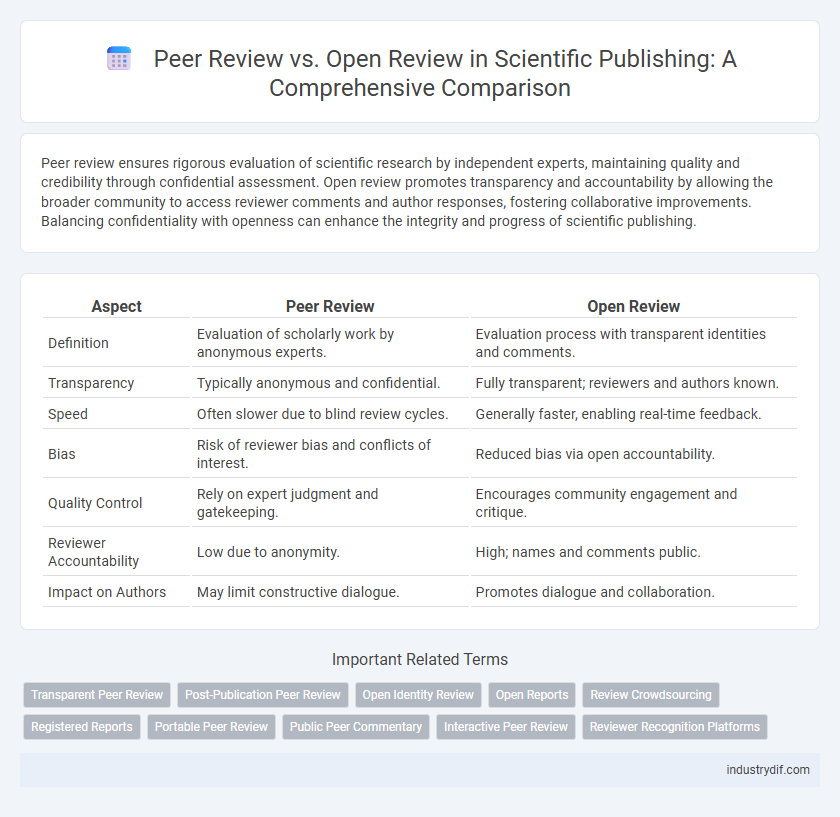
Peer review ensures rigorous evaluation of scientific research by independent experts, maintaining quality and credibility through confidential assessment. Open review promotes transparency and accountability by allowing the broader community to access reviewer comments and author responses, fostering collaborative improvements. Balancing confidentiality with openness can enhance the integrity and progress of scientific publishing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Peer Review | Open Review |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation of scholarly work by anonymous experts. | Evaluation process with transparent identities and comments. |
| Transparency | Typically anonymous and confidential. | Fully transparent; reviewers and authors known. |
| Speed | Often slower due to blind review cycles. | Generally faster, enabling real-time feedback. |
| Bias | Risk of reviewer bias and conflicts of interest. | Reduced bias via open accountability. |
| Quality Control | Rely on expert judgment and gatekeeping. | Encourages community engagement and critique. |
| Reviewer Accountability | Low due to anonymity. | High; names and comments public. |
| Impact on Authors | May limit constructive dialogue. | Promotes dialogue and collaboration. |
Introduction to Peer Review and Open Review
Peer review is a traditional evaluation process where experts assess the quality and validity of scientific manuscripts before publication, ensuring rigor and credibility. Open review enhances transparency by making reviewer comments and author responses publicly accessible, promoting accountability and collaborative improvement. Both methods aim to uphold scientific integrity but differ in openness and interaction between authors and reviewers.
Historical Evolution of Scientific Review Processes
The historical evolution of scientific review processes reveals a shift from traditional peer review, established in the 18th century, to the more transparent and collaborative open review systems emerging in the 21st century. Early peer review mechanisms contributed to validating research through anonymous expert evaluations, while open review fosters inclusivity by allowing broader community participation and public accountability. This transition reflects increasing demands for transparency, reproducibility, and interdisciplinary dialogue in scientific publishing.
Key Principles of Traditional Peer Review
Traditional peer review upholds rigorous standards by relying on anonymous experts to evaluate research quality, validity, and originality before publication. This process ensures accountability and maintains the integrity of scientific literature through impartial assessments, often involving multiple reviewers. Confidentiality protects reviewers' identities, encouraging honest critiques that drive scholarly excellence.
Core Concepts of Open Review Systems
Open review systems prioritize transparency by making reviewer comments and author responses publicly accessible, enhancing accountability and constructive feedback. These systems often allow for broader community participation, enabling diverse expertise to improve research quality beyond traditional peer review boundaries. Core concepts include openness, collaboration, and ongoing evaluation, fostering a more dynamic and inclusive scientific discourse.
Comparative Analysis: Peer Review vs Open Review
Peer review involves anonymous evaluation by selected experts ensuring rigorous quality control and confidentiality, while open review promotes transparency through public access to reviewer comments and author identities, fostering collaborative discourse. Comparative analysis reveals peer review's strength in maintaining unbiased assessments versus open review's advantage in accountability and faster feedback loops. Study outcomes highlight that open review increases community engagement but may risk reviewer hesitation, whereas peer review preserves traditional academic standards and credibility.
Advantages of Peer Review in Scientific Integrity
Peer review enhances scientific integrity by ensuring rigorous evaluation of research by experts in the field, reducing errors and biases. It maintains quality control and credibility by verifying methodologies, data accuracy, and ethical standards before publication. This traditional system fosters trust within the scientific community and the public by upholding transparency and accountability in disseminating validated knowledge.
Benefits and Challenges of Open Review Models
Open review models enhance transparency and accountability by allowing public access to reviewers' comments, fostering constructive dialogue and improving research quality. Challenges include potential reviewer bias, reluctance to provide critical feedback openly, and increased administrative burden for managing public interactions. Despite these issues, open review promotes greater collaboration, accelerates knowledge dissemination, and strengthens trust in scientific findings.
Impact on Transparency and Accountability
Peer review maintains confidentiality, which can limit transparency but enhances accountability by ensuring expert evaluation before publication. Open review increases transparency by making reviewer comments and identities accessible, fostering greater accountability through public scrutiny. Studies show open review can reduce biases and improve trust in scientific findings, although concerns about reviewer candor persist.
Technological Innovations in Review Practices
Technological innovations in review practices have revolutionized peer review by incorporating automated plagiarism detection, AI-assisted content analysis, and blockchain for transparent tracking of manuscript revisions. Open review platforms leverage digital tools that enable real-time collaboration, public commenting, and enhanced reviewer accountability, fostering greater transparency and inclusivity in scientific publishing. These advancements address traditional peer review limitations by accelerating review cycles and ensuring the integrity and reproducibility of research outputs.
Future Trends in Scientific Publishing Models
Emerging scientific publishing models increasingly favor open review systems that enhance transparency, reproducibility, and collaborative critique over traditional peer review's anonymous evaluation. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid platforms integrating blockchain technology for immutable review records and AI-powered tools for bias detection and efficiency. These innovations aim to democratize knowledge dissemination while maintaining rigorous scientific standards.
Related Important Terms
Transparent Peer Review
Transparent peer review enhances accountability by publicly sharing reviewers' reports alongside published articles, increasing the credibility and reproducibility of scientific research. Unlike traditional peer review, it promotes openness and constructive dialogue, accelerating knowledge dissemination and reducing bias in the evaluation process.
Post-Publication Peer Review
Post-publication peer review enhances scientific transparency and rigor by allowing ongoing critical evaluation of published research, integrating community feedback to identify errors or biases missed during traditional pre-publication peer review. This open review process accelerates the dissemination of knowledge while fostering collaborative improvements, thereby increasing the reliability and reproducibility of scientific findings.
Open Identity Review
Open Identity Review enhances transparency and accountability in scientific publishing by revealing reviewer identities, which promotes constructive feedback and reduces biased assessments. This method contrasts with traditional Peer Review by fostering a collaborative environment that encourages ethical conduct and rigorous evaluation.
Open Reports
Open Reports enhance transparency in scientific publishing by making the peer review comments publicly accessible alongside the published article, fostering accountability and constructive discourse. This approach contrasts with traditional peer review, where reviewer insights remain confidential, potentially limiting the evaluation's depth and community engagement.
Review Crowdsourcing
Peer review traditionally relies on a limited group of expert reviewers to evaluate scientific manuscripts, ensuring rigorous quality control, whereas open review invites broader participation, promoting transparency and diverse perspectives. Review crowdsourcing leverages this open review model by engaging large, varied communities to accelerate feedback, enhance the detection of errors, and improve the overall robustness of scientific publications.
Registered Reports
Registered Reports enhance transparency and reproducibility by conducting peer review before data collection, contrasting with traditional peer review where the analysis is evaluated post hoc. Open Review further increases accountability by publishing reviewers' comments and author responses, fostering constructive dialogue throughout the research process.
Portable Peer Review
Portable Peer Review enables the transfer of peer review reports between journals, increasing efficiency and reducing redundant evaluations in scientific publishing. Unlike traditional Peer Review, Open Review encourages transparency by making reviewer comments publicly accessible, but Portable Peer Review specifically streamlines the editorial process by reusing validated critiques across multiple submissions.
Public Peer Commentary
Public peer commentary in open review fosters transparency and broader scholarly engagement by allowing researchers and the public to access, critique, and contribute insights during the evaluation process. Unlike traditional peer review's confidential assessments, this approach enhances accountability and accelerates knowledge dissemination in scientific publishing.
Interactive Peer Review
Interactive Peer Review enhances transparency and collaboration by allowing real-time dialogue between authors and reviewers, improving the quality and clarity of scientific manuscripts. Unlike traditional blind peer review, this approach reduces biases and accelerates the revision process through continuous feedback loops integrated within open review platforms.
Reviewer Recognition Platforms
Reviewer recognition platforms such as Publons and ORCID provide transparent metrics and verifiable acknowledgment for scholars participating in both peer review and open review processes, enhancing academic credit and incentivizing quality contributions. These platforms integrate with journal workflows to track review activity, promote reviewer accountability, and improve visibility within the scientific community.
Peer Review vs Open Review Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com