Brick-and-mortar construction offers proven durability and aesthetic versatility but often involves longer timelines and higher labor costs compared to 3D printed buildings. 3D printing technology enables faster construction with reduced material waste and customization options, revolutionizing how structures are designed and built. Despite initial investment challenges, 3D printed buildings present a sustainable alternative that addresses labor shortages and enhances project efficiency.
Table of Comparison
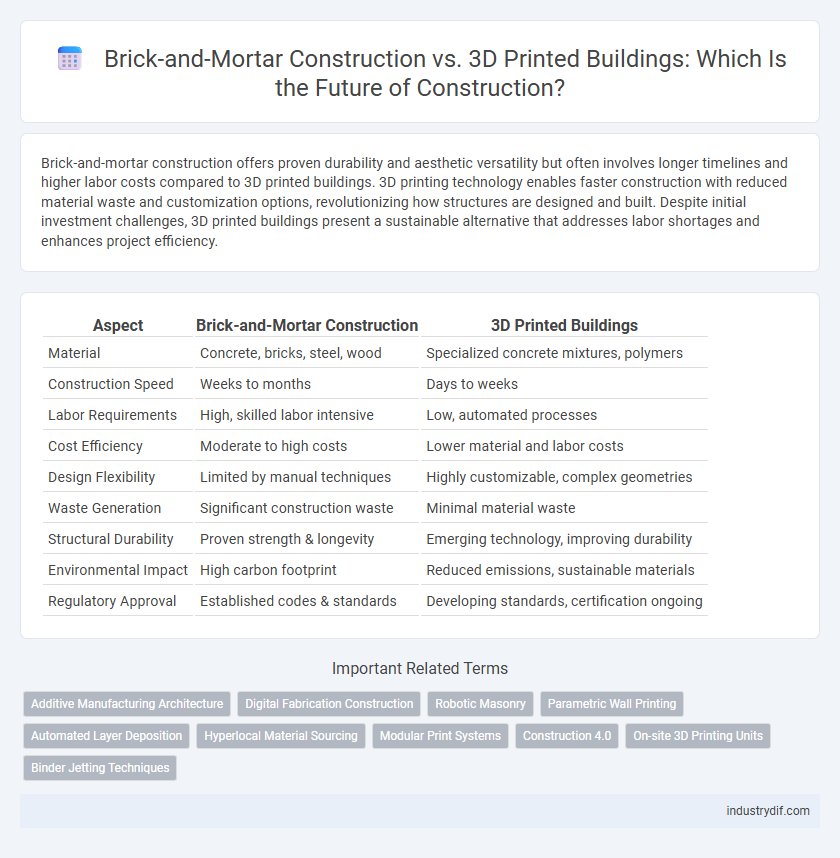
| Aspect | Brick-and-Mortar Construction | 3D Printed Buildings |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Concrete, bricks, steel, wood | Specialized concrete mixtures, polymers |
| Construction Speed | Weeks to months | Days to weeks |
| Labor Requirements | High, skilled labor intensive | Low, automated processes |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate to high costs | Lower material and labor costs |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by manual techniques | Highly customizable, complex geometries |
| Waste Generation | Significant construction waste | Minimal material waste |
| Structural Durability | Proven strength & longevity | Emerging technology, improving durability |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint | Reduced emissions, sustainable materials |
| Regulatory Approval | Established codes & standards | Developing standards, certification ongoing |
Introduction to Brick-and-Mortar and 3D Printed Construction
Brick-and-mortar construction relies on traditional methods involving manual labor, concrete, bricks, and mortar to form durable building structures, widely favored for its proven strength and versatility. In contrast, 3D printed construction uses automated additive manufacturing technology to layer materials like concrete or composites, enabling faster building times and reduced material waste. Both methods have distinct advantages in cost efficiency, scalability, and environmental impact, shaping the future of the construction industry.
Key Differences in Building Processes
Brick-and-mortar construction relies on manual labor and traditional materials such as bricks, mortar, and concrete, requiring extensive scaffolding, formwork, and sequential layering. In contrast, 3D printed buildings utilize advanced additive manufacturing technology, where a robotic arm extrudes concrete or composite materials layer by layer based on digital blueprints, drastically reducing material waste and construction time. The precision of 3D printing enables complex designs and customization that are difficult to achieve with conventional brick-and-mortar methods.
Material Comparison: Traditional vs 3D Printing
Traditional brick-and-mortar construction utilizes materials like clay bricks, concrete blocks, and mortar, known for their durability, thermal mass, and fire resistance. In contrast, 3D printed buildings primarily use composite materials such as fiber-reinforced concrete, polymers, and eco-friendly recycled substances, offering enhanced customization, reduced waste, and faster setting times. The material innovation in 3D printing enables complex architectural designs and efficient resource usage while maintaining structural integrity comparable to traditional methods.
Project Timeline and Speed of Construction
Traditional brick-and-mortar construction projects typically require several months to years for completion due to manual labor, material curing times, and complex logistics. In contrast, 3D printed buildings can significantly reduce project timelines, often completing structures within days or weeks by automating material deposition and minimizing human error. The accelerated speed of 3D printing technology enhances efficiency, reduces labor costs, and enables rapid prototyping for customized architectural designs.
Cost Analysis: Conventional vs 3D Printed Structures
Brick-and-mortar construction typically incurs higher labor and material costs due to skilled workforce requirements and prolonged project timelines, often making it more expensive than 3D printed buildings. In contrast, 3D printed structures leverage automated processes that reduce labor expenses and construction waste, significantly lowering overall costs by up to 50% in some projects. While initial investment in 3D printing technology can be substantial, the long-term savings in construction speed and efficiency position it as a cost-effective alternative for scalable housing solutions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Brick-and-mortar construction significantly contributes to environmental degradation through high carbon emissions and excessive material waste, with traditional cement production accounting for nearly 8% of global CO2 emissions. In contrast, 3D printed buildings leverage sustainable materials such as recycled plastics and geopolymer concrete, reducing waste by up to 60% and lowering energy consumption during construction. The adoption of additive manufacturing techniques in construction also enables precision in material usage, minimizing resource depletion and promoting eco-friendly urban development.
Design Flexibility and Architectural Innovation
Brick-and-mortar construction offers limited design flexibility due to traditional material constraints and manual labor, restricting complex architectural forms. In contrast, 3D printed buildings enable unprecedented architectural innovation by allowing precise layer-by-layer fabrication of intricate shapes and custom designs. This technology expands creative possibilities, reduces material waste, and accelerates project timelines compared to conventional construction methods.
Structural Integrity and Longevity
Brick-and-mortar construction offers proven structural integrity and longevity through time-tested materials like fired clay bricks and mortar, which withstand environmental stress and aging for decades to centuries. 3D printed buildings use advanced composite materials and layer-by-layer fabrication to optimize load distribution and reduce human error, but long-term durability data remains limited due to the technology's novelty. Evaluations of seismic resistance, weather impact, and material degradation continue to focus on bridging gaps between traditional masonry performance and emerging additive manufacturing techniques in construction.
Industry Adoption and Real-World Case Studies
Brick-and-mortar construction remains the dominant industry standard, with over 90% of new commercial buildings worldwide using traditional methods due to established supply chains and regulatory frameworks. In contrast, 3D printed buildings are gaining traction in niche markets, evidenced by case studies such as ICON's 3D-printed homes in Austin, Texas, and Apis Cor's emergency shelters in Russia, highlighting reduced labor costs and construction time. Industry adoption of 3D printing accelerates in regions facing labor shortages and high material costs, signaling a gradual but significant shift towards additive manufacturing technologies in construction.
Future Trends in Construction Technology
Future trends in construction technology are shifting towards the integration of 3D printed buildings, offering faster, more sustainable, and cost-effective alternatives to traditional brick-and-mortar construction methods. Advanced materials and robotic automation enable precise layering and complex designs that reduce waste and labor requirements. As digital fabrication evolves, hybrid construction models combining conventional masonry with additive manufacturing are expected to redefine project timelines and architectural possibilities.
Related Important Terms
Additive Manufacturing Architecture
Additive manufacturing architecture transforms traditional brick-and-mortar construction by enabling precise layer-by-layer fabrication of complex building components, reducing material waste and construction time. This innovative technology allows for customizable, sustainable structures with enhanced design flexibility, outperforming conventional methods in efficiency and environmental impact.
Digital Fabrication Construction
Digital fabrication construction leverages 3D printing technology to rapidly produce building components with high precision, reducing waste and labor costs compared to traditional brick-and-mortar methods. This innovative approach enables complex architectural designs and sustainable material usage, revolutionizing the efficiency and scalability of construction projects.
Robotic Masonry
Robotic masonry in brick-and-mortar construction enhances precision and efficiency by automating the laying of bricks, reducing human error and labor costs while maintaining traditional structural integrity. In contrast, 3D printed buildings leverage additive manufacturing to create complex geometries with minimal material waste, offering rapid construction timelines but currently facing limitations in material strength and regulatory approval.
Parametric Wall Printing
Parametric wall printing in 3D printed buildings enables precise customization of wall geometry and material composition, significantly reducing construction time and waste compared to traditional brick-and-mortar methods. This advanced technology supports complex architectural designs with enhanced structural integrity while optimizing resource allocation and labor efficiency on-site.
Automated Layer Deposition
Automated layer deposition in 3D printed buildings enables precise, continuous, and rapid construction by extruding construction materials layer by layer, significantly reducing labor costs and material waste compared to traditional brick-and-mortar methods. This technology allows for complex architectural designs and faster project timelines, revolutionizing the efficiency and sustainability of building construction.
Hyperlocal Material Sourcing
Brick-and-mortar construction relies heavily on locally sourced materials such as clay bricks, sand, and timber, supporting regional economies and reducing transportation emissions. In contrast, 3D printed buildings utilize hyperlocal materials like recycled plastic, concrete blends, or soil composites derived directly from the construction site, minimizing waste and enabling sustainable, site-specific manufacturing.
Modular Print Systems
Modular print systems in 3D printed buildings offer enhanced precision and rapid assembly compared to traditional brick-and-mortar construction, significantly reducing material waste and labor costs. These systems enable customizable, scalable architectural designs while maintaining structural integrity and sustainability through automated layering of concrete or composite materials.
Construction 4.0
Construction 4.0 integrates digital technologies like BIM, IoT, and robotics to enhance efficiency in both brick-and-mortar construction and 3D printed buildings. While traditional brick-and-mortar methods provide proven durability, 3D printed buildings offer rapid construction, reduced material waste, and design flexibility driven by advanced automation and data analytics.
On-site 3D Printing Units
On-site 3D printing units revolutionize construction by enabling precise layer-by-layer deposition of concrete or composite materials directly at the build site, significantly reducing material waste and labor costs compared to traditional brick-and-mortar methods. These units facilitate rapid construction timelines, complex architectural designs, and real-time adjustments, enhancing efficiency and customization in modern building projects.
Binder Jetting Techniques
Traditional brick-and-mortar construction relies on layering bricks and mortar for structural integrity, while 3D printed buildings using binder jetting techniques utilize a precise binder to selectively fuse powder materials, enabling complex geometries and faster build times. Binder jetting in construction enhances material efficiency and design flexibility, reducing waste and labor costs compared to conventional masonry methods.
Brick-and-Mortar Construction vs 3D Printed Buildings Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com