Property management traditionally involves overseeing leasing, maintenance, and tenant relations, while smart building management integrates advanced technologies like IoT sensors and automation to optimize energy use, security, and system performance. Smart building management enhances efficiency by providing real-time data and predictive analytics that can reduce operational costs and improve occupant comfort. Incorporating smart systems within property management strategies creates a more sustainable and responsive environment that meets the evolving demands of modern real estate.
Table of Comparison
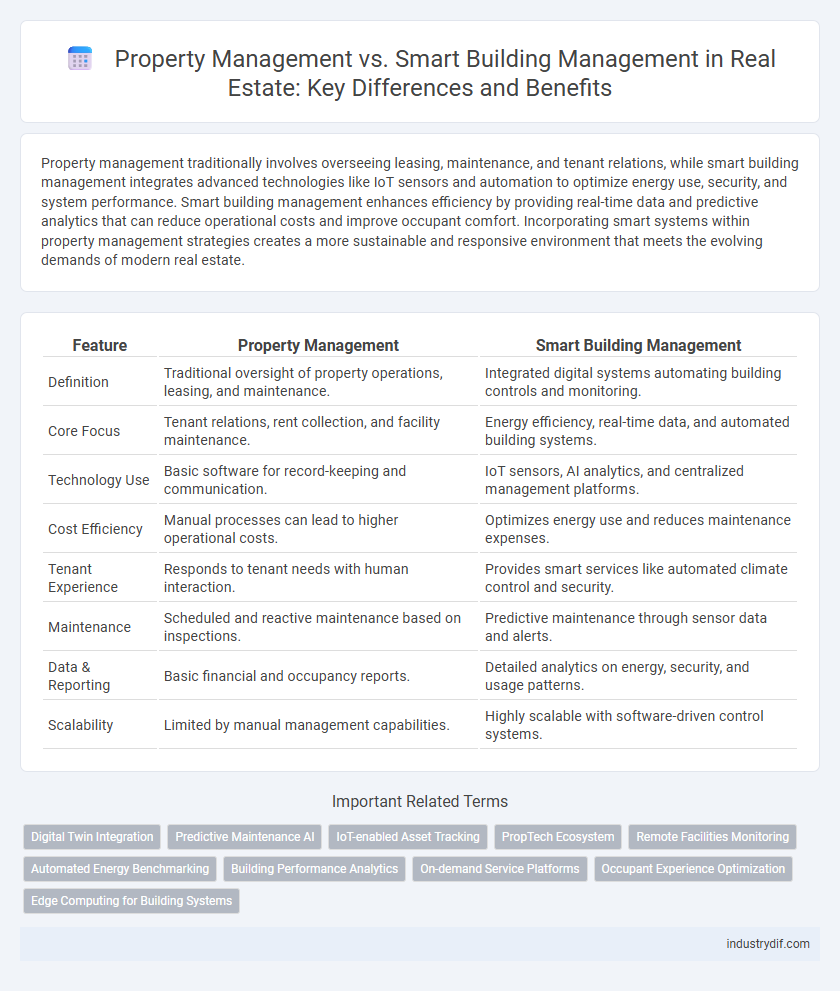
| Feature | Property Management | Smart Building Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional oversight of property operations, leasing, and maintenance. | Integrated digital systems automating building controls and monitoring. |
| Core Focus | Tenant relations, rent collection, and facility maintenance. | Energy efficiency, real-time data, and automated building systems. |
| Technology Use | Basic software for record-keeping and communication. | IoT sensors, AI analytics, and centralized management platforms. |
| Cost Efficiency | Manual processes can lead to higher operational costs. | Optimizes energy use and reduces maintenance expenses. |
| Tenant Experience | Responds to tenant needs with human interaction. | Provides smart services like automated climate control and security. |
| Maintenance | Scheduled and reactive maintenance based on inspections. | Predictive maintenance through sensor data and alerts. |
| Data & Reporting | Basic financial and occupancy reports. | Detailed analytics on energy, security, and usage patterns. |
| Scalability | Limited by manual management capabilities. | Highly scalable with software-driven control systems. |
Defining Property Management and Smart Building Management
Property management involves overseeing residential or commercial real estate operations, including tenant relations, rent collection, maintenance, and compliance with local regulations. Smart building management integrates advanced technology such as IoT sensors, automated systems, and data analytics to optimize energy efficiency, security, and occupant comfort. This digital approach enhances traditional property management by enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance to reduce costs and improve asset value.
Core Functions of Traditional Property Management
Traditional property management primarily focuses on tenant relations, rent collection, maintenance coordination, and lease administration to ensure smooth daily operations of residential or commercial real estate. Core functions also include property inspections, handling tenant complaints, and ensuring compliance with local regulations and safety standards. These tasks aim to maintain property value, optimize occupancy rates, and provide basic facilities management without integrating advanced automation or IoT technologies typical of smart building management.
Key Features of Smart Building Management
Smart building management integrates advanced IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and automated control systems to optimize energy efficiency, security, and occupant comfort. Unlike traditional property management, it leverages AI-driven insights to predict maintenance needs and dynamically adjust building operations. Core features include centralized monitoring, remote access, and adaptive environment controls that enhance sustainability and reduce operational costs.
Technology Integration in Building Operations
Property management primarily relies on traditional systems such as manual maintenance schedules and basic digital tools, whereas smart building management integrates advanced IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and automation platforms to optimize energy use and enhance occupant comfort. Technology integration in smart building operations enables real-time monitoring of HVAC, lighting, and security systems, leading to predictive maintenance and significant cost savings. Enhanced connectivity through centralized building management systems promotes seamless control and data-driven decision-making, revolutionizing building efficiency and sustainability.
Efficiency and Cost Savings Comparisons
Property management typically involves routine maintenance, tenant communication, and rent collection, which can be labor-intensive and costly without advanced technology. Smart building management integrates IoT sensors and automation to optimize energy usage, enhance security, and predict maintenance needs, resulting in significant efficiency gains and reduced operational expenses. Compared to traditional property management, smart systems offer real-time data analytics that enable proactive decision-making and lower overall building management costs.
Tenant Experience: Traditional vs Smart Solutions
Traditional property management often relies on manual processes and limited communication channels, resulting in slower issue resolution and less personalized tenant experiences. Smart building management leverages IoT sensors, automated systems, and real-time data to enhance comfort, security, and energy efficiency, directly improving tenant satisfaction. Integrating smart technologies enables proactive maintenance and seamless interactions, fostering stronger tenant engagement and retention.
Data Analytics and Remote Monitoring
Property management leverages data analytics primarily for tenant behavior insights and operational efficiency, while smart building management integrates advanced sensors and IoT devices for real-time remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. Data analytics in smart building systems enables proactive energy optimization and automated fault detection, surpassing traditional monitoring capabilities in property management. Remote access to building systems enhances decision-making speed and reduces maintenance costs by addressing issues before they escalate.
Sustainability and Energy Management Differences
Property management primarily focuses on operational efficiency, tenant relations, and maintenance, while smart building management leverages IoT sensors and automation to optimize energy consumption and enhance sustainability. Smart building systems enable real-time monitoring and data analytics for HVAC, lighting, and water usage, significantly reducing carbon footprints compared to traditional property management approaches. Energy management in smart buildings integrates renewable energy sources and predictive maintenance, driving cost savings and meeting stringent environmental regulations.
Security and Risk Management Approaches
Property management employs traditional security measures such as on-site personnel, surveillance cameras, and access control systems to mitigate risks and ensure tenant safety. Smart building management integrates advanced IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and automated threat detection to proactively monitor security and respond in real-time to potential risks. Combining these approaches enhances overall risk management by leveraging human oversight and intelligent technology for comprehensive building security.
Future Trends in Property and Smart Building Management
Future trends in property management emphasize integrating Internet of Things (IoT) devices and AI-driven analytics to optimize tenant experience and operational efficiency. Smart building management advances with predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and real-time monitoring systems that reduce costs and enhance sustainability. The convergence of cloud-based platforms and data-driven insights propels the transformation of traditional property management into fully automated, intelligent facility ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Integration
Property management increasingly incorporates digital twin integration to enhance real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, optimizing operational efficiency and tenant satisfaction. Smart building management leverages digital twins for advanced data analytics, enabling automated control systems that reduce energy consumption and improve building performance metrics.
Predictive Maintenance AI
Predictive Maintenance AI in property management leverages data analytics and IoT sensors to forecast equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Smart building management integrates AI-driven predictive maintenance with automated systems to optimize asset performance and enhance energy efficiency across commercial and residential properties.
IoT-enabled Asset Tracking
IoT-enabled asset tracking in property management optimizes maintenance schedules and enhances tenant satisfaction by providing real-time location and condition data on critical equipment. Smart building management leverages these IoT insights to automate energy use, security, and operational workflows, creating more efficient and responsive environments.
PropTech Ecosystem
Property management traditionally encompasses tenant relations, maintenance coordination, and lease administration, relying heavily on manual processes and human oversight. Smart building management integrates IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and automated control systems within the PropTech ecosystem to optimize energy efficiency, predictive maintenance, and real-time space utilization, enhancing operational performance and tenant experience.
Remote Facilities Monitoring
Property management traditionally focuses on tenant relations, rent collection, and maintenance coordination, while smart building management leverages IoT sensors and AI for remote facilities monitoring, optimizing energy efficiency and predictive maintenance. Remote facilities monitoring enables real-time data analytics on HVAC systems, lighting, and security, reducing operational costs and improving building performance through proactive issue detection.
Automated Energy Benchmarking
Automated energy benchmarking in property management enhances operational efficiency by systematically tracking and comparing energy usage across multiple properties, enabling data-driven decisions for cost savings. In contrast, smart building management integrates IoT sensors and AI to optimize energy consumption in real time, improving sustainability and occupant comfort within individual buildings.
Building Performance Analytics
Property management traditionally oversees maintenance and tenant relations, while smart building management integrates IoT sensors and AI to optimize energy efficiency, security, and occupant comfort through advanced building performance analytics. These analytics provide real-time data on system operations, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing operational costs substantially.
On-demand Service Platforms
Property management focuses on maintaining and leasing residential or commercial assets, while smart building management integrates IoT technologies to optimize energy efficiency, security, and occupant comfort through automated systems. On-demand service platforms enhance smart building management by providing real-time data analytics and seamless access to maintenance, security, and operational services.
Occupant Experience Optimization
Property management traditionally handles tenant relations, maintenance requests, and lease administration, aiming to maintain basic occupant comfort and satisfaction. Smart building management leverages IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and automated systems to optimize indoor air quality, lighting, and energy efficiency, significantly enhancing occupant experience and well-being.
Edge Computing for Building Systems
Edge computing enhances property management by enabling real-time data processing and analytics on-site, improving operational efficiency and reducing latency in building systems control. Smart building management leverages edge computing to optimize energy consumption, security, and maintenance by integrating IoT sensors and automated responses directly within the infrastructure.
Property Management vs Smart Building Management Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com