Last-mile delivery remains a critical challenge in transportation logistics, often involving manual handling and high operational costs. Autonomous delivery leverages drones and self-driving vehicles to enhance efficiency, reduce delivery times, and minimize human error. Integrating autonomous technologies in last-mile delivery can significantly optimize resource use and improve customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
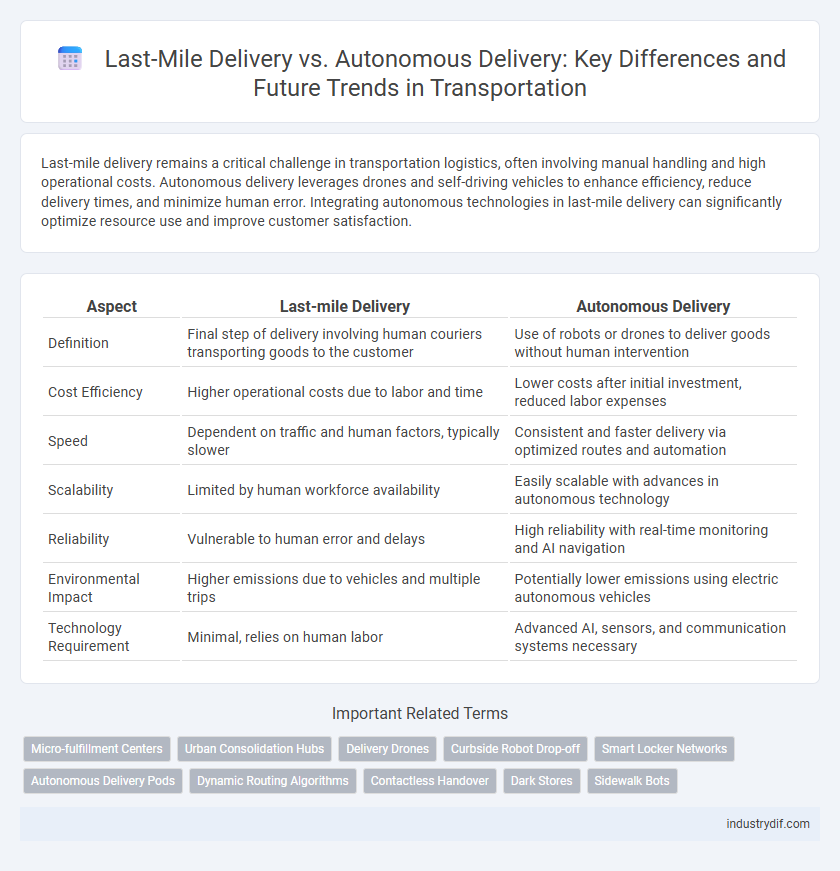
| Aspect | Last-mile Delivery | Autonomous Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final step of delivery involving human couriers transporting goods to the customer | Use of robots or drones to deliver goods without human intervention |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to labor and time | Lower costs after initial investment, reduced labor expenses |
| Speed | Dependent on traffic and human factors, typically slower | Consistent and faster delivery via optimized routes and automation |
| Scalability | Limited by human workforce availability | Easily scalable with advances in autonomous technology |
| Reliability | Vulnerable to human error and delays | High reliability with real-time monitoring and AI navigation |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions due to vehicles and multiple trips | Potentially lower emissions using electric autonomous vehicles |
| Technology Requirement | Minimal, relies on human labor | Advanced AI, sensors, and communication systems necessary |
Understanding Last-Mile Delivery: Key Concepts
Last-mile delivery represents the final step in the supply chain, where products are transported from a distribution hub directly to the customer's location, significantly impacting delivery speed and cost efficiency. This segment accounts for up to 53% of total shipping expenses, emphasizing the importance of optimizing route planning and delivery methods. Autonomous delivery leverages technologies such as drones, robots, and autonomous vehicles to streamline last-mile logistics, reducing human labor costs and improving delivery accuracy in urban and suburban environments.
What Is Autonomous Delivery? An Overview
Autonomous delivery refers to the use of self-driving vehicles and drones to transport goods without human intervention, enhancing efficiency in last-mile delivery logistics. This technology leverages AI, sensors, and GPS navigation to optimize routes, reduce delivery times, and lower operational costs. Autonomous delivery systems are rapidly evolving, offering scalability and improved customer satisfaction in urban and rural environments.
Benefits of Traditional Last-Mile Delivery
Traditional last-mile delivery ensures reliable and timely parcel drop-offs through established human-operated logistics networks, providing personalized customer service and flexibility in handling complex delivery scenarios. Its well-developed infrastructure supports adaptability to diverse urban environments and real-time problem-solving during deliveries. This familiarity fosters trust and accountability, which are crucial for handling sensitive or high-value shipments.
Advantages of Autonomous Delivery Technologies
Autonomous delivery technologies enhance last-mile delivery by improving efficiency through reduced labor costs and faster delivery times, leveraging AI-driven route optimization and real-time traffic data. These systems increase reliability with 24/7 operation capabilities and minimize human error, contributing to consistent service quality. Furthermore, autonomous vehicles reduce carbon emissions by utilizing electric-powered platforms, supporting sustainable urban logistics initiatives.
Challenges Facing Last-Mile Delivery
Last-mile delivery faces significant challenges such as high operational costs, inefficient route planning, and delivery delays due to urban congestion and unpredictable customer availability. Autonomous delivery aims to address these issues by leveraging technologies like drones, autonomous vehicles, and AI-driven logistics to enhance speed, reduce labor dependency, and optimize delivery routes. However, regulatory hurdles, technological limitations, and public acceptance remain critical obstacles in scaling autonomous last-mile solutions.
Obstacles to Widespread Autonomous Delivery Adoption
Last-mile delivery faces challenges such as traffic congestion and complex urban layouts, while autonomous delivery encounters obstacles including regulatory hurdles, limited technological maturity, and high initial investment costs. Ensuring safety and reliability in diverse environments remains a significant barrier to widespread autonomous vehicle deployment. Integration with existing logistics networks and public acceptance also restrict the scalability of autonomous delivery solutions.
Cost Comparison: Last-Mile vs Autonomous Delivery
Last-mile delivery typically incurs higher costs due to labor-intensive processes, including driver wages, fuel, and vehicle maintenance, accounting for up to 53% of total shipping expenses. Autonomous delivery systems reduce operational expenses by eliminating driver wages and optimizing route efficiency, potentially lowering last-mile delivery costs by 40% or more. Initial investments in technology and infrastructure for autonomous delivery remain significant, but long-term savings and scalability offer substantial cost advantages over traditional last-mile methods.
Impact on Supply Chain and Logistics Efficiency
Last-mile delivery directly influences supply chain efficiency by addressing the final step of product transit, often incurring the highest costs and time delays. Autonomous delivery systems enhance logistics efficiency by reducing human labor expenses, minimizing delivery errors, and enabling continuous operation through AI-driven vehicles and drones. Integrating autonomous delivery in last-mile logistics accelerates distribution speed, improves route optimization, and decreases carbon emissions, transforming supply chain dynamics.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Last-mile delivery faces stringent regulatory challenges involving driver certifications, vehicle emissions, and urban traffic restrictions, directly impacting operational efficiency and compliance costs. Autonomous delivery systems must navigate emerging regulations on AI safety protocols, data privacy, and liability frameworks, with ongoing legislative developments shaping deployment strategies. Safety considerations for last-mile delivery emphasize human error reduction and accident prevention, while autonomous delivery prioritizes sensor accuracy, cybersecurity measures, and fail-safe mechanisms to ensure public safety.
The Future of Urban Delivery: Trends and Predictions
Last-mile delivery is evolving rapidly with autonomous delivery vehicles and drones poised to reduce costs and improve efficiency in dense urban environments. Integration of AI-powered route optimization and real-time tracking enhances urban logistics, minimizing delivery times and environmental impact. Industry forecasts predict that by 2030, autonomous systems will handle over 40% of last-mile deliveries, reshaping urban transportation networks and consumer expectations.
Related Important Terms
Micro-fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by reducing delivery distances and enabling faster order processing through localized inventory storage. Autonomous delivery integrates with these centers by utilizing robots and drones to navigate urban environments, minimizing human labor and accelerating delivery times while lowering operational costs.
Urban Consolidation Hubs
Urban consolidation hubs significantly enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by reducing traffic congestion and emissions through centralized parcel sorting and distribution. Autonomous delivery systems integrated with these hubs further optimize urban logistics by enabling contactless, cost-effective, and scalable delivery solutions in dense city environments.
Delivery Drones
Delivery drones enhance last-mile delivery by reducing transit times, lowering operational costs, and enabling access to remote or congested areas. Autonomous delivery systems, utilizing drones equipped with GPS navigation and real-time obstacle detection, optimize parcel handling efficiency and improve the sustainability of urban logistics networks.
Curbside Robot Drop-off
Curbside robot drop-off optimizes last-mile delivery by enabling autonomous vehicles to deliver packages directly to a customer's doorstep, eliminating the need for human couriers and reducing delivery times. This technology leverages AI-powered navigation and real-time tracking to enhance efficiency and curbside accessibility, transforming urban logistics and minimizing traffic congestion.
Smart Locker Networks
Smart locker networks revolutionize last-mile delivery by offering secure, contactless package retrieval, reducing failed delivery attempts and operational costs. Autonomous delivery systems integrated with smart lockers enhance efficiency by enabling seamless, 24/7 access while minimizing human intervention and urban congestion.
Autonomous Delivery Pods
Autonomous delivery pods revolutionize last-mile delivery by enabling contactless, efficient, and scalable parcel transport within urban environments, utilizing advanced sensors and AI for navigation. These pods reduce reliance on human labor and traffic congestion, offering a sustainable solution for timely, secure package delivery in smart cities.
Dynamic Routing Algorithms
Dynamic routing algorithms enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by optimizing route selection in real-time based on traffic, demand, and delivery constraints, significantly reducing delivery times and costs. In autonomous delivery, these algorithms integrate with AI-powered vehicles to enable adaptive navigation and precise resource allocation, improving reliability and scalability in urban logistics.
Contactless Handover
Last-mile delivery faces challenges in achieving efficient contactless handover due to dependency on human interaction, whereas autonomous delivery leverages advanced robotics and AI to enable seamless, secure, and fully contactless parcel transfer at the final destination. Integration of IoT sensors and real-time tracking enhances autonomous delivery systems, minimizing physical contact and improving customer convenience in urban logistics.
Dark Stores
Last-mile delivery efficiency is significantly enhanced by autonomous delivery systems, especially when integrated with dark store networks that minimize fulfillment times through strategic urban locations. Employing autonomous vehicles and robots in dark stores reduces human labor costs and optimizes delivery speed, meeting rising consumer demands for rapid, contactless service.
Sidewalk Bots
Sidewalk bots revolutionize last-mile delivery by autonomously navigating pedestrian pathways to efficiently transport packages directly to consumers, reducing reliance on human couriers and minimizing urban traffic congestion. These autonomous delivery robots leverage advanced sensors and AI algorithms to ensure safe, timely deliveries while optimizing route efficiency in densely populated areas.
Last-mile delivery vs Autonomous delivery Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com