Lab research offers controlled environments and precise methodologies to produce consistent, replicable scientific data critical for advancing knowledge. Citizen science engages non-professional volunteers in data collection and observation, expanding research scope and fostering public involvement in scientific discovery. Combining both approaches enriches data diversity, enhances research outreach, and accelerates the pace of innovation.
Table of Comparison
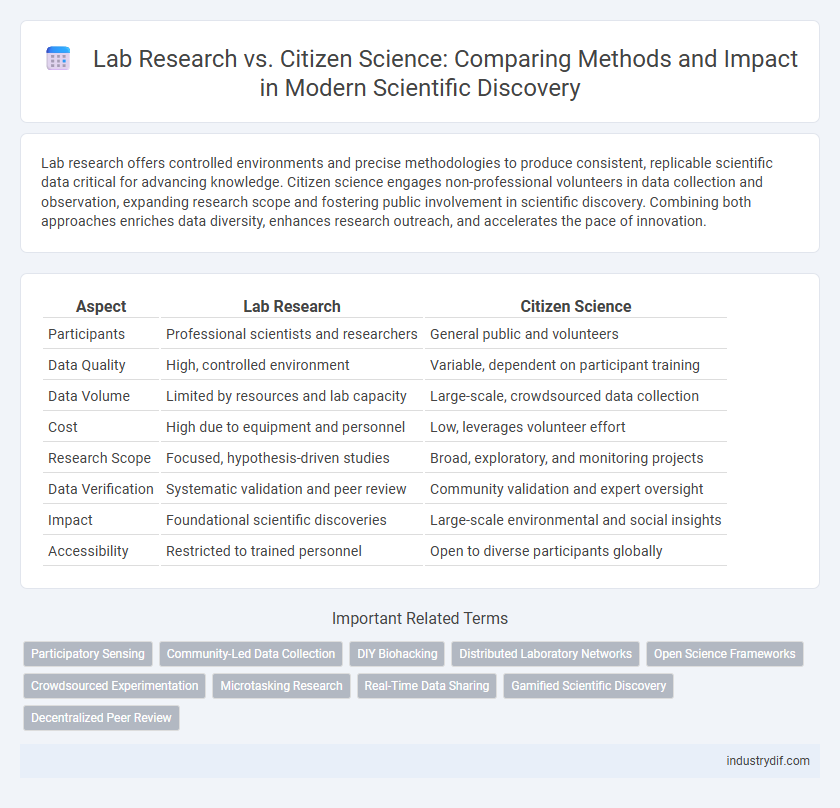
| Aspect | Lab Research | Citizen Science |
|---|---|---|
| Participants | Professional scientists and researchers | General public and volunteers |
| Data Quality | High, controlled environment | Variable, dependent on participant training |
| Data Volume | Limited by resources and lab capacity | Large-scale, crowdsourced data collection |
| Cost | High due to equipment and personnel | Low, leverages volunteer effort |
| Research Scope | Focused, hypothesis-driven studies | Broad, exploratory, and monitoring projects |
| Data Verification | Systematic validation and peer review | Community validation and expert oversight |
| Impact | Foundational scientific discoveries | Large-scale environmental and social insights |
| Accessibility | Restricted to trained personnel | Open to diverse participants globally |
Introduction to Lab Research and Citizen Science
Lab research involves controlled experiments conducted in specialized facilities using advanced instruments and protocols to generate precise and replicable data. Citizen science engages non-professional volunteers in data collection, observation, and analysis, expanding research reach and fostering public involvement in scientific discovery. Both approaches contribute complementary strengths to advancing scientific knowledge across diverse disciplines.
Key Definitions: Lab Research vs Citizen Science
Lab research involves controlled experiments conducted by trained scientists within specialized facilities to generate precise and replicable data, often using advanced instrumentation and standardized protocols. Citizen science engages non-professional volunteers in data collection, observation, or analysis to contribute to large-scale scientific projects, leveraging community participation and diverse geographic coverage. Both approaches complement scientific discovery by balancing rigorous methodological control with broad data acquisition and public involvement.
Historical Evolution of Scientific Research
Scientific research has evolved from exclusive lab-based investigations to inclusive citizen science initiatives, reflecting a shift in data collection and analysis methods. Early scientific breakthroughs predominantly emerged from controlled laboratory environments, while contemporary research increasingly integrates public participation to enhance data diversity and scale. This historical evolution highlights the democratization of science, with citizen science accelerating discoveries in fields such as ecology, astronomy, and epidemiology by harnessing collective observational power.
Methodological Approaches in Lab Research
Lab research employs controlled experimental designs with precise variables manipulation and standardized protocols to ensure reproducibility and statistical rigor. Advanced instrumentation and data acquisition systems enable accurate measurements and quantitative analysis, facilitating hypothesis-driven investigations. This methodological approach contrasts with the more flexible, large-scale observational data collection found in citizen science projects.
Methodological Approaches in Citizen Science
Citizen science employs participatory methodologies that leverage large-scale volunteer involvement for data collection, enabling extensive geographic and temporal coverage often unattainable in traditional lab research. These approaches prioritize standardized protocols, user-friendly tools, and real-time data validation to maintain data quality while maximizing inclusivity and community engagement. Methodologically, citizen science integrates crowd-sourced observations with digital platforms and machine learning algorithms to enhance data analysis and foster collaborative scientific discovery.
Data Accuracy and Reliability Concerns
Lab research typically offers higher data accuracy and reliability due to controlled environments and standardized methodologies. Citizen science, while valuable for large-scale data collection, often faces challenges in consistency and precision because of participant variability. Enhancing training protocols and data verification mechanisms can improve citizen-generated data quality to approach the rigor of professional laboratory research.
Collaboration Models Between Scientists and Citizens
Collaboration models between scientists and citizens in lab research often involve structured frameworks where citizens contribute data collection, analysis, or local knowledge under scientific oversight. Citizen science projects leverage large-scale public participation to enhance data diversity and geographic coverage, complementing traditional lab research methodologies. Hybrid models integrate rigorous experimental protocols with community-driven inquiry, fostering reciprocal learning and increasing the scope and impact of scientific investigations.
Impact on Scientific Discovery and Innovation
Lab research drives scientific discovery through controlled experiments and advanced methodologies, ensuring precise data collection and reproducibility. Citizen science accelerates innovation by harnessing diverse public participation, expanding data sets, and enabling large-scale observations beyond traditional lab constraints. Combining both approaches enhances scientific breakthroughs, integrating rigor with broad experiential data to address complex challenges.
Ethical Considerations in Research Practices
Lab research protocols prioritize strict adherence to institutional review boards (IRBs) and ethical guidelines to ensure participant safety and data integrity, while citizen science projects emphasize transparency, informed consent, and community engagement to address ethical challenges. Ethical considerations in citizen science often include data privacy, participant anonymity, and equitable collaboration between scientists and non-professionals. Balancing rigorous ethical standards in lab research with inclusive and responsible practices in citizen science enhances overall research credibility and societal trust.
Future Trends in Collaborative Scientific Research
Future trends in collaborative scientific research emphasize the integration of traditional lab research methodologies with citizen science contributions, leveraging large-scale data collection and real-time analysis. Advances in digital platforms and AI-driven tools enable seamless coordination between professional scientists and distributed citizen scientists, enhancing accuracy and accelerating discovery processes. The evolution of open-access databases and participatory data validation fosters transparency and inclusivity, positioning collaborative efforts as pivotal drivers of innovation in fields like environmental monitoring and epidemiology.
Related Important Terms
Participatory Sensing
Participatory sensing leverages citizen science to collect diverse environmental and health data through mobile devices, complementing controlled lab research by providing real-world, large-scale datasets. This approach enhances scientific understanding by integrating community engagement with technological tools, enabling continuous monitoring and more extensive spatial-temporal analysis than traditional laboratory settings.
Community-Led Data Collection
Community-led data collection in citizen science enables diverse participants to gather large-scale environmental data, increasing temporal and spatial coverage beyond the capacity of traditional lab research. This approach fosters public engagement and democratizes scientific inquiry while complementing controlled lab experiments with real-world observations.
DIY Biohacking
DIY biohacking in citizen science democratizes lab research by enabling individuals to conduct genetic experiments outside traditional institutions, fostering innovation and personalized solutions in biotechnology. This grassroots approach accelerates data collection and experimentation, often leading to novel insights that complement formal scientific studies while challenging regulatory frameworks.
Distributed Laboratory Networks
Distributed laboratory networks enhance scientific research by integrating traditional lab methodologies with citizen science contributions, enabling large-scale data collection and real-time analysis. This collaborative approach leverages diverse participant expertise and geographic distribution, accelerating innovation and improving data robustness across various scientific disciplines.
Open Science Frameworks
Open Science frameworks enhance transparency and reproducibility in both lab research and citizen science by facilitating data sharing and collaborative workflow management. Empowering citizen scientists through accessible platforms bridges gaps in traditional lab research, accelerating innovation and inclusivity.
Crowdsourced Experimentation
Crowdsourced experimentation leverages the collective intelligence and diverse perspectives of citizen scientists, enabling large-scale data collection and increased sample diversity that traditional lab research often cannot achieve. This approach accelerates hypothesis testing and expands experimental reach while maintaining rigorous data validation protocols to ensure scientific reliability.
Microtasking Research
Lab research employs controlled environments and specialized equipment to ensure precise data collection, while citizen science leverages microtasking to crowdsource large-scale data annotation and analysis from diverse public contributors. Microtasking in citizen science enhances scalability and accelerates data processing, compensating for the limited capacity often encountered in traditional lab research settings.
Real-Time Data Sharing
Lab research benefits from controlled environments and precise instrumentation, enabling accurate real-time data sharing through specialized platforms that maintain data integrity and reproducibility. Citizen science leverages diverse participant networks for large-scale, real-time data collection and sharing, enhancing data volume and geographic coverage but often requiring robust validation protocols to ensure scientific reliability.
Gamified Scientific Discovery
Lab research offers controlled environments and precise methodologies for gamified scientific discovery, ensuring data reliability and reproducibility. Citizen science leverages diverse public participation, increasing data volume and fostering engagement through gamified tasks that democratize complex research processes.
Decentralized Peer Review
Decentralized peer review in lab research enhances transparency and accountability by distributing evaluation across multiple independent experts, reducing bias inherent in traditional centralized models. Citizen science projects leverage this approach to democratize data validation, enabling diverse participants to collaboratively assess findings and improve research reliability outside formal institutional settings.
Lab Research vs Citizen Science Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com