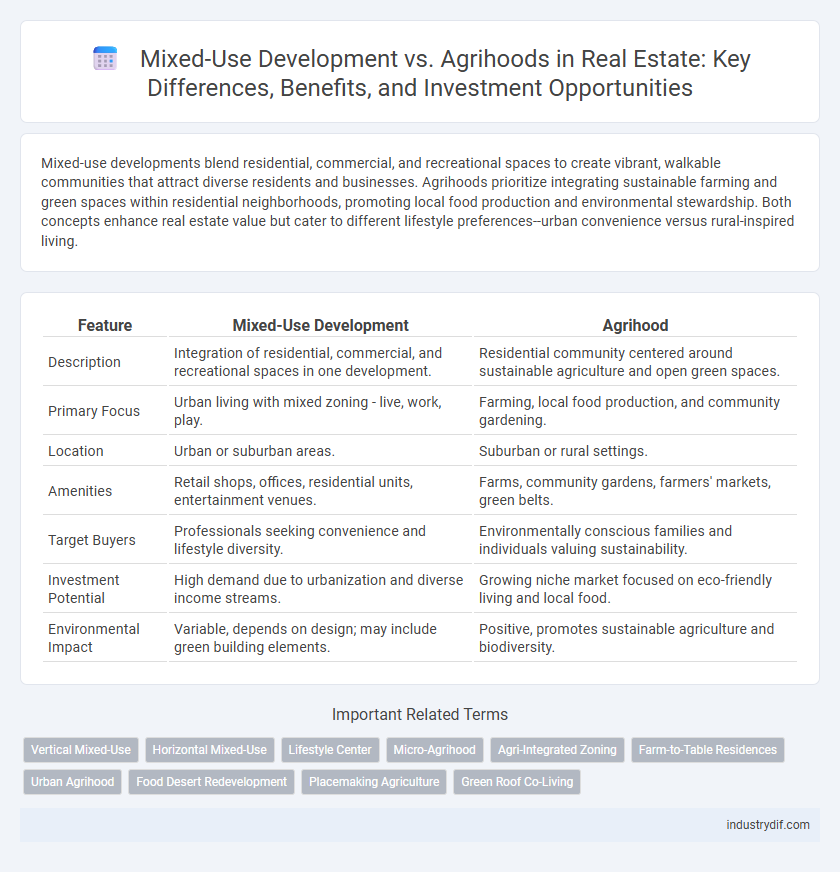
Mixed-use developments blend residential, commercial, and recreational spaces to create vibrant, walkable communities that attract diverse residents and businesses. Agrihoods prioritize integrating sustainable farming and green spaces within residential neighborhoods, promoting local food production and environmental stewardship. Both concepts enhance real estate value but cater to different lifestyle preferences--urban convenience versus rural-inspired living.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mixed-Use Development | Agrihood |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Integration of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces in one development. | Residential community centered around sustainable agriculture and open green spaces. |
| Primary Focus | Urban living with mixed zoning - live, work, play. | Farming, local food production, and community gardening. |
| Location | Urban or suburban areas. | Suburban or rural settings. |
| Amenities | Retail shops, offices, residential units, entertainment venues. | Farms, community gardens, farmers' markets, green belts. |
| Target Buyers | Professionals seeking convenience and lifestyle diversity. | Environmentally conscious families and individuals valuing sustainability. |
| Investment Potential | High demand due to urbanization and diverse income streams. | Growing niche market focused on eco-friendly living and local food. |
| Environmental Impact | Variable, depends on design; may include green building elements. | Positive, promotes sustainable agriculture and biodiversity. |
Understanding Mixed-Use Development: Definition and Purpose
Mixed-use development integrates residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single community to create a dynamic, walkable environment that promotes convenience and sustainability. This urban planning approach maximizes land use efficiency by blending housing, offices, retail, and entertainment venues, catering to diverse lifestyle needs. The purpose of mixed-use development is to foster vibrant neighborhoods that reduce commuting times, support local economies, and encourage social interaction.
What is an Agrihood? Key Characteristics
An agrihood is a residential community centered around sustainable agriculture, integrating active farms, community gardens, and green spaces to promote local food production and environmental stewardship. These developments prioritize organic farming, farm-to-table living, and community engagement through shared agricultural activities. Unlike mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and office spaces, agrihoods focus primarily on blending housing with productive farmland and natural landscapes to create a unique lifestyle centered on sustainability and wellness.
Land Use Strategies: Mixed-Use vs. Agrihood
Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces to maximize land efficiency and promote walkability, reducing urban sprawl. Agrihoods integrate agricultural landscapes with residential areas, prioritizing sustainable land use by preserving green spaces and local food production within community planning. Both land use strategies offer unique benefits: mixed-use developments optimize density and connectivity, while agrihoods enhance environmental sustainability and community wellness.
Community Design and Resident Experience
Mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces to foster vibrant urban communities with walkable neighborhoods and diverse amenities. Agrihoods center around agricultural elements like farms or community gardens, promoting sustainable living and direct access to fresh produce, enhancing residents' connection to nature. Both models prioritize community interaction but differ in design focus--mixed-use emphasizes urban convenience while agrihoods cultivate a rural, eco-friendly lifestyle.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, promoting walkability and reducing reliance on vehicles, which lowers carbon emissions and urban sprawl. Agrihoods prioritize agricultural land use within residential communities, enhancing local food production and biodiversity while supporting natural ecosystems and soil health. Both models contribute to environmental sustainability, but agrihoods offer a distinct advantage by fostering regenerative land practices and local resource use.
Economic Benefits and Investment Potential
Mixed-use developments offer diverse economic benefits by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, fostering higher property values and steady rental income streams. Agrihoods, centered around sustainable agriculture and community living, attract eco-conscious buyers and promote local food economies, which can enhance long-term investment stability. Investors benefit from mixed-use developments' urban appeal and agrihoods' niche market growth, both presenting unique opportunities for portfolio diversification and capital appreciation.
Lifestyle Amenities: Shops, Green Spaces, and Agriculture
Mixed-use developments offer a dynamic lifestyle with integrated shops, restaurants, and entertainment venues, creating vibrant urban environments that promote convenience and social interaction. Agrihoods emphasize green spaces and on-site agriculture, providing residents with access to community gardens, fresh produce, and open natural areas that encourage sustainable living and outdoor activities. Both concepts prioritize lifestyle amenities but diverge in focus: mixed-use prioritizes commercial and social hubs, while agrihoods center around agriculture and green living.
Regulatory and Zoning Considerations
Mixed-use developments often face complex zoning regulations designed to integrate commercial, residential, and recreational spaces within urban areas, requiring compliance with mixed zoning codes and municipal planning guidelines. Agrihoods are subject to agricultural zoning laws that prioritize land use for farming activities while integrating residential components, necessitating adherence to both agricultural conservation easements and local land-use policies. Navigating regulatory frameworks in both scenarios involves coordinating with planning agencies to ensure compliance with environmental assessments, infrastructure requirements, and community impact standards.
Market Trends and Consumer Demand
Mixed-use developments continue to gain traction in urban areas due to rising demand for integrated live-work-play environments that prioritize convenience and sustainability. Agrihoods, combining residential living with active farming and local food production, respond to increasing consumer interest in health, wellness, and community engagement. Market trends indicate that while mixed-use projects appeal to younger, urban professionals seeking connectivity, agrihoods attract families and retirees prioritizing green space and organic lifestyles.
Future Outlook: Mixed-Use Development and Agrihood Integration
Mixed-use development and agrihood integration represent a transformative approach in real estate, combining urban convenience with sustainable living. The future outlook emphasizes the synergy of residential, commercial, and agricultural spaces to promote community engagement and environmental resilience. This evolution drives demand for innovative planning that supports smart growth and enhances quality of life in emerging neighborhoods.
Related Important Terms
Vertical Mixed-Use
Vertical mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within high-rise structures, maximizing urban land efficiency and promoting walkability. In contrast to agrihoods, which center around agricultural amenities and open green space, vertical mixed-use projects prioritize density and connectivity to public transit, catering to urban lifestyles.
Horizontal Mixed-Use
Horizontal mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces in a low-rise layout, fostering walkable communities with diversified amenities. Unlike agrihoods, which emphasize agricultural elements and green spaces, horizontal mixed-use projects prioritize seamless urban living while enhancing local economic activity through varied land uses.
Lifestyle Center
Mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, creating vibrant lifestyle centers that promote walkability and community engagement. Agrihoods combine modern living with sustainable agriculture, offering lifestyle centers centered around farm-to-table experiences and green spaces for a healthy, connected community.
Micro-Agrihood
Micro-agrihoods integrate sustainable urban farming with residential living, creating tight-knit communities focused on local food production and green space, contrasting with mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and recreational facilities to maximize land efficiency and economic activity. Emphasizing micro-agrihoods enhances property value through eco-friendly amenities and promotes a healthier lifestyle by embedding agriculture into suburban and urban real estate projects.
Agri-Integrated Zoning
Agri-integrated zoning in agrihoods promotes sustainable living by combining residential spaces with active agricultural land, enhancing local food production and community engagement. Unlike mixed-use developments that blend commercial, residential, and retail spaces, agrihoods prioritize farmland integration to foster environmental stewardship and healthier lifestyles.
Farm-to-Table Residences
Mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and retail spaces to create vibrant urban living environments, while agrihoods center around agricultural land, promoting farm-to-table residences that offer fresh, locally grown produce directly to residents. Farm-to-table residences in agrihoods enhance community sustainability and health by combining modern living with access to organic farming and green spaces.
Urban Agrihood
Urban Agrihoods integrate sustainable agriculture with residential living, promoting community engagement and local food production within city environments. Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, but Urban Agrihoods uniquely prioritize green spaces and farming to enhance urban sustainability and residents' quality of life.
Food Desert Redevelopment
Mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, creating vibrant communities that improve access to fresh food and essential services in food deserts. Agrihoods, designed around sustainable farming and community agriculture, directly tackle food insecurity by embedding local food production within residential neighborhoods.
Placemaking Agriculture
Mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces to create dynamic urban environments, while agrihoods emphasize placemaking agriculture by centralizing community farms and green spaces to foster sustainable living and local food production. Agrihoods enhance social cohesion and environmental benefits through on-site agriculture, contrasting with mixed-use projects that prioritize diverse amenities and urban density.
Green Roof Co-Living
Green roof co-living spaces in mixed-use developments enhance urban sustainability by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational areas with eco-friendly rooftop gardens that improve air quality and reduce energy consumption. In contrast, agrihoods emphasize community-centered living with large-scale agricultural spaces, but typically lack the dense, multifunctional infrastructure and vertical gardening innovations characteristic of green roof co-living environments.
Mixed-Use Development vs Agrihood Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com