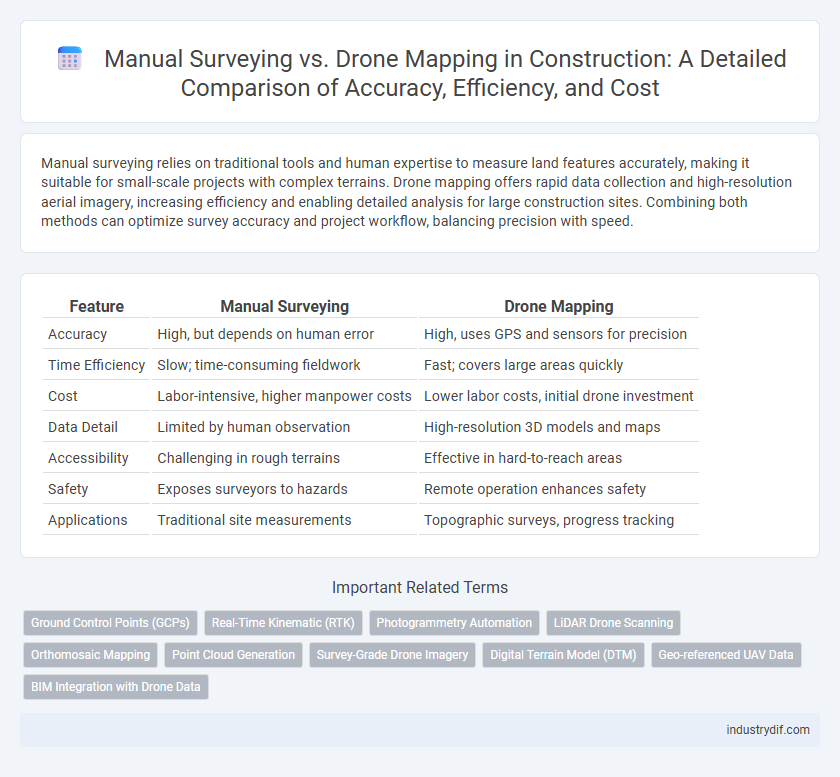
Manual surveying relies on traditional tools and human expertise to measure land features accurately, making it suitable for small-scale projects with complex terrains. Drone mapping offers rapid data collection and high-resolution aerial imagery, increasing efficiency and enabling detailed analysis for large construction sites. Combining both methods can optimize survey accuracy and project workflow, balancing precision with speed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Surveying | Drone Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High, but depends on human error | High, uses GPS and sensors for precision |
| Time Efficiency | Slow; time-consuming fieldwork | Fast; covers large areas quickly |
| Cost | Labor-intensive, higher manpower costs | Lower labor costs, initial drone investment |
| Data Detail | Limited by human observation | High-resolution 3D models and maps |
| Accessibility | Challenging in rough terrains | Effective in hard-to-reach areas |
| Safety | Exposes surveyors to hazards | Remote operation enhances safety |
| Applications | Traditional site measurements | Topographic surveys, progress tracking |
Introduction to Manual Surveying and Drone Mapping
Manual surveying employs traditional tools like theodolites, total stations, and measuring tapes to capture precise land measurements and topographical data, often requiring skilled surveyors on-site. Drone mapping utilizes unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-resolution cameras and GPS technology to rapidly generate detailed orthophotos and 3D models for construction site analysis. Both methods serve critical roles in construction, with manual surveying providing accuracy in small-scale measurements and drone mapping enabling efficient large-area data collection.
Key Differences Between Manual Surveying and Drone Mapping
Manual surveying relies on traditional tools like theodolites and total stations to measure land features with high accuracy but requires significant time and labor. Drone mapping uses unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-resolution cameras and GPS technology to quickly capture extensive terrain data, enabling faster project turnaround and improved coverage. While manual surveying excels in precise detail for small areas, drone mapping offers efficient large-scale topographic surveys and real-time data processing for dynamic construction site monitoring.
Accuracy and Precision in Construction Surveys
Manual surveying in construction provides high precision through direct human control and immediate adjustments, but it is time-consuming and subject to human error. Drone mapping enhances accuracy by capturing comprehensive aerial data quickly over large areas, reducing positional errors with advanced GPS and photogrammetry technologies. Combining both methods can optimize survey accuracy and precision, ensuring reliable site measurements for construction projects.
Time Efficiency: Manual vs. Drone-Based Methods
Manual surveying in construction often requires days to complete detailed measurements due to limited coverage and slower data processing. Drone mapping significantly reduces time by capturing large-scale, high-resolution aerial data within hours, accelerating project timelines. Integrating drone technology enhances time efficiency, enabling faster decision-making and resource allocation on construction sites.
Cost Considerations: Traditional Surveying vs. Drone Mapping
Manual surveying often incurs higher labor costs and longer project timelines due to the extensive fieldwork required. Drone mapping significantly reduces expenses by minimizing manpower and accelerating data collection with high-resolution aerial imaging. Overall, drone technology offers a cost-effective alternative for construction site surveys without compromising accuracy.
Safety Implications for Survey Teams
Manual surveying exposes teams to physical hazards such as uneven terrain, heavy machinery, and extreme weather conditions, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries on construction sites. Drone mapping significantly enhances safety by reducing the need for personnel to enter hazardous areas, enabling remote data collection with minimal physical risk. Incorporating drones minimizes human exposure to dangerous environments, promoting safer working conditions and reducing liability for construction firms.
Equipment and Technology Requirements
Manual surveying demands traditional equipment, such as total stations, theodolites, measuring tapes, and GPS receivers, requiring skilled operators for precise data collection. Drone mapping utilizes advanced UAVs equipped with high-resolution cameras, LiDAR sensors, and GPS systems, offering rapid data acquisition over extensive areas with minimal human intervention. The technology shift from handheld instruments to automated aerial platforms significantly enhances efficiency, accuracy, and safety in construction site surveying.
Data Collection and Processing Workflow
Manual surveying relies on traditional tools such as total stations and GPS receivers, requiring extensive fieldwork to collect precise geospatial data, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Drone mapping streamlines data collection by capturing high-resolution aerial imagery and generating accurate 3D models using photogrammetry software, significantly reducing field time and improving data density. The processing workflow in drone mapping integrates automated data stitching, georeferencing, and orthomosaic generation, enabling faster analysis and decision-making compared to manual surveying's step-by-step data validation and manual input.
Applications in Modern Construction Projects
Manual surveying remains essential for precise measurements in confined or complex sites, providing high accuracy in elevation and boundary assessments. Drone mapping accelerates data collection over large or inaccessible areas, generating detailed topographic maps and 3D models that enhance project planning and monitoring. Integrating both techniques optimizes construction workflows by combining the detailed accuracy of manual surveys with the comprehensive spatial insights from drone-generated data.
Future Trends in Construction Surveying
Future trends in construction surveying indicate an increasing shift towards drone mapping due to its high accuracy, real-time data collection, and cost-efficiency, revolutionizing site monitoring and progress tracking. Manual surveying remains relevant for complex terrain and detailed measurements but is gradually supplemented by advanced technologies like LiDAR-equipped drones and AI-powered data analysis. Integration of BIM (Building Information Modeling) with drone-generated survey data enhances project planning, risk assessment, and decision-making, driving innovation in construction workflows.
Related Important Terms
Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Ground Control Points (GCPs) serve as precise reference markers essential for aligning drone mapping data with real-world coordinates, enhancing the spatial accuracy of aerial surveys in construction. Manual surveying relies heavily on physical GCP placement and measurement, while drone mapping integrates these points with high-resolution imagery for efficient and scalable site analysis.
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK)
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) technology enhances drone mapping by providing centimeter-level accuracy in geospatial data collection, significantly surpassing the precision of traditional manual surveying methods. RTK-equipped drones streamline construction site surveys, reduce human error, and accelerate project timelines through rapid, high-resolution topographic mapping.
Photogrammetry Automation
Manual surveying relies on traditional tools like total stations and GPS, requiring extensive human labor and time, while drone mapping leverages photogrammetry automation to rapidly create highly accurate 3D models and topographic maps from aerial imagery. Photogrammetry automation in drone mapping enhances precision, reduces errors, and streamlines data acquisition and processing, significantly improving construction site monitoring and project management efficiency.
LiDAR Drone Scanning
LiDAR drone scanning offers higher accuracy and faster data collection in construction site surveys compared to traditional manual surveying methods, enabling precise topographic mapping and 3D modeling. Manual surveying remains labor-intensive and time-consuming, while LiDAR technology integrates with drones to capture detailed point clouds even in challenging environments, enhancing project planning and reducing errors.
Orthomosaic Mapping
Manual surveying provides precise ground-level data critical for small-scale orthomosaic mapping but is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Drone mapping accelerates orthomosaic generation by capturing high-resolution aerial images, enabling rapid processing and extensive coverage for large construction sites with enhanced accuracy and efficiency.
Point Cloud Generation
Manual surveying relies on traditional tools like total stations and GNSS receivers to generate point clouds through precise ground measurements, often requiring significant time and labor. Drone mapping uses aerial photogrammetry and LiDAR sensors to quickly capture high-density point clouds over large construction sites, enhancing efficiency and spatial data accuracy.
Survey-Grade Drone Imagery
Survey-grade drone imagery provides high-precision data with centimeter-level accuracy, significantly improving the efficiency and safety of construction site surveys compared to traditional manual surveying methods. The advanced GPS technology and multispectral sensors in drones enable rapid data collection and detailed topographic mapping, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error.
Digital Terrain Model (DTM)
Manual surveying provides precise ground-level data but is time-consuming and limited in coverage for Digital Terrain Model (DTM) creation. Drone mapping accelerates DTM generation by capturing high-resolution aerial images, producing accurate terrain models with enhanced spatial detail and efficiency in large-scale construction projects.
Geo-referenced UAV Data
Geo-referenced UAV data in drone mapping offers precise topographic measurements with enhanced spatial accuracy compared to manual surveying, enabling faster data acquisition and real-time geospatial analytics. This integration reduces human error and improves project efficiency by providing comprehensive 3D models and orthomosaic maps critical for construction site monitoring and progress tracking.
BIM Integration with Drone Data
Drone mapping generates high-resolution geospatial data that integrates seamlessly with Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in construction planning. Manual surveying, while traditional, often lacks the detailed spatial datasets provided by drones, limiting the depth of BIM visualization and project coordination.
Manual Surveying vs Drone Mapping Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com