Brick and mortar construction offers proven durability and traditional aesthetic appeal, relying on skilled labor and time-tested materials. In contrast, 3D printed concrete enables faster, more cost-effective building with complex designs, reducing material waste and labor costs. The choice between these methods depends on project scale, budget, and desired architectural flexibility.
Table of Comparison
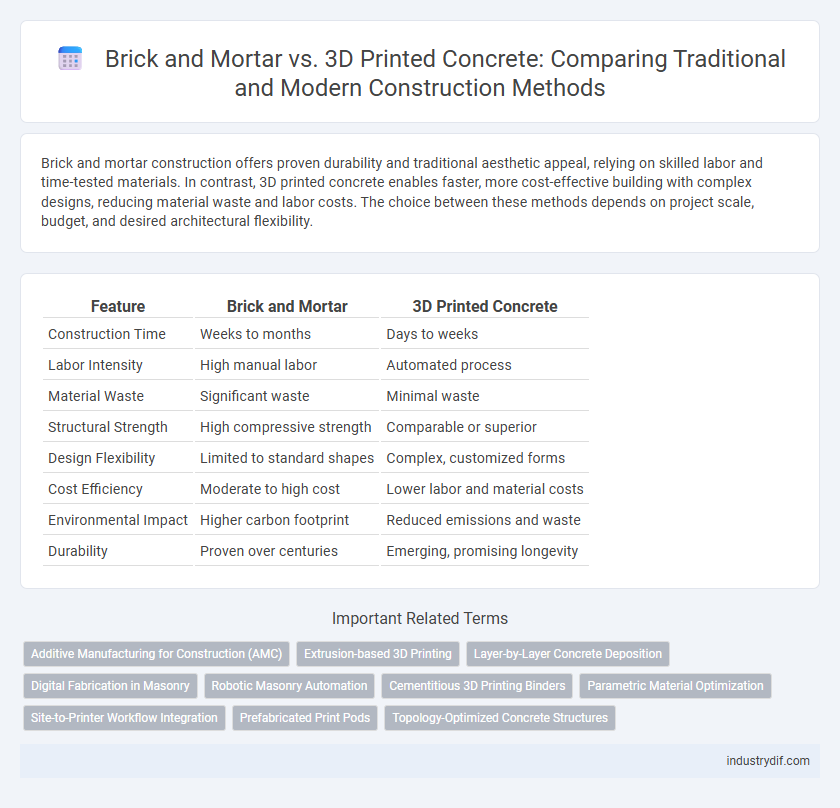
| Feature | Brick and Mortar | 3D Printed Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Time | Weeks to months | Days to weeks |
| Labor Intensity | High manual labor | Automated process |
| Material Waste | Significant waste | Minimal waste |
| Structural Strength | High compressive strength | Comparable or superior |
| Design Flexibility | Limited to standard shapes | Complex, customized forms |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate to high cost | Lower labor and material costs |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Reduced emissions and waste |
| Durability | Proven over centuries | Emerging, promising longevity |
Introduction to Brick and Mortar and 3D Printed Concrete
Brick and mortar construction relies on traditional techniques using individual bricks bonded with mortar to form durable structures, known for their strength and thermal insulation properties. In contrast, 3D printed concrete employs layer-by-layer extrusion of cementitious material, enabling rapid, precise construction with reduced material waste and labor costs. Innovations in 3D printing technology are transforming construction by offering scalable solutions for complex architectural designs unachievable with conventional brick and mortar methods.
Historical Overview of Construction Methods
Traditional brick and mortar construction, dating back thousands of years, has relied on manual labor and skilled craftsmanship to assemble durable structures, with bricks kiln-fired and bonded by cement mortar. The emergence of 3D printed concrete in the 21st century revolutionizes building by automating layer-by-layer construction using digital blueprints and specialized extrusion technologies. Historical methods emphasize craftsmanship and repetitive manual processes, while 3D printing introduces precision, customization, and reduced material waste in modern construction practices.
Material Properties: Bricks vs 3D Printed Concrete
Bricks offer high compressive strength and thermal insulation due to their dense clay composition, making them durable for traditional masonry structures. 3D printed concrete enables customized material mixes with improved tensile strength and enhanced bonding properties, allowing for complex shapes and rapid curing. The porosity and density of 3D printed concrete can be optimized for durability and resistance to environmental stresses, often surpassing conventional brick performance in specific applications.
Speed and Efficiency in Construction
3D printed concrete significantly accelerates construction timelines by automating the layering process, reducing labor costs and human error compared to traditional brick and mortar methods. Unlike conventional construction, which relies on sequential brick laying and mortar drying, 3D printing allows for continuous operation, enabling the rapid creation of complex structures. This technology enhances efficiency by minimizing material waste and streamlining project workflows, resulting in faster project completion and optimized resource utilization.
Cost Comparison: Traditional vs 3D Printing
Traditional brick and mortar construction typically involves higher labor costs and extended project timelines, often resulting in increased overall expenses. In contrast, 3D printed concrete can reduce material waste and labor requirements, significantly lowering construction costs by up to 30%. The automation and precision of 3D printing technology also enhance efficiency, offering a cost-effective alternative for complex architectural designs.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Traditional brick and mortar construction generates significant carbon emissions due to energy-intensive manufacturing and transportation of materials. In contrast, 3D printed concrete reduces waste by precisely depositing material, lowers labor requirements, and enables the use of eco-friendly, recyclable components. Lifecycle assessments indicate 3D printed concrete structures offer enhanced sustainability through minimal raw material consumption and reduced onsite environmental disruption.
Design Flexibility and Customization
3D printed concrete offers unparalleled design flexibility and customization, enabling complex geometries and intricate architectural details that are challenging with traditional brick and mortar methods. Unlike conventional construction, 3D printing allows for precise control over material placement, reducing waste and enabling rapid iteration of bespoke design elements. This innovative technique supports adaptive building forms tailored to specific project requirements, elevating functional and aesthetic possibilities beyond standard masonry limitations.
Labor Requirements and Workforce Evolution
Brick and mortar construction demands a large, skilled labor force for tasks such as bricklaying, mortar mixing, and alignment, resulting in higher labor costs and longer project timelines. In contrast, 3D printed concrete drastically reduces manual labor needs by automating the building process through robotic arms and computer-controlled extrusion, enhancing precision and efficiency. Workforce evolution in construction now emphasizes technical skills in operating and maintaining 3D printing machinery, signaling a shift from traditional craftsmanship to digital proficiency.
Structural Performance and Durability
Brick and mortar construction offers proven structural performance and long-term durability due to centuries of material testing and traditional building techniques. In contrast, 3D printed concrete provides enhanced design flexibility and rapid construction, but its structural performance varies depending on print quality and material composition, requiring further validation for widespread durability. Ongoing research aims to optimize 3D printed concrete mixes and layering methods to meet or exceed the robustness of conventional masonry structures.
Future Trends in Building Technology
Future trends in building technology emphasize the increasing adoption of 3D printed concrete, driven by its potential for rapid construction, reduced material waste, and enhanced design flexibility compared to traditional brick and mortar methods. Innovations in printable concrete mixtures and robotic printing systems are enabling the creation of complex architectural forms with improved structural performance. The integration of sustainable materials and automation positions 3D printed concrete as a transformative solution for scalable, cost-efficient, and environmentally friendly construction practices.
Related Important Terms
Additive Manufacturing for Construction (AMC)
Additive Manufacturing for Construction (AMC) leverages 3D printed concrete to revolutionize traditional brick and mortar methods by enabling faster build times, reduced material waste, and customizable architectural designs with enhanced structural precision. This innovative technology improves sustainability and cost-efficiency in construction projects while maintaining high durability and strength standards.
Extrusion-based 3D Printing
Extrusion-based 3D printing in construction offers precise layering of concrete, enabling faster build times and reduced material waste compared to traditional brick and mortar methods. This technology enhances structural customization and complex design capabilities while minimizing labor costs and on-site human error.
Layer-by-Layer Concrete Deposition
Layer-by-layer concrete deposition in 3D printed construction enables precise control over material placement, reducing waste and accelerating build times compared to traditional brick and mortar methods. This technique enhances structural integrity by allowing customized reinforcement within each layer, optimizing strength and durability in complex architectural designs.
Digital Fabrication in Masonry
Digital fabrication in masonry transforms traditional brick and mortar methods by enabling precise 3D printed concrete structures that reduce material waste and construction time. Advanced robotics and computer-aided design streamline the building process, enhancing structural integrity and allowing for complex architectural forms unattainable through conventional masonry.
Robotic Masonry Automation
Robotic masonry automation in 3D printed concrete offers enhanced precision, speed, and reduced labor costs compared to traditional brick and mortar construction methods. This technology enables complex architectural designs with less material waste and improved structural integrity through layer-by-layer concrete deposition.
Cementitious 3D Printing Binders
Cementitious 3D printing binders, composed of specialized mixes of Portland cement, silica fume, and additives, enable rapid setting, high early strength, and enhanced flowability compared to traditional brick and mortar methods. These binders optimize layer adhesion, reduce material waste, and allow complex geometries, significantly advancing construction efficiency and sustainability.
Parametric Material Optimization
Parametric material optimization in 3D printed concrete enables precise control over material distribution, enhancing structural performance and reducing waste compared to traditional brick and mortar methods. This approach leverages computational design to tailor concrete properties at a micro-level, resulting in innovative shapes and stronger, lighter constructions.
Site-to-Printer Workflow Integration
Brick and mortar construction relies heavily on manual site-to-printer workflow integration, involving labor-intensive material transport and alignment processes that can cause delays and inconsistencies. In contrast, 3D printed concrete streamlines site-to-printer integration through automated digital modeling and precise on-site material extrusion, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing human error.
Prefabricated Print Pods
Prefabricated print pods in 3D printed concrete construction enable rapid assembly with precise, uniform components, reducing labor costs and construction time compared to traditional brick and mortar methods. This technology enhances structural accuracy and sustainability by minimizing material waste and improving onsite efficiency through modular prefabrication.
Topology-Optimized Concrete Structures
Topology-optimized concrete structures enable the design of lightweight, material-efficient forms that traditional brick and mortar construction cannot achieve due to its uniform and repetitive modular constraints. 3D printed concrete leverages computational algorithms to precisely deposit material only where needed, significantly reducing waste and improving structural performance compared to conventional masonry methods.
Brick and Mortar vs 3D Printed Concrete Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com