Tower cranes provide exceptional height and lifting capacity, making them ideal for large-scale construction projects requiring heavy material handling at significant elevations. Self-erecting cranes offer greater mobility and quicker setup times, suited for smaller sites or urban areas with space constraints. Choosing between the two depends on project scale, site accessibility, and lifting requirements to optimize efficiency and safety.
Table of Comparison
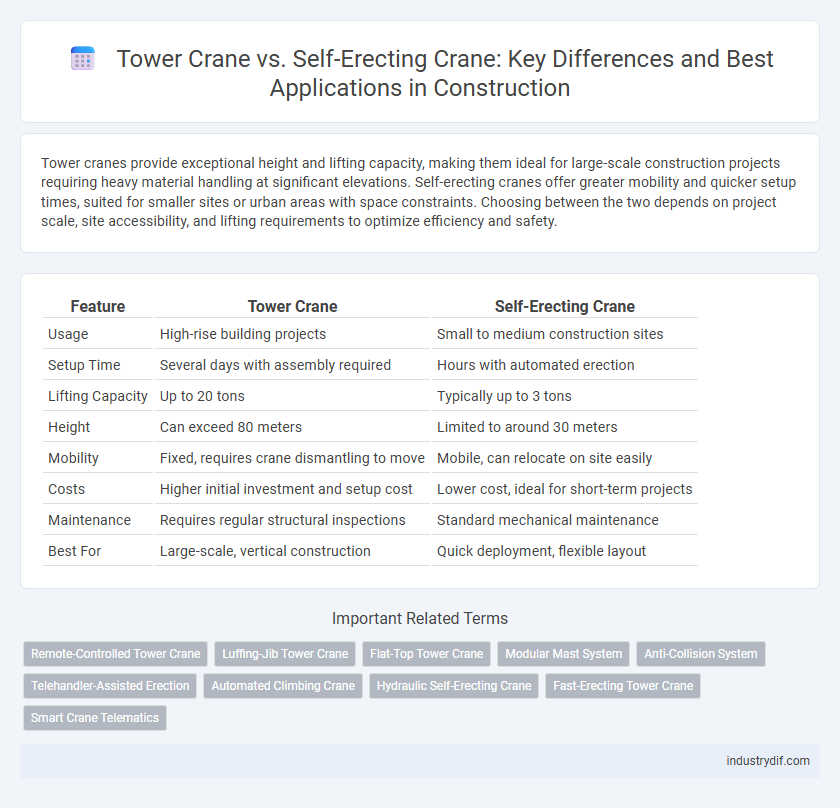
| Feature | Tower Crane | Self-Erecting Crane |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | High-rise building projects | Small to medium construction sites |
| Setup Time | Several days with assembly required | Hours with automated erection |
| Lifting Capacity | Up to 20 tons | Typically up to 3 tons |
| Height | Can exceed 80 meters | Limited to around 30 meters |
| Mobility | Fixed, requires crane dismantling to move | Mobile, can relocate on site easily |
| Costs | Higher initial investment and setup cost | Lower cost, ideal for short-term projects |
| Maintenance | Requires regular structural inspections | Standard mechanical maintenance |
| Best For | Large-scale, vertical construction | Quick deployment, flexible layout |
Overview of Tower Cranes and Self-Erecting Cranes
Tower cranes are fixed to the ground or attached to buildings, offering high lifting capacity and reaching great heights, making them ideal for large-scale construction projects like skyscrapers. Self-erecting cranes are smaller, mobile units that assemble themselves on site without the need for additional equipment, suited for medium-sized constructions and urban areas with limited space. Both crane types enhance efficiency but differ significantly in setup, height capability, and mobility.
Key Applications in Construction Projects
Tower cranes are essential for high-rise building projects due to their ability to reach great heights and lift heavy materials with precision. Self-erecting cranes excel in small to medium-sized construction sites, offering quick setup and versatility for residential buildings or urban infrastructure. Selecting the right crane depends on project scale, site accessibility, and lifting requirements to optimize efficiency and safety.
Structural Differences and Design Features
Tower cranes feature a fixed, tall mast anchored to a concrete foundation, allowing them to reach impressive heights and handle heavy loads over extended radii, while self-erecting cranes incorporate a compact, mobile base with a hinged mast designed for rapid assembly and limited height applications. Structural differences include the tower crane's segmented mast sections bolted together for stability and scalability, contrasting with the self-erecting crane's integrated hydraulic system that enables it to fold and unfold without external assistance. Design features of tower cranes emphasize maximum load capacity and height adaptability suited for large-scale construction, whereas self-erecting cranes prioritize mobility, ease of setup, and versatility for smaller projects or urban sites with space constraints.
Operational Efficiency and Setup Time
Tower cranes offer high operational efficiency for large-scale construction projects due to their extended reach and heavy lifting capacity but require significant setup time and specialized crews. Self-erecting cranes provide faster assembly, typically within a few hours, minimizing downtime and enhancing flexibility on smaller sites. Choosing between these cranes depends on balancing the need for rapid deployment against the scale and load requirements of the construction project.
Height and Lifting Capacity Comparison
Tower cranes typically achieve greater heights, reaching up to 265 feet or more with additional jib extensions, making them ideal for skyscraper construction. In contrast, self-erecting cranes generally max out at around 65 feet, suitable for low to mid-rise buildings but limited in reach. Regarding lifting capacity, tower cranes can handle loads exceeding 20 tons, whereas self-erecting cranes usually support up to 3-5 tons, reflecting their design for lighter, more versatile site tasks.
Site Requirements and Space Utilization
Tower cranes require extensive site preparation and a solid foundation, making them ideal for large-scale construction projects with ample space. Self-erecting cranes occupy a smaller footprint and can be assembled quickly on confined sites, optimizing space utilization in urban or restricted environments. Efficient site planning must consider these factors to maximize crane performance and project productivity.
Transportation and Mobility Factors
Tower cranes require specialized trucks and often multiple trips for transport due to their large, disassembled components, impacting setup time on construction sites. Self-erecting cranes, designed for compactness, can be transported on standard flatbed trucks and quickly installed without heavy lifting equipment. Their enhanced mobility suits smaller projects and urban sites with limited access and space constraints.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Tower cranes typically incur higher initial investment and transportation costs but offer greater height and load capacity, making them suitable for large-scale construction projects with extended timelines. Self-erecting cranes present lower upfront expenses and reduced assembly time, resulting in cost savings for smaller, shorter-duration jobs and urban sites with space constraints. Budget planning must weigh the project scale, site conditions, and duration to optimize equipment cost-efficiency.
Safety Standards and Risk Management
Tower cranes and self-erecting cranes must comply with stringent safety standards such as OSHA regulations and ISO 4301-1 to ensure operational safety on construction sites. Effective risk management involves regular inspections, proper operator training, and adherence to load capacity limits to prevent accidents and equipment failure. Implementing advanced safety features like overload sensors and emergency stop systems enhances the overall risk mitigation strategy for both crane types.
Choosing the Right Crane for Your Project
Selecting the right crane depends on project scale, site constraints, and load requirements. Tower cranes offer exceptional height and lifting capacity for large, complex construction sites, while self-erecting cranes provide quick setup and mobility ideal for smaller projects or urban areas with limited space. Evaluating factors like assembly time, transportation logistics, and operational range ensures optimal crane performance and project efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Remote-Controlled Tower Crane
Remote-controlled tower cranes offer enhanced safety and precision on construction sites by allowing operators to control the crane from a distance, reducing the risk of accidents and improving efficiency compared to traditional self-erecting cranes. These advanced tower cranes provide greater lifting capacity and reach, making them ideal for complex urban projects requiring high maneuverability and remote monitoring capabilities.
Luffing-Jib Tower Crane
Luffing-jib tower cranes offer superior maneuverability in confined construction sites compared to self-erecting cranes, thanks to their ability to adjust jib angles for precise load placement. These cranes provide higher lifting capacities and greater height reach, making them ideal for high-rise building projects and urban construction environments.
Flat-Top Tower Crane
Flat-top tower cranes provide enhanced site safety and easier section assembly compared to traditional tower cranes, making them ideal for urban construction projects with height restrictions. Self-erecting cranes offer faster setup and mobility but have lower maximum lifting capacities, whereas flat-top tower cranes excel in heavy lifting and extended reach for high-rise buildings.
Modular Mast System
The modular mast system in tower cranes offers enhanced flexibility for height adjustment and adaptability to complex construction sites, allowing for seamless extension by adding or removing mast sections. Self-erecting cranes typically use a fixed mast system, limiting their maximum reach but enabling quicker setup and dismantling on smaller-scale projects.
Anti-Collision System
Tower cranes and self-erecting cranes utilize advanced anti-collision systems featuring radar, GPS, and infrared sensors to prevent accidents on congested construction sites. These systems enable real-time monitoring and automatic braking to ensure safe distances between cranes, improving overall site safety and operational efficiency.
Telehandler-Assisted Erection
Telehandler-assisted erection significantly enhances the setup efficiency of self-erecting cranes by leveraging their compact design and mobility, allowing rapid deployment in confined urban sites. In contrast, tower cranes generally require extensive external crane support for assembly, increasing project timelines and equipment costs in large-scale construction projects.
Automated Climbing Crane
Automated climbing cranes offer significant advantages over traditional tower cranes and self-erecting cranes by enabling faster vertical movement without dismantling, reducing downtime on high-rise construction projects. Their integrated automation systems enhance precision and safety during climbs, making them ideal for constructing tall structures efficiently.
Hydraulic Self-Erecting Crane
Hydraulic self-erecting cranes offer rapid setup and dismantling, making them ideal for urban construction sites with limited space compared to traditional tower cranes that require extensive assembly. Their hydraulic systems provide precise load control and enhanced lifting capacity, optimizing efficiency and safety on medium-rise building projects.
Fast-Erecting Tower Crane
Fast-erecting tower cranes significantly reduce setup time on construction sites by utilizing modular components and hydraulic systems, allowing rapid assembly and disassembly compared to traditional tower cranes. Their enhanced mobility and efficiency make them ideal for projects with tight deadlines and limited space, outperforming self-erecting cranes in heavy-load capacity and height reach.
Smart Crane Telematics
Smart crane telematics enhances operational efficiency and safety in both tower cranes and self-erecting cranes by providing real-time data on load weight, wind speed, and equipment status. Integrating IoT sensors and GPS tracking allows better monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized crane utilization on construction sites.
Tower Crane vs Self-Erecting Crane Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com