Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers to distribute to retailers or customers, ensuring consistent supply and brand recognition. Ghost distribution operates as a behind-the-scenes method where products are delivered to retailers without the distributor's identity being disclosed, maintaining the manufacturer's market control. Understanding the differences between wholesale and ghost distribution helps businesses optimize supply chain transparency and control.
Table of Comparison
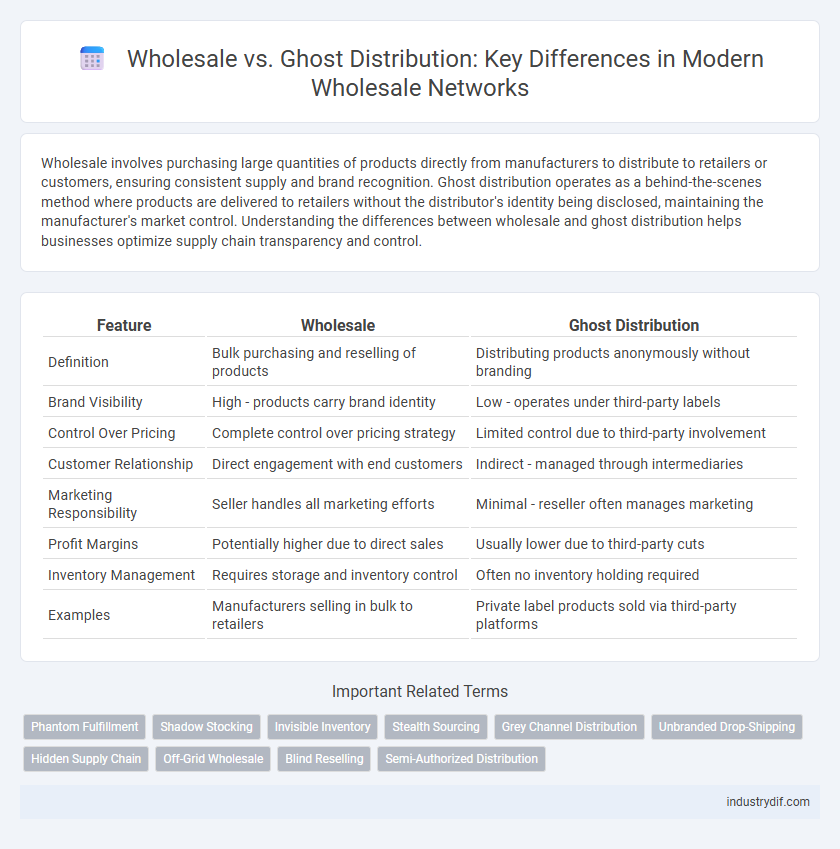
| Feature | Wholesale | Ghost Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk purchasing and reselling of products | Distributing products anonymously without branding |
| Brand Visibility | High - products carry brand identity | Low - operates under third-party labels |
| Control Over Pricing | Complete control over pricing strategy | Limited control due to third-party involvement |
| Customer Relationship | Direct engagement with end customers | Indirect - managed through intermediaries |
| Marketing Responsibility | Seller handles all marketing efforts | Minimal - reseller often manages marketing |
| Profit Margins | Potentially higher due to direct sales | Usually lower due to third-party cuts |
| Inventory Management | Requires storage and inventory control | Often no inventory holding required |
| Examples | Manufacturers selling in bulk to retailers | Private label products sold via third-party platforms |
Understanding Wholesale Distribution: Key Concepts
Wholesale distribution involves purchasing large quantities of goods directly from manufacturers to sell them in smaller quantities to retailers or businesses, enabling economies of scale and efficient supply chain management. Ghost distribution bypasses traditional wholesalers, where products are shipped directly from the manufacturer to the retailer without holding physical inventory, reducing overhead but requiring advanced logistics coordination. Understanding these models helps businesses optimize inventory control, reduce costs, and improve order fulfillment strategies.
What is Ghost Distribution? Definition and Overview
Ghost distribution is a wholesale method where products are shipped directly from the manufacturer to the retailer without passing through traditional wholesale warehouses. This approach eliminates the need for physical inventory at the distributor level, reducing storage costs and speeding up delivery times. Retailers benefit from streamlined supply chains and improved inventory management by leveraging ghost distribution models.
Wholesale vs Ghost Distribution: Core Differences
Wholesale involves the bulk purchase and sale of goods to retailers or other businesses, allowing for inventory control and direct brand representation. Ghost distribution relies on third-party intermediaries who manage product distribution discreetly, often without visible branding or direct contact with retailers. The core differences lie in ownership of inventory, transparency in the supply chain, and the level of control over brand presence and customer relationships.
Advantages of Traditional Wholesale Models
Traditional wholesale models provide direct control over inventory, pricing, and customer relationships, ensuring consistent product availability and personalized service. This approach fosters stronger supplier-retailer partnerships, enabling faster response to market demands and tailored promotional strategies. Efficient logistics and bulk purchasing in traditional wholesale reduce costs, enhancing profit margins and market competitiveness.
The Rise of Ghost Distribution in Modern Supply Chains
Ghost distribution has emerged as a transformative model in modern supply chains, offering wholesalers reduced overhead by eliminating traditional inventory holding and warehousing costs. This method leverages third-party logistics providers and direct-to-retailer shipments, enabling faster delivery times and increased flexibility compared to conventional wholesale distribution. The rise of ghost distribution reflects a growing trend toward leaner, technology-driven supply chains that prioritize speed, cost efficiency, and real-time inventory management.
Challenges Facing Wholesale and Ghost Distribution
Wholesale faces challenges such as inventory management complexities, high upfront costs, and maintaining robust supplier relationships to ensure product availability. Ghost distribution struggles with brand recognition, limited control over product presentation, and dependency on third-party platforms for customer reach. Both models must navigate issues of pricing competitiveness and adapting to rapidly changing market demands.
Impact on Manufacturers and Brands
Wholesale offers manufacturers and brands direct control over product placement, pricing, and brand reputation through established retail channels, fostering long-term partnerships and predictable revenue streams. Ghost distribution, by bypassing traditional intermediaries, often reduces manufacturer visibility and limits brand influence, which can lead to pricing inconsistencies and diluted brand identity. The choice between wholesale and ghost distribution significantly impacts manufacturer strategies in supply chain management, market reach, and brand equity preservation.
Legal and Compliance Issues in Distribution Methods
Wholesale distribution involves direct transactions between manufacturers and retailers, requiring strict adherence to licensing, tax regulations, and product safety standards to ensure legal compliance. Ghost distribution, often operating without transparent record-keeping or proper authorization, poses significant legal risks including potential violations of intellectual property rights and regulatory requirements. Ensuring compliance in wholesale systems demands rigorous documentation and transparent supply chain practices to mitigate risks associated with counterfeit products and regulatory penalties.
Technology's Role in Wholesale and Ghost Distribution
Technology accelerates efficiency in wholesale by enabling real-time inventory management, automated order processing, and enhanced supply chain visibility. Ghost distribution leverages cloud-based platforms and AI-driven analytics to optimize delivery routes, reduce costs, and facilitate seamless communication between manufacturers and retailers. The integration of IoT devices provides predictive maintenance and demand forecasting, transforming both wholesale and ghost distribution into data-driven operations.
Choosing the Right Distribution Model for Your Business
Wholesale offers direct purchasing from manufacturers or distributors, enabling bulk buying at lower costs and greater control over inventory. Ghost distribution relies on intermediaries who manage product delivery without appearing as the seller, reducing logistical burdens but often increasing costs and limiting brand visibility. Selecting the right distribution model depends on factors such as business size, product type, market reach, and the desired level of control over supply chain and customer experience.
Related Important Terms
Phantom Fulfillment
Phantom Fulfillment in wholesale involves fulfilling orders without holding physical inventory, streamlining supply chain costs and reducing overhead. Unlike traditional wholesale that requires stock management and storage, ghost distribution leverages third-party logistics to ship products directly from manufacturers to customers, enhancing operational efficiency.
Shadow Stocking
Shadow stocking in wholesale involves distributors holding inventory without official acknowledgment, allowing for rapid fulfillment without impacting reported stock levels. This practice contrasts with traditional wholesale where stock is fully accounted, enabling ghost distribution models to meet market demands discreetly and efficiently.
Invisible Inventory
Invisible inventory in ghost distribution allows wholesalers to bypass physical stock holding by leveraging third-party warehouses, enhancing supply chain agility and reducing overhead costs. This approach contrasts with traditional wholesale, which requires maintaining visible inventory, leading to increased capital investment and potential stock obsolescence.
Stealth Sourcing
Stealth sourcing in wholesale bypasses traditional distribution channels, enabling businesses to acquire products directly from manufacturers without revealing buyer identity, ensuring competitive pricing and exclusive inventory. Unlike ghost distribution, where intermediaries obscure supply chain origins, stealth sourcing maintains confidentiality while streamlining procurement processes for large-volume buyers.
Grey Channel Distribution
Grey channel distribution operates outside authorized wholesale networks, often involving products sourced from unauthorized distributors that bypass official channels. This unmanaged supply chain can undermine brand integrity, disrupt pricing strategies, and complicate inventory control compared to traditional wholesale distribution.
Unbranded Drop-Shipping
Wholesale involves purchasing bulk products directly from manufacturers or distributors to sell under your own brand, while ghost distribution centers on unbranded drop-shipping where retailers sell products without holding inventory or branding rights. Unbranded drop-shipping enables sellers to offer a wide product range without upfront stock costs, relying on third-party suppliers to handle fulfillment and shipping.
Hidden Supply Chain
Ghost distribution operates through a hidden supply chain that obscures product origins and transaction transparency, unlike traditional wholesale models that maintain clear and traceable supply routes. This lack of visibility in ghost distribution can lead to challenges in quality control, inventory management, and regulatory compliance across the wholesale industry.
Off-Grid Wholesale
Off-grid wholesale leverages decentralized supply chains and direct manufacturer partnerships to bypass traditional ghost distribution methods, enhancing transparency and reducing intermediary costs. This approach boosts efficiency in bulk procurement and supports sustainable logistics practices tailored for remote or underserved markets.
Blind Reselling
Wholesale involves purchasing products in bulk at discounted rates for resale under the buyer's brand, ensuring transparency in sourcing and pricing. Blind reselling, a key aspect of ghost distribution, conceals the original supplier from the end customer, allowing retailers to market goods without revealing wholesale origins.
Semi-Authorized Distribution
Semi-authorized distribution in wholesale operates between fully authorized and ghost distribution models, enabling manufacturers to maintain partial control over product flow while leveraging third-party networks. This approach balances brand protection with market expansion, minimizing risks associated with unauthorized sales typically seen in ghost distribution.
Wholesale vs Ghost Distribution Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com