Bulk buying offers businesses the advantage of purchasing large quantities directly from suppliers, often resulting in lower per-unit costs and improved inventory control. Group purchasing pools the orders of multiple buyers, leveraging collective bargaining power to negotiate better prices and favorable terms. Both strategies maximize cost savings, but bulk buying relies on individual capacity, whereas group purchasing benefits from shared demand.
Table of Comparison
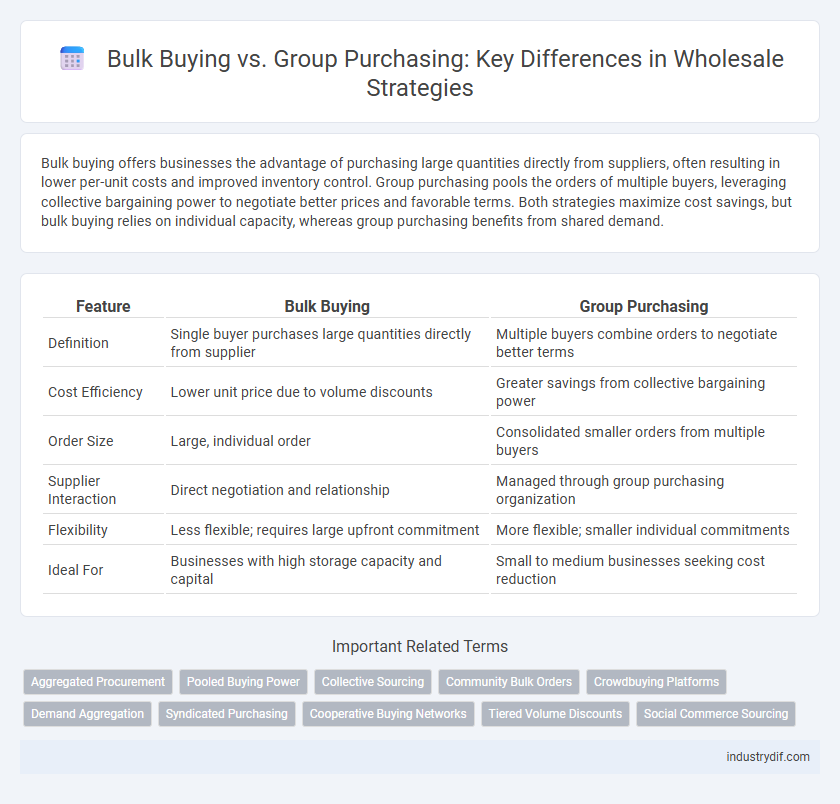
| Feature | Bulk Buying | Group Purchasing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single buyer purchases large quantities directly from supplier | Multiple buyers combine orders to negotiate better terms |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower unit price due to volume discounts | Greater savings from collective bargaining power |
| Order Size | Large, individual order | Consolidated smaller orders from multiple buyers |
| Supplier Interaction | Direct negotiation and relationship | Managed through group purchasing organization |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; requires large upfront commitment | More flexible; smaller individual commitments |
| Ideal For | Businesses with high storage capacity and capital | Small to medium businesses seeking cost reduction |
Understanding Bulk Buying and Group Purchasing
Bulk buying involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from suppliers or manufacturers, often at discounted rates due to volume. Group purchasing consolidates orders from multiple buyers to leverage collective bargaining power, securing better prices and terms than individual purchases. Both strategies are essential in wholesale for reducing costs, optimizing inventory, and improving profit margins.
Key Differences Between Bulk Buying and Group Purchasing
Bulk buying involves a single buyer purchasing large quantities of a product directly from a wholesaler, leveraging volume discounts to reduce costs per unit. Group purchasing aggregates demand from multiple buyers to negotiate better prices and payment terms, optimizing purchasing power collectively. Key differences include the scale of buyers involved and the negotiation dynamics, where bulk buying suits individual buyers aiming for immediate stock, while group purchasing benefits smaller buyers pooling orders for shared savings.
Benefits of Bulk Buying for Wholesalers
Bulk buying allows wholesalers to secure products at significantly lower unit costs by purchasing large quantities directly from manufacturers, enhancing profit margins. This method reduces supply chain complexities and minimizes reliance on intermediaries, leading to faster inventory turnover and improved cash flow management. Access to exclusive bulk discounts and priority stock allocation further strengthens a wholesaler's competitive edge in the market.
How Group Purchasing Organizations Operate
Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs) leverage the collective buying power of multiple businesses to negotiate lower prices and better terms with suppliers. By aggregating demand, GPOs enable members to access discounted rates typically unavailable to individual buyers, streamlining procurement processes and reducing administrative costs. This collaborative approach contrasts with traditional bulk buying, where a single entity purchases large quantities directly from wholesalers.
Cost Savings Analysis: Bulk Buying vs Group Purchasing
Bulk buying offers cost savings through volume discounts by purchasing large quantities directly from suppliers, reducing per-unit prices significantly. Group purchasing leverages collective bargaining power among multiple buyers, enabling access to lower prices and better terms than individual bulk orders alone. Comparing both, bulk buying suits single entities with high storage capacity, while group purchasing benefits smaller businesses combining orders to achieve competitive rates.
Risk Factors in Bulk Buying and Group Purchasing
Bulk buying involves purchasing large quantities from a single supplier, which can lead to risks such as overstocking, cash flow constraints, and potential inventory obsolescence. Group purchasing mitigates these risks by aggregating demand from multiple buyers, increasing negotiating power and reducing individual financial exposure. However, group purchasing requires coordination among participants, which may introduce delays and complexities in order fulfillment.
Supplier Relationships: Bulk Buyers vs Group Purchasers
Bulk buyers establish direct relationships with suppliers, enabling them to negotiate better prices and customized terms due to high-volume commitments. Group purchasers leverage collective buying power by pooling orders from multiple buyers, which strengthens their negotiating position with suppliers and often results in lower costs. Both approaches prioritize supplier collaboration but differ in control and flexibility, with bulk buyers maintaining more direct influence over supply chain dynamics.
Volume Discounts: Maximizing Savings
Bulk buying leverages large single orders from wholesalers to secure significant volume discounts, reducing per-unit costs significantly for businesses. Group purchasing combines orders from multiple buyers to increase order size and purchasing power, enabling access to competitive pricing and exclusive deals. Both strategies maximize savings by exploiting economies of scale inherent in volume discounts within wholesale markets.
Ideal Industries for Bulk Buying and Group Purchasing
Bulk buying suits industries with high-volume consumption such as manufacturing, food service, and retail, where cost savings and inventory efficiency are critical. Group purchasing benefits healthcare, education, and hospitality sectors by leveraging collective buying power to secure better pricing and contract terms. Both strategies optimize supply chain management but align differently with industry-specific procurement needs.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Bulk Buying or Group Purchasing
Selecting the right wholesale procurement strategy depends on factors like order volume, cost savings, and supplier relationships. Bulk buying offers direct discounts and inventory control when purchasing large quantities from a single supplier, while group purchasing leverages collective bargaining power to secure better rates for smaller buyers through consortiums or cooperatives. Evaluating internal storage capacity, cash flow, and negotiation leverage helps businesses determine whether bulk buying or group purchasing maximizes cost efficiency and supply chain reliability.
Related Important Terms
Aggregated Procurement
Aggregated procurement leverages the collective purchasing power of multiple buyers to secure lower prices and better terms than individual bulk buying. By consolidating demand, group purchasing organizations optimize supply chain efficiencies and reduce costs through volume discounts and streamlined negotiation processes.
Pooled Buying Power
Bulk buying allows businesses to leverage significant pooled buying power by purchasing large quantities directly from suppliers, often securing lower per-unit costs and better terms. Group purchasing aggregates demand from multiple buyers, increasing collective bargaining strength to access volume discounts and shared resources that individual buyers might not achieve alone.
Collective Sourcing
Bulk buying involves a single buyer purchasing large quantities directly from suppliers, maximizing cost savings through volume discounts. Group purchasing leverages collective sourcing by aggregating orders from multiple buyers, enhancing negotiating power and access to better terms than individual bulk purchases.
Community Bulk Orders
Community bulk orders leverage collective buying power to secure lower prices and better terms by aggregating demand from multiple buyers. This approach contrasts with individual bulk buying, which focuses on a single entity purchasing large quantities, often limiting negotiation leverage and flexibility.
Crowdbuying Platforms
Crowdbuying platforms enable businesses to leverage collective demand, achieving lower prices through bulk buying without individual inventory risk. These platforms streamline group purchasing by connecting multiple buyers, optimizing cost-efficiency and negotiation power in wholesale markets.
Demand Aggregation
Bulk buying consolidates large quantities under a single buyer, optimizing economies of scale for lower unit costs, while group purchasing aggregates demand across multiple buyers to leverage collective bargaining power and access better wholesale prices. Demand aggregation in group purchasing enhances volume discounts and supply chain efficiency, benefiting small to medium enterprises by reducing procurement costs and improving supplier negotiation leverage.
Syndicated Purchasing
Syndicated purchasing leverages the combined buying power of multiple businesses to secure lower prices and better terms from suppliers, surpassing traditional bulk buying advantages. This collaborative approach enhances negotiation leverage, reduces individual risk, and optimizes inventory management across participating entities.
Cooperative Buying Networks
Cooperative buying networks aggregate demand from multiple buyers to negotiate better prices and terms, enhancing purchasing power beyond typical bulk buying discounts. These networks streamline supply chain efficiency by leveraging collective volume while reducing individual risk and inventory costs.
Tiered Volume Discounts
Bulk buying leverages tiered volume discounts by allowing individual buyers to purchase large quantities directly from wholesalers at progressively lower prices per unit, enhancing cost savings. Group purchasing combines multiple smaller buyers to meet volume thresholds, unlocking higher-tier discounts that might be inaccessible individually, optimizing purchase power across members.
Social Commerce Sourcing
Bulk buying allows businesses to purchase large quantities directly from suppliers, optimizing cost-efficiency and inventory control in wholesale operations. Group purchasing leverages social commerce sourcing by aggregating demand from multiple buyers to negotiate better prices, enhancing purchasing power and fostering collaborative sourcing networks.
Bulk Buying vs Group Purchasing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com