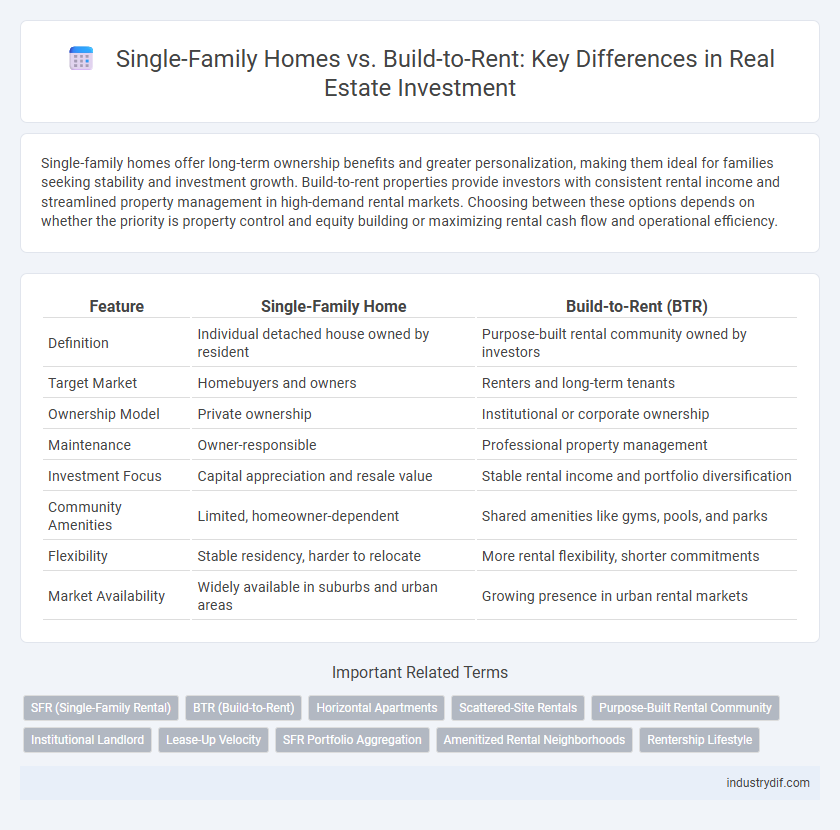
Single-family homes offer long-term ownership benefits and greater personalization, making them ideal for families seeking stability and investment growth. Build-to-rent properties provide investors with consistent rental income and streamlined property management in high-demand rental markets. Choosing between these options depends on whether the priority is property control and equity building or maximizing rental cash flow and operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single-Family Home | Build-to-Rent (BTR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual detached house owned by resident | Purpose-built rental community owned by investors |
| Target Market | Homebuyers and owners | Renters and long-term tenants |
| Ownership Model | Private ownership | Institutional or corporate ownership |
| Maintenance | Owner-responsible | Professional property management |
| Investment Focus | Capital appreciation and resale value | Stable rental income and portfolio diversification |
| Community Amenities | Limited, homeowner-dependent | Shared amenities like gyms, pools, and parks |
| Flexibility | Stable residency, harder to relocate | More rental flexibility, shorter commitments |
| Market Availability | Widely available in suburbs and urban areas | Growing presence in urban rental markets |
Definition of Single-Family Homes
Single-family homes are standalone residential buildings designed to house one family, featuring private yards and individual entrances. These properties typically include multiple bedrooms, a kitchen, living areas, and garages, providing exclusive ownership of both the structure and the land. Unlike build-to-rent communities, single-family homes offer long-term ownership opportunities, making them highly desirable for personal residence or investment in traditional homeownership markets.
Understanding Build-to-Rent Properties
Build-to-rent properties are residential developments specifically designed for long-term rental, offering turnkey homes managed by professional property management companies. Unlike traditional single-family homes sold to individual homeowners, build-to-rent communities emphasize standardized quality, amenities, and maintenance services, enhancing tenant experience and investment stability. This model appeals to renters seeking modern, well-maintained homes with community features, while providing investors with steady rental income and scalability.
Key Differences Between Single-Family and Build-to-Rent
Single-family homes are individually owned properties designed for single households, offering long-term ownership and personalization, whereas build-to-rent communities consist of purpose-built rental homes managed by institutional investors. Single-family homes typically appeal to homeowners seeking equity growth and property control, while build-to-rent properties target renters desiring modern amenities and maintenance-free living. The key differences include ownership structure, investment goals, tenant demographics, and property management models.
Investment Potential: Single-Family vs Build-to-Rent
Single-family homes often appeal to long-term investors seeking stable appreciation and owner-occupant demand, while build-to-rent properties offer consistent rental income and scalable portfolios tailored to institutional investors. Build-to-rent developments typically provide higher yields due to professional management and economies of scale, whereas single-family rentals may experience variable vacancy rates and maintenance costs. Assessing local market trends, tenant demographics, and regulatory environments is crucial to maximize investment potential in either property type.
Target Tenant Demographics
Single-family homes primarily attract established families seeking long-term residency with space for children and pets, valuing privacy and neighborhood stability. Build-to-rent properties cater to younger professionals and transient tenants who prioritize modern amenities, flexibility, and lower maintenance responsibilities. Understanding these target tenant demographics helps investors optimize property development and marketing strategies for higher occupancy and returns.
Operational Management in Each Model
Operational management in single-family homes typically involves individualized maintenance, tenant screening, and property-specific repairs, often requiring more hands-on involvement per unit. Build-to-rent communities benefit from centralized management systems, streamlined maintenance services, and scalable tenant relations, enabling cost-efficient and consistent operations across multiple units. Efficient property management software and on-site maintenance teams are critical for optimizing operational workflows in build-to-rent models.
Financing and Acquisition Strategies
Single-family home financing often relies on conventional mortgages with lower down payments, appealing to individual investors and homeowners seeking long-term equity. Build-to-rent projects require substantial capital investment, typically sourced through institutional financing, private equity, or syndication due to their scale and cash flow potential. Acquisition strategies for single-family properties focus on individual purchases in growth markets, while build-to-rent targets bulk acquisitions or ground-up developments to optimize operational efficiencies and rental income.
Market Trends Shaping Both Sectors
Single-family homes continue to dominate traditional real estate markets due to strong demand from owner-occupiers seeking long-term stability and community-oriented living. The build-to-rent sector experiences rapid growth driven by millennial and Gen Z renters prioritizing flexibility, modern amenities, and professional management in suburban and urban areas. Market trends reveal increased investor focus on build-to-rent projects as affordable housing shortages and shifting demographics reshape residential preferences across key metropolitan regions.
Regulatory Considerations and Zoning
Single-family home developments often face stringent zoning laws that limit density and preserve neighborhood character, impacting project scale and profitability. Build-to-rent communities benefit from evolving regulations that encourage multi-unit developments in urban and suburban areas, offering greater flexibility for higher-density housing models. Understanding local zoning codes and regulatory frameworks is essential for optimizing land use and ensuring compliance in both single-family and build-to-rent projects.
Long-Term Outlook for Investors
Single-family homes offer long-term appreciation potential supported by steady demand and limited housing supply, making them attractive for investors seeking capital growth and rental income diversification. Build-to-rent communities provide scalable cash flow and reduced vacancy risk through professionally managed properties tailored to renters prioritizing quality and amenities. Investors prioritizing portfolio stability and sustained returns should weigh single-family equity growth against build-to-rent's operational efficiencies and market resilience.
Related Important Terms
SFR (Single-Family Rental)
Single-Family Rentals (SFR) offer investors scalable income opportunities with lower tenant turnover compared to traditional Build-to-Rent developments, leveraging existing housing stock for faster market entry. SFR properties typically attract long-term tenants seeking suburban living, driving steady cash flow and enhancing portfolio diversification in real estate investment trusts (REITs) and private equity strategies.
BTR (Build-to-Rent)
Build-to-Rent (BTR) communities offer purpose-built rental homes designed for long-term tenants, providing consistent income streams and lower vacancy rates compared to traditional single-family rentals. These developments often include amenity-rich environments that attract renters seeking convenience and community, driving higher tenant retention and enhanced property values in competitive real estate markets.
Horizontal Apartments
Horizontal apartments in single-family developments offer more private outdoor space, appealing to families seeking suburban living, while build-to-rent communities emphasize shared amenities and maintenance-free lifestyles, attracting renters prioritizing convenience. Market trends indicate horizontal apartments in build-to-rent projects command higher rental yields due to their blend of space and community features, reshaping the suburban rental landscape.
Scattered-Site Rentals
Scattered-site rentals in single-family homes offer diversified geographic locations, reducing neighborhood-specific risks and providing stable cash flow for investors. Build-to-rent communities consolidate properties in one area, enabling streamlined management and economies of scale but may face localized market volatility.
Purpose-Built Rental Community
Purpose-built rental communities in the build-to-rent sector offer tailored amenities, professional management, and consistent rental income streams, distinguishing them from traditional single-family homes often purchased for owner-occupancy or individual investment. These developments prioritize tenant experience and long-term community value, driving higher occupancy rates and stable returns in real estate portfolios.
Institutional Landlord
Institutional landlords increasingly favor build-to-rent communities due to scalable investment returns, reduced maintenance complexity, and long-term tenant stability compared to traditional single-family homes. This strategic shift leverages centralized asset management and economies of scale, optimizing portfolio diversification and cash flow predictability.
Lease-Up Velocity
Single-family homes typically experience slower lease-up velocity due to individualized leasing processes and buyer financing timelines, whereas build-to-rent communities benefit from streamlined leasing operations and bulk marketing strategies that accelerate occupancy rates. Data from recent market analyses indicate build-to-rent projects achieve full lease-up 30-40% faster than traditional single-family rentals, driven by standardized construction and consistent tenant demand.
SFR Portfolio Aggregation
Single-family rental (SFR) portfolio aggregation enables investors to acquire diversified collections of homes, maximizing occupancy rates and stabilizing cash flow compared to standalone properties. Build-to-rent (BTR) developments offer scalable, purpose-built communities designed to meet growing rental demand, providing streamlined management and higher tenant retention in aggregated single-family home portfolios.
Amenitized Rental Neighborhoods
Amenitized rental neighborhoods in build-to-rent communities offer single-family-style homes with shared amenities such as parks, pools, and fitness centers, enhancing lifestyle and community engagement compared to traditional single-family home rentals. These integrated features increase tenant satisfaction and retention, making build-to-rent properties a competitive option in the real estate market.
Rentership Lifestyle
Single-family homes provide tenants with privacy and a sense of ownership while build-to-rent communities emphasize shared amenities and social engagement, catering to renters seeking a lifestyle-driven living experience. The rise of build-to-rent properties aligns with increasing demand for convenient, maintenance-free housing options that combine the benefits of homeownership with the flexibility of renting.
Single-Family vs Build-to-Rent Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com