Property valuation conducted by professional appraisers offers a comprehensive analysis, incorporating local market trends, property condition, and unique features to determine accurate value. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) rely on algorithms and large datasets to provide quick estimates but may lack nuance in capturing specific property attributes or market fluctuations. Combining expert appraisals with AVMs can enhance decision-making by balancing precision and efficiency in real estate valuations.
Table of Comparison
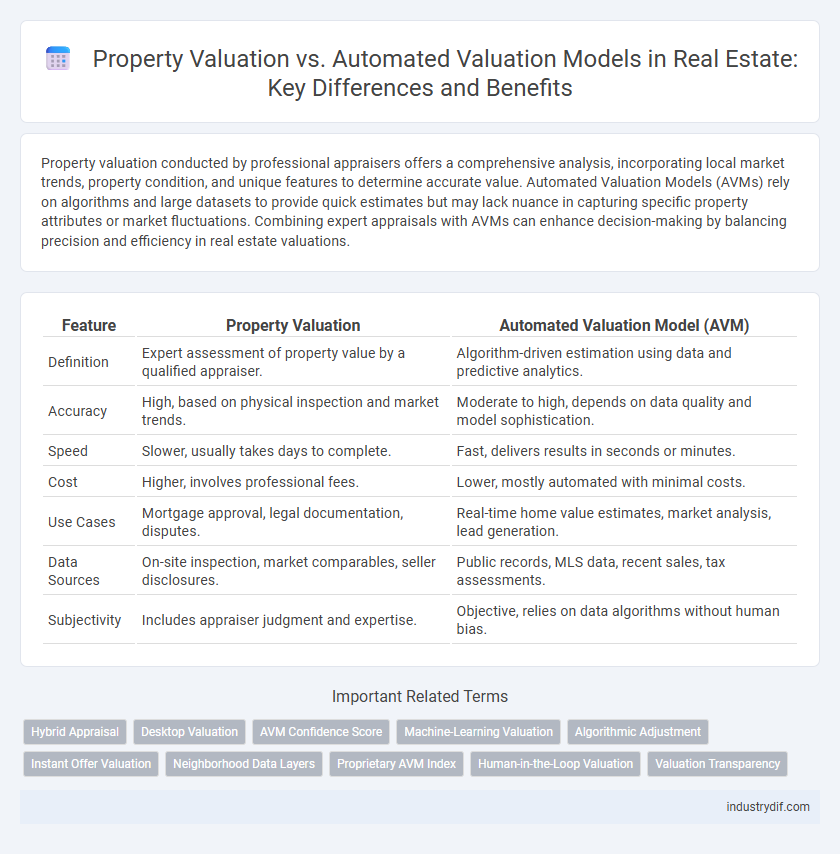
| Feature | Property Valuation | Automated Valuation Model (AVM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expert assessment of property value by a qualified appraiser. | Algorithm-driven estimation using data and predictive analytics. |
| Accuracy | High, based on physical inspection and market trends. | Moderate to high, depends on data quality and model sophistication. |
| Speed | Slower, usually takes days to complete. | Fast, delivers results in seconds or minutes. |
| Cost | Higher, involves professional fees. | Lower, mostly automated with minimal costs. |
| Use Cases | Mortgage approval, legal documentation, disputes. | Real-time home value estimates, market analysis, lead generation. |
| Data Sources | On-site inspection, market comparables, seller disclosures. | Public records, MLS data, recent sales, tax assessments. |
| Subjectivity | Includes appraiser judgment and expertise. | Objective, relies on data algorithms without human bias. |
Understanding Property Valuation: Key Concepts
Property valuation involves a comprehensive assessment of a property's market value, incorporating factors such as location, condition, comparable sales, and current market trends. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use algorithms and large datasets to estimate property values quickly, but may lack the nuanced analysis of a professional appraiser. Understanding key concepts like market value, appraisal methods, and the limitations of AVMs is essential for accurate property valuation and informed real estate decisions.
What is an Automated Valuation Model (AVM)?
An Automated Valuation Model (AVM) is a technology-driven tool that estimates property values using mathematical modeling combined with extensive real estate data, including recent sales, property characteristics, and market trends. It leverages algorithms and statistical techniques to provide rapid, data-supported property valuations without the need for physical inspection. AVMs enhance efficiency in the real estate market by offering scalable and objective property price estimates for buyers, sellers, lenders, and appraisers.
Traditional Property Valuation Methods
Traditional property valuation methods rely on expert appraisers who conduct thorough site inspections, analyze comparable sales, and assess property condition to determine market value. These methods prioritize nuanced factors such as neighborhood trends, unique property features, and local market dynamics that automated valuation models (AVMs) may overlook. Despite advances in technology, traditional valuations remain essential for accuracy in complex or unique real estate transactions.
How AVMs Work in Real Estate
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) in real estate analyze vast datasets including recent sales, property characteristics, and market trends to estimate property values quickly and cost-effectively. These models use algorithms and statistical techniques such as regression analysis and machine learning to generate accurate valuations without the need for physical inspections. AVMs provide real-time value estimates essential for lenders, investors, and buyers seeking fast and data-driven insights into property worth.
Accuracy: Manual Valuation vs AVMs
Manual property valuation relies on experienced appraisers who assess physical property characteristics, market trends, and neighborhood factors to provide a highly accurate and detailed estimate of property value. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use algorithms and vast datasets to generate rapid value estimates, but often lack the nuanced understanding of unique property conditions, leading to potential inaccuracies in complex markets. While AVMs offer efficiency and scalability, manual valuations remain the most precise method for properties requiring in-depth analysis and market insight.
Pros and Cons of Automated Valuation Models
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) provide quick and cost-effective property value estimates by leveraging algorithms and large datasets, making them ideal for preliminary assessments and portfolio analysis. However, AVMs can lack accuracy and fail to capture unique property features or market nuances, leading to potential valuation errors compared to detailed, professional appraisals. Their reliance on historical and public data may not reflect recent market changes, limiting reliability in volatile or emerging real estate markets.
When to Use Traditional Valuation over AVMs
Traditional property valuation is preferable over Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) when dealing with unique or luxury properties that lack comparable market data, as expert appraisers can assess specific features and neighborhood nuances. Complex transactions, such as those involving commercial real estate, often require detailed inspections and localized market knowledge that AVMs cannot replicate accurately. In rapidly changing or volatile markets, relying on traditional valuations ensures more precise and context-aware property assessments.
Industry Adoption of AVMs in Real Estate
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) have gained significant industry adoption in real estate due to their efficiency and data-driven accuracy in property valuation. Leading real estate firms and financial institutions increasingly rely on AVMs to streamline appraisal processes, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making with real-time market data integration. Despite some limitations compared to traditional property valuation by experts, AVMs continue to advance with machine learning algorithms, improving predictive accuracy and expanding their acceptance across residential and commercial property markets.
Regulatory Considerations for Property Valuation
Regulatory considerations for property valuation emphasize adherence to established appraisal standards such as USPAP or IVS, ensuring accurate and transparent valuation reports. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) require validation and oversight to comply with financial regulations and maintain reliability in lending decisions. Compliance with data privacy laws and regular model auditing is critical to uphold the integrity of valuations in both traditional and automated methods.
The Future of Valuation: Integrating Technology and Expertise
The future of property valuation lies in the seamless integration of expert appraisers and Automated Valuation Models (AVMs), combining human insight with advanced algorithms for enhanced accuracy. Machine learning and big data analytics within AVMs streamline property assessments, but expert judgment remains crucial for interpreting unique market variables and property conditions. Hybrid valuation approaches promise faster, more reliable property appraisals, driving efficiency in real estate transactions and investment decisions.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Appraisal
Hybrid appraisal combines traditional property valuation methods with automated valuation models (AVMs), leveraging machine learning algorithms alongside expert appraisers to enhance accuracy and reduce bias. This approach utilizes comprehensive data analysis and on-site inspections, resulting in more reliable property value estimates for informed real estate decisions.
Desktop Valuation
Desktop valuation leverages Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) to estimate property values using extensive databases and algorithms, offering quick, cost-effective insights without physical inspections. Unlike traditional property valuation, desktop valuation provides scalable, data-driven appraisals ideal for market analysis and preliminary assessments.
AVM Confidence Score
Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use algorithms and data such as recent sales, property characteristics, and market trends to estimate property values with an AVM Confidence Score indicating the reliability of the valuation. The AVM Confidence Score quantifies the model's accuracy by measuring data quality, comparables availability, and local market volatility, guiding stakeholders in assessing the risk and dependability of automated property valuations.
Machine-Learning Valuation
Property valuation involves comprehensive analysis by experts using market trends, property condition, and comparable sales, while Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) rely on machine-learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets for rapid and scalable property price estimates. Machine-learning valuation enhances AVMs by continuously improving accuracy through pattern recognition in diverse real estate data, optimizing investment decisions and market assessments.
Algorithmic Adjustment
Property valuation relies on expert appraisal integrating market trends, location, and property specifics, while Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) utilize algorithmic adjustment techniques to analyze large datasets and predict property values with increased efficiency. Algorithmic adjustments in AVMs refine price estimates by automatically processing variables like recent sales, property features, and neighborhood changes for accurate, data-driven valuations.
Instant Offer Valuation
Instant Offer Valuation leverages Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) to provide fast, data-driven property assessments based on recent sales, market trends, and property characteristics. While traditional Property Valuation relies on detailed appraisals by experts, AVMs enable instant, scalable offers that streamline the real estate selling process with increased efficiency and accuracy.
Neighborhood Data Layers
Neighborhood data layers significantly enhance property valuation accuracy by incorporating factors such as school quality, crime rates, and local amenities to reflect true market conditions. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) leverage these layers alongside historical sales and geographic data to provide rapid, data-driven price estimates often used in online real estate platforms.
Proprietary AVM Index
Property valuation traditionally relies on expert appraisals and market analysis, whereas Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) use proprietary AVM indices to generate instant, data-driven property value estimates by analyzing large datasets and market trends. The proprietary AVM index enhances accuracy and consistency in valuation by integrating diverse real estate metrics, providing a scalable solution for lenders, investors, and real estate professionals.
Human-in-the-Loop Valuation
Human-in-the-loop valuation integrates expert appraisers with Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) to enhance accuracy by combining data-driven algorithms with contextual market insights. This hybrid approach reduces errors commonly found in purely automated valuations, ensuring more reliable property price estimates in dynamic real estate markets.
Valuation Transparency
Property valuation by licensed appraisers offers comprehensive transparency through detailed inspections and customizable reports, ensuring stakeholders understand each valuation factor. Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) provide rapid estimates using algorithms and large datasets but often lack clear insights into the specific criteria driving their valuations.
Property Valuation vs Automated Valuation Model Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com