Prefab construction involves manufacturing building components off-site, which are then transported and assembled on-site, offering precision and reduced construction time. Modular volumetric construction takes this a step further by creating fully finished 3D modules in a factory, allowing for faster installation and higher quality control. Both methods enhance efficiency and sustainability, but modular volumetric construction typically provides greater flexibility for complex designs and faster project completion.
Table of Comparison
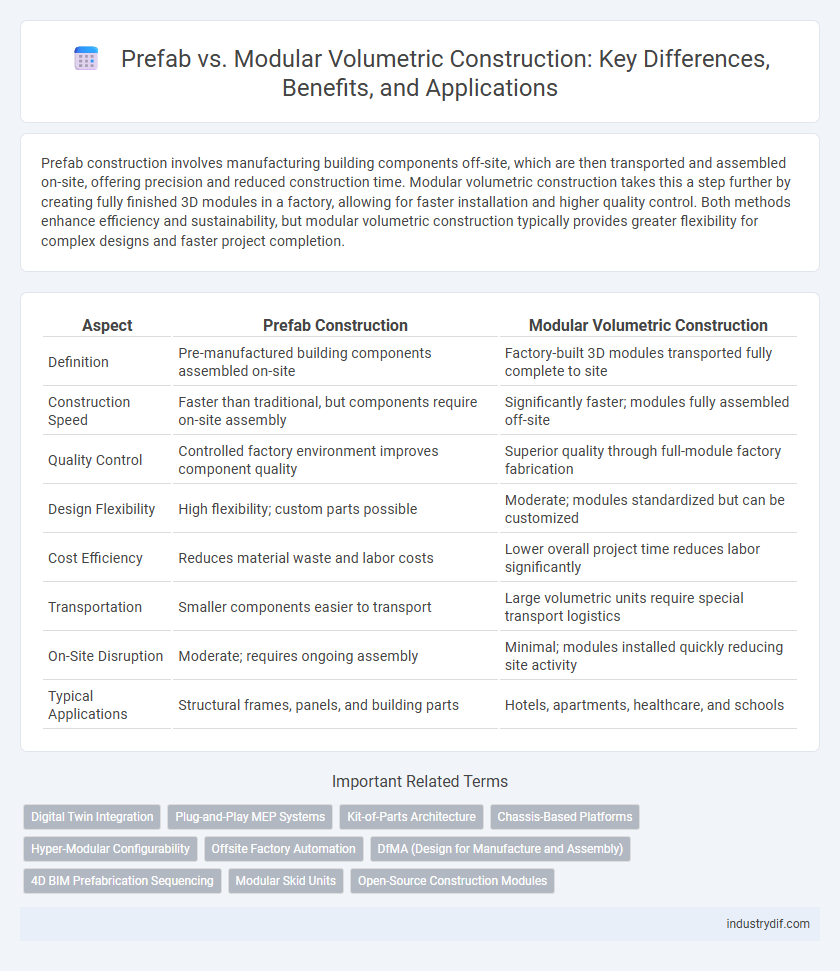
| Aspect | Prefab Construction | Modular Volumetric Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured building components assembled on-site | Factory-built 3D modules transported fully complete to site |
| Construction Speed | Faster than traditional, but components require on-site assembly | Significantly faster; modules fully assembled off-site |
| Quality Control | Controlled factory environment improves component quality | Superior quality through full-module factory fabrication |
| Design Flexibility | High flexibility; custom parts possible | Moderate; modules standardized but can be customized |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces material waste and labor costs | Lower overall project time reduces labor significantly |
| Transportation | Smaller components easier to transport | Large volumetric units require special transport logistics |
| On-Site Disruption | Moderate; requires ongoing assembly | Minimal; modules installed quickly reducing site activity |
| Typical Applications | Structural frames, panels, and building parts | Hotels, apartments, healthcare, and schools |
Definition of Prefab and Modular Volumetric Construction
Prefab construction, short for prefabrication, involves manufacturing building components off-site in controlled factory settings before transporting them to the construction site for assembly. Modular volumetric construction specifically refers to the process of constructing fully enclosed, three-dimensional modules or units off-site, which are then transported and stacked on-site to create complete buildings. Both methods enhance efficiency and reduce on-site labor but differ in the scale and complexity of pre-assembled components.
Key Differences Between Prefab and Modular Volumetric Methods
Prefab construction involves manufacturing building components off-site in standard sizes, which are later assembled on-site, while modular volumetric construction creates fully finished three-dimensional modules that are transported and installed as complete units. Prefab methods offer flexibility in design and easier transportation of flat components, whereas modular volumetric construction enables faster on-site assembly and higher quality control by integrating all building systems within each module. The key difference lies in the degree of off-site completion, with modular volumetric providing more comprehensive pre-construction and resulting in reduced site disruption compared to traditional prefab approaches.
Components and Materials Used in Each Approach
Prefab construction typically involves factory-produced components like wall panels, roof trusses, and floor systems made from materials such as wood, steel, concrete, and engineered composites. Modular volumetric construction utilizes fully finished, three-dimensional modules built off-site, often incorporating steel frames or reinforced concrete, along with insulation, drywall, and complete interior finishes. Both methods prioritize precision manufacturing but differ in the extent of off-site assembly and integration of materials into deliverable building units.
Construction Speed and Project Timelines
Modular volumetric construction significantly reduces project timelines by fabricating fully finished three-dimensional units off-site, allowing parallel progress of on-site groundwork and unit assembly. Prefabrication involves producing flat components or assemblies, which still require substantial on-site labor, resulting in longer construction durations compared to volumetric methods. Utilizing modular volumetric techniques can cut construction schedules by up to 50%, enhancing overall project delivery speed and efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Prefab vs Modular Volumetric
Prefab construction typically involves off-site manufacturing of flat panels or components, resulting in lower initial material costs but higher onsite labor expenses. Modular volumetric construction assembles fully finished, three-dimensional units in factories, leading to greater upfront investment but significant savings in construction time and reduced onsite labor costs. Overall, modular volumetric methods offer better cost efficiency in large-scale projects through minimized delays and waste, while prefab remains cost-effective for simpler or smaller-scale applications.
Quality Control and Manufacturing Standards
Prefab construction involves assembling building components in a factory setting, allowing for consistent quality control through standardized processes and inspections. Modular volumetric construction takes this further by fabricating complete, fully finished units in controlled environments, ensuring higher manufacturing standards and reduced on-site variability. Both methods enhance precision, but modular volumetric construction offers superior integration and quality assurance due to its comprehensive off-site production.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Prefab construction minimizes waste by manufacturing components in controlled factory settings, enhancing material efficiency and reducing on-site pollution. Modular volumetric construction further advances sustainability by enabling complete building units to be assembled off-site, significantly cutting transportation emissions and on-site construction time. Both methods improve energy efficiency and resource management, supporting greener building practices and lowering the carbon footprint of construction projects.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Prefab construction offers limited design flexibility due to standardized components, while modular volumetric construction allows greater customization with fully fabricated, three-dimensional units tailored to specific architectural requirements. Modular volumetric systems support intricate design variations and complex layouts that prefab panels cannot easily achieve. Enhanced adaptability in modular volumetric construction streamlines on-site assembly without compromising unique design features.
Transportation and On-Site Assembly Challenges
Prefab construction components are typically transported in flat-packed or panelized form, requiring careful handling to avoid damage during transit, while modular volumetric construction involves shipping fully assembled volumetric units that demand larger transport logistics and specialized vehicles. On-site assembly for prefab systems often requires precise alignment and connection of multiple panels, which can extend installation time and complexity compared to modular volumetric units that are craned directly into place. Transportation restrictions such as road width, weight limits, and permits play a critical role in planning modular volumetric projects, potentially increasing costs and site access challenges.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Prefab construction offers significant efficiency in repetitive projects such as affordable housing and schools, enabling faster on-site assembly and reduced labor costs. Modular volumetric construction excels in healthcare facilities and hospitality sectors by delivering fully finished, volumetric units that maintain rigorous quality control and allow easier customization. Case studies from urban residential developments and hospital expansions demonstrate modular methods reducing construction timelines by up to 50% compared to traditional prefab approaches.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Integration
Prefab construction involves assembling components off-site and transporting them for installation, while modular volumetric construction creates fully finished sections with integrated systems ready for immediate assembly onsite. Integrating digital twin technology in modular volumetric construction enhances real-time monitoring, precise quality control, and optimized facility management throughout the building lifecycle.
Plug-and-Play MEP Systems
Plug-and-play MEP systems in modular volumetric construction enable rapid installation by integrating mechanical, electrical, and plumbing components within factory-built modules, reducing on-site labor and minimizing project timelines. This contrasts with traditional prefab methods where MEP systems are often installed separately on-site, leading to potential coordination challenges and longer assembly durations.
Kit-of-Parts Architecture
Kit-of-parts architecture in prefab construction emphasizes standardized components manufactured offsite for flexible assembly, enhancing design customization and site efficiency. Modular volumetric construction integrates fully finished 3D modules, providing rapid installation but less adaptability compared to the kit-of-parts approach.
Chassis-Based Platforms
Chassis-based platforms in prefab and modular volumetric construction provide structural support and mobility, enabling rapid assembly and transportation of building modules. These systems enhance efficiency by integrating mechanical, electrical, and plumbing components within factory-built units, reducing on-site labor and construction timelines.
Hyper-Modular Configurability
Hyper-modular configurability in modular volumetric construction allows for rapid assembly and scalable customization of pre-manufactured units, outperforming traditional prefab methods by enabling seamless integration of complex building components. This approach significantly reduces on-site labor, enhances design flexibility, and accelerates project timelines through standardized, factory-built volumetric modules.
Offsite Factory Automation
Offsite factory automation in prefab construction streamlines repetitive tasks through standardized component production, enhancing efficiency but limiting design flexibility. Modular volumetric construction leverages advanced robotics and digital workflows to assemble fully finished volumetric units, significantly reducing onsite time and improving quality control across large-scale projects.
DfMA (Design for Manufacture and Assembly)
Prefab construction involves manufacturing building components off-site for on-site assembly, emphasizing standardized parts, while modular volumetric construction creates fully finished 3D modules assembled on-site, enhancing speed and quality control. Leveraging DfMA principles, modular volumetric construction optimizes design for streamlined manufacturing and efficient assembly, reducing waste and construction time compared to traditional prefab methods.
4D BIM Prefabrication Sequencing
4D BIM prefabrication sequencing enhances both prefab and modular volumetric construction by integrating time-based scheduling with 3D modeling, optimizing on-site assembly and resource allocation. Modular volumetric construction benefits from this approach through improved precision in factory-based fabrication and streamlined assembly workflows, reducing project timelines and construction waste.
Modular Skid Units
Modular skid units offer enhanced flexibility and rapid installation compared to traditional prefab components by integrating complete mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems within a transportable frame. This volumetric construction method reduces onsite labor, shortens project timelines, and improves quality control through factory precision engineering.
Open-Source Construction Modules
Open-source construction modules enhance modular volumetric construction by providing standardized, customizable building components that streamline assembly and reduce costs compared to traditional prefab methods. These openly shared designs foster innovation and collaboration within the construction industry, accelerating project timelines and improving sustainability through reusable, scalable solutions.
Prefab vs Modular Volumetric Construction Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com