuation Models (AVMs)
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) leverage algorithms and extensive datasets, including recent sales, tax assessments, and market trends, to provide instantaneous property valuations with consistent accuracy. Unlike conventional appraisals that rely on physical inspections and subjective judgment by licensed appraisers, AVMs offer scalable, cost-effective solutions ideal for preliminary property assessments and portfolio analysis. Real estate professionals increasingly use AVMs to complement traditional appraisals, enhancing decision-making speed while understanding the limitations related to unique property features and local market nuances.
How Conventional Appraisals Work
Conventional appraisals involve licensed appraisers conducting on-site property inspections to assess the condition, features, and location of the home. Appraisers analyze comparable sales, market trends, and physical property details to provide an accurate, unbiased valuation report. This method ensures detailed, personalized assessments crucial for mortgage lending and real estate transactions.
Key Components of Automated Valuation Models
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) integrate extensive property data, recent sales, and market trends using sophisticated algorithms to provide rapid and objective property valuations. Key components include data input from Multiple Listing Services (MLS), public records, and historical transaction prices combined with statistical modeling techniques such as regression analysis and machine learning to enhance accuracy. These models deliver standardized, scalable, and cost-effective appraisals compared to traditional conventional appraisals, which rely heavily on human expertise and physical inspections.
Accuracy: Manual Appraisal vs AVM
Manual appraisals typically provide higher accuracy in real estate valuation due to on-site inspections and expert judgment, capturing property condition nuances and local market trends. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) rely on algorithms analyzing large datasets to offer rapid estimates but may lack precision in unique or rapidly changing markets. The choice between manual appraisal and AVM hinges on balancing accuracy needs with speed and cost efficiency in valuation processes.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Conventional appraisal involves a licensed appraiser conducting an in-person inspection and detailed analysis, typically requiring several days to complete, which can delay real estate transactions. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use algorithm-driven data analysis to generate property value estimates within seconds, significantly enhancing speed and efficiency. AVMs rely on vast datasets and machine learning to provide rapid valuations but may sacrifice some accuracy and contextual insight compared to conventional appraisals.
Cost Differences in Valuation Approaches
Conventional appraisals typically cost between $300 and $500 due to the involvement of licensed appraisers conducting on-site inspections and detailed property analyses. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) offer a more cost-effective alternative, often priced under $100, leveraging algorithms and large datasets to estimate property values quickly. Choosing AVMs reduces expenses significantly but may sacrifice the nuanced insights and physical assessments that conventional appraisals provide.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Conventional appraisal relies on licensed appraisers conducting thorough property inspections and comparative market analysis, widely used in mortgage lending, estate planning, and legal disputes where precise valuation is critical. Automated valuation models (AVMs) use algorithms and extensive real estate data to generate rapid property value estimates, commonly applied in portfolio management, property tax assessments, and online real estate platforms for quick decision-making. Both methods complement each other by balancing accuracy and efficiency, with AVMs providing scalability while conventional appraisals ensure detailed evaluation in complex cases.
Future Trends in Real Estate Valuation
Conventional appraisal relies on professional appraisers conducting thorough property inspections and market analysis to determine value, while Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) utilize algorithms and big data for rapid, data-driven estimates. Future trends in real estate valuation emphasize integrating AI, machine learning, and real-time market data to improve AVM accuracy and predictive capabilities. Hybrid approaches combining human expertise and automated technology are expected to dominate, enhancing efficiency and reliability in property valuation.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Appraisal
Hybrid appraisal combines the accuracy of conventional appraisals, which involve detailed property inspections by licensed appraisers, with the efficiency of automated valuation models (AVMs) that analyze extensive market data using algorithms. This approach enhances valuation reliability by integrating human expertise and real-time data analytics, providing more precise property assessments in dynamic real estate markets.
Desktop Appraisal
Desktop appraisals rely on Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) that use algorithms and extensive property data to estimate home values quickly without physical inspections. Conventional appraisals involve licensed appraisers conducting in-person evaluations, providing detailed and context-sensitive property assessments that desktop appraisals may lack.
AVM Confidence Score
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use algorithms to estimate property values based on extensive data, offering a confidence score that quantifies the reliability of their valuations by analyzing property characteristics, recent sales, and market trends. Conventional appraisals rely on expert appraisers conducting on-site inspections and subjective judgments, often yielding more nuanced but less scalable valuations compared to the standardized confidence scoring provided by AVMs.
Model Transparency
Conventional appraisals provide detailed, transparent assessments conducted by licensed professionals who consider property condition, location, and recent comparable sales, ensuring clarity in valuation methodology. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use algorithms and large datasets for rapid estimates but often lack full transparency, making it difficult for users to understand how input variables and market trends influence the property value.
Collateral Risk Scoring
Conventional appraisals rely on expert judgments and physical inspections, providing detailed insights but often involving higher costs and longer turnaround times, impacting the accuracy of collateral risk scoring. Automated valuation models (AVMs) utilize algorithms and large data sets to quickly generate property valuations, enhancing efficiency and consistency in collateral risk assessment but sometimes lacking the nuance captured in traditional appraisals.
Appraisal Waiver
An appraisal waiver allows qualified buyers to skip the conventional appraisal process by relying on an Automated Valuation Model (AVM) that uses algorithm-driven property data for a faster, cost-effective home valuation. While conventional appraisals provide detailed, expert property assessments through on-site inspections, appraisal waivers use AVMs to streamline lending decisions, primarily benefiting low-risk transactions with stable market data.
Machine-Learning Valuation
Machine-learning valuation models leverage large datasets and algorithms to provide rapid, data-driven property value estimates, enhancing accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional appraisals. Unlike conventional appraisals that rely on expert judgment and manual inspection, automated valuation models integrate real-time market trends, historical sales, and property characteristics for scalable and consistent real estate valuations.
Data Enrichment (for AVM)
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) leverage extensive data enrichment by incorporating up-to-date property records, market trends, neighborhood statistics, and comparable sales to generate accurate real estate valuations. Conventional appraisals often rely on manual inspections and subjective judgment, limiting the scope and timeliness of data compared to the comprehensive datasets utilized in AVMs.
Property Data Aggregators
Property data aggregators compile extensive real estate information used by both conventional appraisals and automated valuation models (AVMs) to assess property values accurately. AVMs leverage this aggregated data with algorithms to provide faster, scalable valuations, while conventional appraisals rely on human expertise to interpret the data in context.
Digital Inspection Tools
Digital inspection tools enhance automated valuation models by providing real-time, high-resolution property data, improving accuracy and reducing human error compared to conventional appraisals. Integrating 3D imaging, drone footage, and AI-driven analysis allows for faster property assessments, streamlining the valuation process and increasing efficiency in real estate transactions.
Conventional appraisal vs Automated valuation model Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com