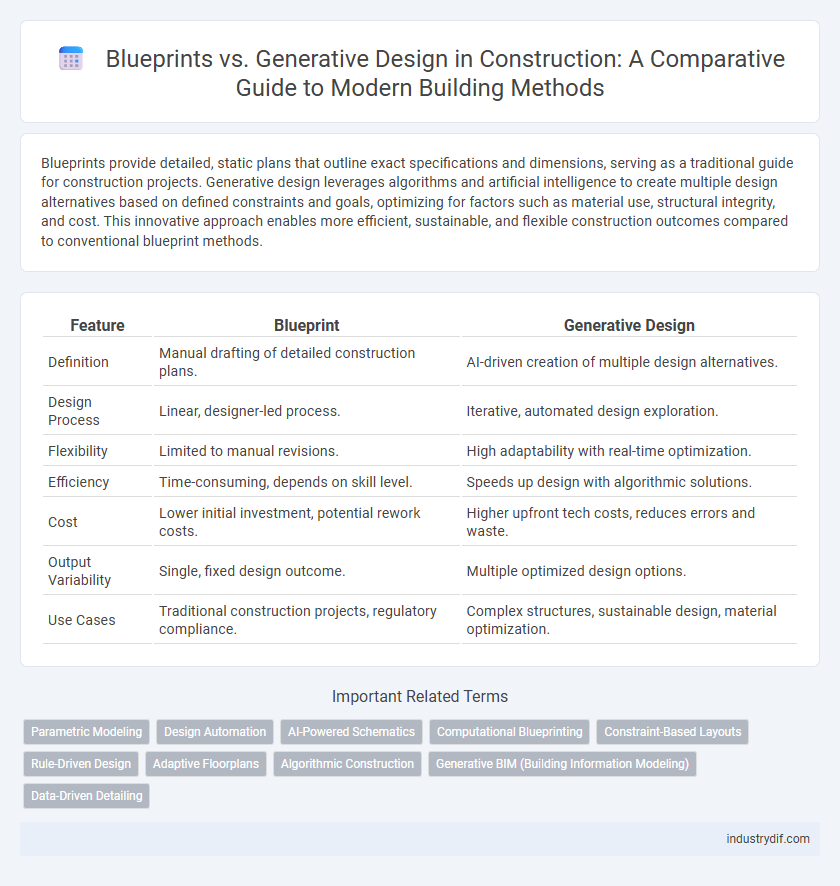
Blueprints provide detailed, static plans that outline exact specifications and dimensions, serving as a traditional guide for construction projects. Generative design leverages algorithms and artificial intelligence to create multiple design alternatives based on defined constraints and goals, optimizing for factors such as material use, structural integrity, and cost. This innovative approach enables more efficient, sustainable, and flexible construction outcomes compared to conventional blueprint methods.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Blueprint | Generative Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual drafting of detailed construction plans. | AI-driven creation of multiple design alternatives. |
| Design Process | Linear, designer-led process. | Iterative, automated design exploration. |
| Flexibility | Limited to manual revisions. | High adaptability with real-time optimization. |
| Efficiency | Time-consuming, depends on skill level. | Speeds up design with algorithmic solutions. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, potential rework costs. | Higher upfront tech costs, reduces errors and waste. |
| Output Variability | Single, fixed design outcome. | Multiple optimized design options. |
| Use Cases | Traditional construction projects, regulatory compliance. | Complex structures, sustainable design, material optimization. |
Introduction: Understanding Blueprint and Generative Design
Blueprints serve as detailed, traditional architectural plans that outline specific measurements, materials, and construction processes, providing a fixed framework for building projects. Generative design leverages advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to explore multiple design alternatives, optimizing for factors such as cost, sustainability, and structural performance. Understanding these methodologies reveals how blueprints ensure precision and compliance, while generative design enables innovation and adaptability in modern construction workflows.
Defining Traditional Blueprints in Construction
Traditional blueprints in construction are detailed technical drawings that provide precise measurements, layouts, and specifications essential for building structures. These blueprints serve as a fixed reference for contractors, architects, and engineers, ensuring consistency and adherence to design standards throughout the construction process. Unlike generative design, blueprints rely on manual drafting and predefined criteria rather than algorithm-driven optimization.
What is Generative Design?
Generative design is an advanced construction technology that uses algorithms and artificial intelligence to create optimized building plans based on specific parameters such as materials, budget, and environmental conditions. Unlike traditional blueprints, which are manually drafted and fixed, generative design produces multiple design alternatives to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. This approach accelerates the decision-making process by evaluating countless scenarios to identify the most innovative and practical solutions for construction projects.
Key Differences: Blueprint vs Generative Design
Blueprints provide detailed, fixed architectural plans with predefined specifications, enabling precise construction based on human expertise and standardized methods. Generative design utilizes advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to create multiple optimized design alternatives by analyzing constraints such as materials, budget, and environmental impact. The key difference lies in blueprints offering static, manually drawn plans, while generative design delivers dynamic, data-driven solutions that adapt to project parameters for enhanced efficiency and innovation.
Benefits of Using Blueprints in Construction
Blueprints provide precise and detailed architectural plans that ensure accurate communication of design specifications to construction teams, minimizing errors and rework. Their standardized format facilitates regulatory approvals and compliance with building codes, streamlining project timelines. By offering a clear visual guide, blueprints enable efficient resource allocation and coordination among contractors, enhancing overall project management.
Advantages of Generative Design for Modern Projects
Generative design revolutionizes modern construction projects by optimizing material usage and reducing waste through algorithm-driven iterations, resulting in cost-effective and sustainable building solutions. Its ability to explore numerous design alternatives quickly outperforms traditional blueprint methods, enhancing innovation and structural performance. Integration with BIM (Building Information Modeling) further streamlines collaboration and project management for complex architectural challenges.
Workflow Comparison: Manual Drafting vs Algorithmic Design
Manual drafting in blueprint creation relies on skilled architects meticulously drawing plans, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error but allows for detailed customization. Generative design uses algorithms to automatically generate multiple design options based on predefined parameters, significantly accelerating the workflow and optimizing material usage. This algorithmic approach enhances efficiency by rapidly iterating solutions, whereas manual drafting depends heavily on individual expertise and iterative revisions.
Impact on Project Efficiency and Cost
Blueprints provide precise, detailed instructions ensuring construction accuracy but can limit flexibility, potentially increasing rework costs. Generative design leverages AI algorithms to explore multiple design options rapidly, optimizing materials and labor use, significantly reducing project timelines and expenses. Integrating generative design with traditional blueprints enhances decision-making accuracy, leading to improved project efficiency and cost savings.
Real-world Applications in Construction
Blueprints serve as traditional, detailed construction plans that guide project execution with precision, while generative design uses advanced algorithms to create multiple design options based on specified constraints. In real-world construction, generative design enhances efficiency by optimizing layouts for materials, cost, and structural integrity, as seen in complex architectural projects and infrastructure planning. Companies leveraging generative design report significant reductions in waste and project timelines compared to conventional blueprint-dependent processes.
Future Trends: Integrating Blueprints and Generative Design
Future trends in construction emphasize the integration of traditional blueprints with generative design to enhance project efficiency and innovation. Combining detailed architectural blueprints with AI-driven generative design allows for optimized material usage, cost reduction, and improved structural performance. This hybrid approach supports sustainable building practices and accelerates the design-to-construction timeline through better collaboration and data-driven decision-making.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Modeling
Blueprints represent static, two-dimensional designs essential for traditional construction planning, while generative design leverages parametric modeling to create dynamic, data-driven models that optimize structural efficiency and material use. Parametric modeling enables rapid iteration by adjusting design parameters, facilitating innovative solutions that adapt to complex construction constraints and performance goals.
Design Automation
Blueprints serve as traditional, static construction plans detailing every element, while generative design uses algorithm-driven automation to create multiple design alternatives rapidly. Design automation in generative design accelerates project timelines, reduces human errors, and optimizes resource allocation by adapting blueprints dynamically based on performance criteria and constraints.
AI-Powered Schematics
AI-powered schematics transform construction by generating optimized blueprints through generative design algorithms that analyze structural efficiency, material use, and environmental impact. Unlike traditional blueprints created manually, AI-driven models adapt designs in real-time, reducing costs and accelerating project timelines while enhancing precision in complex architectural planning.
Computational Blueprinting
Computational blueprinting in construction integrates algorithm-driven processes to automate and optimize traditional blueprint creation, enhancing design precision and project efficiency. Unlike generative design, which explores multiple design iterations through AI, computational blueprinting streamlines detailed schematic production based on predefined parameters and construction standards.
Constraint-Based Layouts
Constraint-based layouts prioritize predefined rules and specifications to ensure structural integrity and functional efficiency in construction blueprints. Generative design leverages algorithms to explore numerous layout permutations, optimizing space utilization and material use while adhering to those constraints for innovative building solutions.
Rule-Driven Design
Rule-driven design in construction relies on predefined blueprints that ensure consistency, compliance with building codes, and efficient resource allocation. Unlike generative design, which explores multiple design alternatives through algorithms, blueprint methods provide a structured, predictable framework essential for regulatory approval and straightforward project execution.
Adaptive Floorplans
Blueprints provide fixed, detailed architectural plans that outline specific measurements and structures, while generative design leverages algorithms to create adaptive floorplans that optimize space, light, and functionality based on user-defined parameters and environmental data. Adaptive floorplans generated through generative design enhance flexibility, allowing dynamic modifications that respond to changing occupant needs and site conditions, which traditional blueprints cannot easily accommodate.
Algorithmic Construction
Blueprints provide detailed, static construction plans, while generative design leverages algorithms to create multiple optimized building solutions based on specific parameters such as materials, structural integrity, and spatial constraints. Algorithmic construction enables real-time iteration and adaptability, enhancing project efficiency and reducing material waste by automating complex design decisions.
Generative BIM (Building Information Modeling)
Generative BIM integrates advanced algorithms and real-time data to automatically produce optimized building designs, enhancing efficiency and precision compared to traditional blueprint methods. This approach enables dynamic modifications, improved clash detection, and sustainable material usage, revolutionizing construction project workflows.
Data-Driven Detailing
Blueprints provide traditional, static plans with predefined specifications, while generative design uses algorithms to analyze data and generate optimized construction details. Data-driven detailing in generative design enhances precision, reduces material waste, and accelerates project timelines by adapting to real-time inputs and performance criteria.
Blueprint vs Generative Design Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com