Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and physical markers, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Drone surveying uses aerial technology to capture high-resolution images and generate accurate 3D maps quickly, improving efficiency and safety. This method enables comprehensive data collection over large or difficult terrain, providing detailed insights for construction planning and monitoring.
Table of Comparison
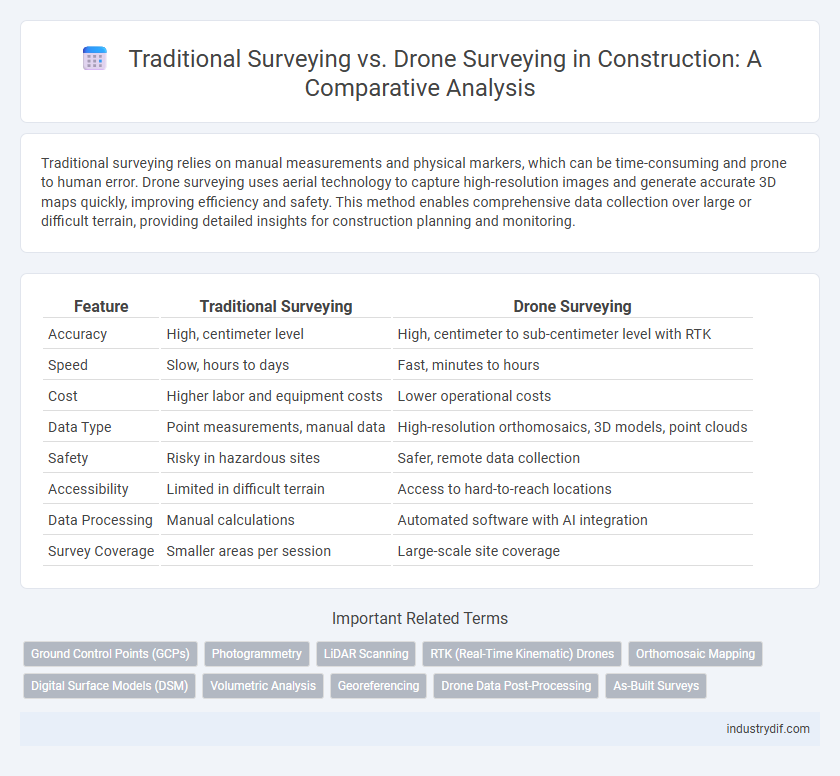
| Feature | Traditional Surveying | Drone Surveying |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High, centimeter level | High, centimeter to sub-centimeter level with RTK |
| Speed | Slow, hours to days | Fast, minutes to hours |
| Cost | Higher labor and equipment costs | Lower operational costs |
| Data Type | Point measurements, manual data | High-resolution orthomosaics, 3D models, point clouds |
| Safety | Risky in hazardous sites | Safer, remote data collection |
| Accessibility | Limited in difficult terrain | Access to hard-to-reach locations |
| Data Processing | Manual calculations | Automated software with AI integration |
| Survey Coverage | Smaller areas per session | Large-scale site coverage |
Introduction to Surveying in Construction
Traditional surveying in construction relies on manual measurements using tools like total stations and theodolites, offering high accuracy but requiring significant time and labor. Drone surveying employs unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with advanced sensors and cameras, enabling faster data collection over large areas with real-time 3D mapping capabilities. Integrating drone technology enhances project efficiency, improves site safety, and provides detailed geospatial data essential for modern construction planning and management.
Overview of Traditional Surveying Methods
Traditional surveying methods rely on instruments such as total stations, theodolites, and level rods to measure distances, angles, and elevations with high precision on construction sites. These methods require skilled surveyors to manually collect data through physical presence, often resulting in longer project timelines and increased labor costs. Despite being time-tested and accurate, traditional surveying can be limited by accessibility challenges and environmental conditions affecting data collection efficiency.
Fundamentals of Drone Surveying Technology
Drone surveying technology utilizes unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-resolution cameras and LiDAR sensors to capture precise geospatial data efficiently. These drones generate detailed 3D maps and orthomosaics through photogrammetry software, significantly reducing field time compared to traditional surveying methods that rely on manual measurements and ground-based equipment. Enhanced data accuracy and rapid site coverage make drone surveying a transformative tool in modern construction project management.
Accuracy Comparison: Traditional vs Drone Surveying
Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and leveling tools, offering centimeter-level accuracy but often requiring extensive time and labor. Drone surveying employs advanced GPS and photogrammetry technology, delivering comparable or superior accuracy with rapid data acquisition and automated processing. While both methods achieve high precision, drone surveying enhances efficiency and consistency in large-scale construction site evaluations.
Time Efficiency and Project Timelines
Traditional surveying typically requires several days or weeks to complete extensive site measurements and data collection, impacting project timelines significantly. Drone surveying captures high-resolution aerial data quickly, often reducing survey time by up to 70%, thereby accelerating decision-making processes and allowing faster project initiation. The integration of drone technology in construction enhances time efficiency, enabling real-time updates and minimizing delays associated with manual data gathering.
Safety Considerations in Surveying Practices
Traditional surveying often exposes workers to hazardous environments such as uneven terrain and heavy traffic, increasing the risk of accidents and physical injuries. Drone surveying significantly enhances safety by remotely capturing site data, minimizing the need for personnel to enter dangerous areas. This technology reduces on-site exposure, thereby lowering the likelihood of falls, collisions, and other safety incidents common in conventional surveying practices.
Cost Analysis: Traditional vs Drone Surveying
Traditional surveying often involves higher labor costs due to the need for specialized personnel and extended project timelines, whereas drone surveying significantly reduces labor expenses by capturing data more rapidly with fewer operators. Equipment costs favor drones over traditional tools since drones provide multifunctional capabilities including aerial imaging and 3D mapping, which eliminate the need for multiple devices. Overall, drone surveying presents a more cost-efficient solution by minimizing time on site and increasing data accuracy, ultimately lowering total project expenditures.
Data Collection and Processing Variations
Traditional surveying relies on manual data collection through total stations and GPS equipment, resulting in point-by-point measurements that require significant time for fieldwork and post-processing. Drone surveying captures aerial imagery and LiDAR data rapidly, enabling the generation of high-resolution orthomosaics and 3D models with automated processing workflows. The enhanced data density and automation in drone surveying reduce human error and accelerate project timelines compared to conventional survey methods.
Applications and Limitations in Construction Projects
Traditional surveying in construction projects relies on manual measurements and physical markers, offering high accuracy for small-scale or intricate site details but requiring extensive time and labor. Drone surveying enhances applications by rapidly capturing aerial data over large or complex terrain, facilitating topographic mapping, progress monitoring, and volumetric analysis with reduced field risk, but it faces limitations in dense urban areas, unfavorable weather, and regulatory restrictions. Combining both methods optimizes construction workflows, balancing precision and efficiency depending on project scale and site conditions.
Future Trends in Construction Surveying Techniques
Future trends in construction surveying indicate a significant shift towards drone surveying due to its increased accuracy, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional surveying methods. Advances in drone technology, such as high-resolution sensors and real-time data processing, enable detailed topographic mapping and progress monitoring with minimal human intervention. Integration of AI and machine learning in drone surveying further enhances predictive analytics and decision-making capabilities on construction sites.
Related Important Terms
Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Ground Control Points (GCPs) are critical in both traditional surveying and drone surveying to ensure spatial accuracy and georeferencing precision. While traditional surveying relies on physical measurement of GCPs using total stations or GPS receivers, drone surveying integrates GCPs captured via aerial imagery, enabling rapid data collection and enhanced consistency across large construction sites.
Photogrammetry
Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and ground-based equipment, which can be time-consuming and limited in capturing large or complex sites. Drone surveying leverages photogrammetry to quickly generate high-resolution 3D maps and models, improving accuracy and efficiency in construction site analysis and progress monitoring.
LiDAR Scanning
LiDAR scanning in drone surveying provides high-resolution, accurate 3D topographic data faster than traditional surveying methods, enabling efficient terrain modeling and precise volume calculations. Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and optical instruments, which can be time-consuming and less effective in complex or inaccessible environments.
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) Drones
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) drones revolutionize construction surveying by delivering precise geospatial data with centimeter-level accuracy, surpassing traditional surveying methods that rely on manual measurements and total stations. These drones accelerate site mapping, enhance topographic data collection, and enable real-time positioning updates, significantly reducing project timelines and improving resource allocation.
Orthomosaic Mapping
Orthomosaic mapping in traditional surveying relies on ground-based equipment and manual data processing, resulting in longer project timelines and limited coverage areas. Drone surveying uses UAVs equipped with high-resolution cameras and GPS, enabling rapid, high-accuracy orthomosaic maps that enhance site analysis and decision-making efficiency in construction projects.
Digital Surface Models (DSM)
Traditional surveying relies on ground-based measurements to create Digital Surface Models (DSM), often resulting in time-intensive data collection with limited spatial coverage. Drone surveying utilizes aerial photogrammetry to rapidly generate high-resolution DSMs, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in construction site analysis and planning.
Volumetric Analysis
Traditional surveying methods for volumetric analysis rely on manual measurements and total stations, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Drone surveying utilizes high-resolution aerial imagery and LiDAR technology to quickly generate accurate volumetric data, improving project efficiency and precision in construction site assessments.
Georeferencing
Traditional surveying relies on manual ground control points and physical markers for georeferencing, often resulting in time-intensive data collection and potential human errors. Drone surveying utilizes GPS-enabled unmanned aerial vehicles combined with photogrammetry software to produce highly accurate georeferenced maps swiftly, improving precision and reducing labor costs.
Drone Data Post-Processing
Drone data post-processing leverages advanced photogrammetry software to convert raw aerial images into accurate 3D models, orthomosaics, and topographic maps, enhancing precision and efficiency compared to traditional surveying methods. Automated workflows and real-time data analysis significantly reduce manual labor and errors, streamlining construction project planning and monitoring.
As-Built Surveys
Traditional surveying for As-Built surveys relies on manual measurements using total stations and GPS, which can be time-consuming and less efficient for large or complex construction sites. Drone surveying utilizes high-resolution aerial imagery and LiDAR, enabling faster data collection, improved accuracy, and comprehensive 3D models essential for verifying construction progress and quality control.
Traditional Surveying vs Drone Surveying Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com