Prefab construction offers faster assembly, reduced on-site labor, and consistent quality through factory-controlled processes. Mass timber provides sustainable building solutions with renewable materials, excellent strength-to-weight ratios, and enhanced aesthetic appeal due to its natural wood appearance. Combining prefab techniques with mass timber components maximizes efficiency, sustainability, and design flexibility in modern construction projects.
Table of Comparison
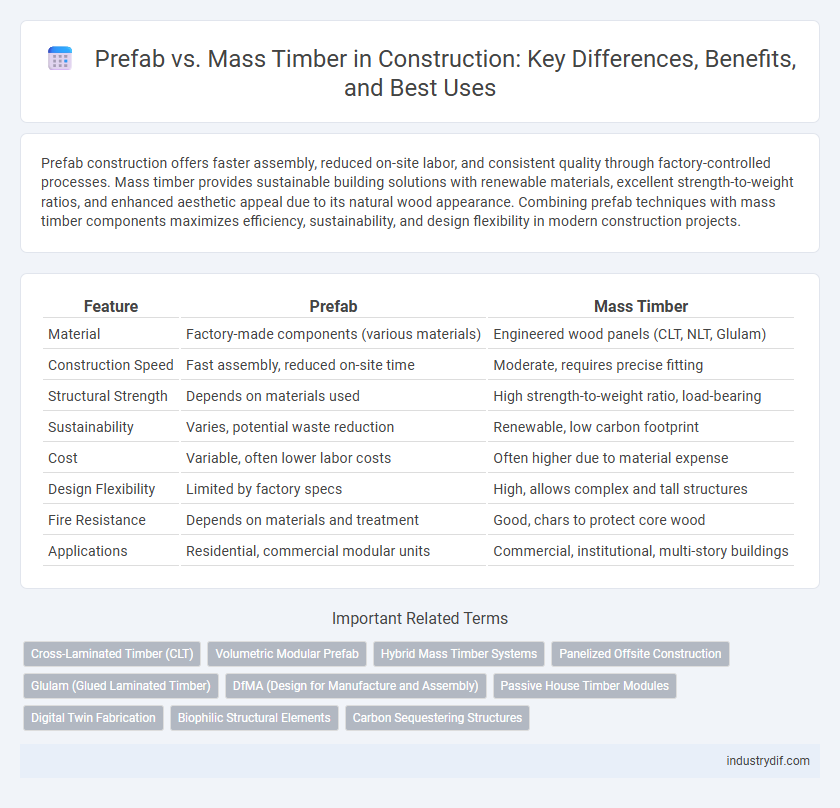
| Feature | Prefab | Mass Timber |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Factory-made components (various materials) | Engineered wood panels (CLT, NLT, Glulam) |
| Construction Speed | Fast assembly, reduced on-site time | Moderate, requires precise fitting |
| Structural Strength | Depends on materials used | High strength-to-weight ratio, load-bearing |
| Sustainability | Varies, potential waste reduction | Renewable, low carbon footprint |
| Cost | Variable, often lower labor costs | Often higher due to material expense |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by factory specs | High, allows complex and tall structures |
| Fire Resistance | Depends on materials and treatment | Good, chars to protect core wood |
| Applications | Residential, commercial modular units | Commercial, institutional, multi-story buildings |
Introduction to Prefab and Mass Timber
Prefab construction involves assembling building components in a controlled factory environment, enabling faster on-site installation and reduced waste. Mass timber, made from engineered wood products such as cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glue-laminated timber (glulam), offers enhanced structural strength and sustainability compared to traditional materials. Integrating prefab techniques with mass timber panels facilitates efficient, eco-friendly building solutions ideal for commercial and residential projects.
Key Differences Between Prefab and Mass Timber
Prefab construction involves assembling building components manufactured off-site in a controlled factory environment, resulting in faster project timelines and reduced on-site labor. Mass timber utilizes engineered wood products like cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glued laminated timber (glulam) to create structural elements, offering benefits such as sustainability, aesthetic warmth, and high strength-to-weight ratios. Key differences include prefab's emphasis on modular assembly and efficiency versus mass timber's renewable material properties and architectural design flexibility.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Prefab construction significantly reduces waste and energy consumption by utilizing factory-controlled processes and precise material measurements, leading to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional on-site building methods. Mass timber offers a sustainable alternative by sequestering carbon throughout the lifespan of the structure and promoting the use of renewable, responsibly sourced wood, which decreases reliance on concrete and steel. Combining prefab techniques with mass timber materials amplifies environmental benefits, optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing the overall ecological footprint of construction projects.
Structural Performance and Durability
Mass timber offers superior structural performance due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for multi-story buildings. Prefabricated components ensure consistent quality and precision, enhancing durability by minimizing onsite errors and moisture exposure. Both methods utilize engineered wood products that resist deformation and provide excellent fire resistance, extending the lifespan of structures.
Cost Comparison: Prefab vs Mass Timber
Prefab construction often reduces overall project costs by minimizing labor expenses and shortening construction timelines through factory-controlled processes. Mass timber, while typically more expensive upfront due to material costs and specialized skills, can provide long-term savings via energy efficiency and faster assembly on-site. Comparing cost effectiveness requires analyzing project scale, design complexity, and local material availability to determine the optimal balance between initial investment and lifecycle benefits.
Speed of Construction and On-Site Efficiency
Prefab construction significantly reduces on-site labor and minimizes weather-related delays by assembling components in controlled environments, leading to faster project completion. Mass timber offers quick installation due to its lightweight and modular nature, allowing large structural elements to be erected rapidly with fewer workers. Combining prefab methods with mass timber panels optimizes construction speed and enhances on-site efficiency through precise manufacturing and streamlined assembly processes.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Prefab construction offers high design flexibility through modular components that can be customized for various architectural styles, facilitating faster assembly and consistent quality. Mass timber provides unique aesthetic options with natural wood finishes, warm textures, and visible grain patterns that enhance interior and exterior visual appeal. Combining prefab techniques with mass timber elements maximizes both efficient construction and sophisticated design versatility.
Building Code Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Prefab construction offers streamlined building code compliance due to factory-controlled environments and standardized components, facilitating easier inspection and certification processes. Mass timber projects must address specific fire-resistance, structural, and acoustical code requirements, with many jurisdictions updating regulations to accommodate engineered wood products. Understanding local building codes and engaging with regulatory agencies early ensures both prefab and mass timber constructions meet necessary safety and performance standards.
Common Applications in Modern Construction
Prefab construction is commonly used for residential buildings, modular offices, and healthcare facilities due to its speed and cost efficiency. Mass timber is prominent in mid-rise commercial buildings, educational institutions, and public infrastructure, valued for its sustainability and aesthetic appeal. Both methods support sustainable construction trends, with prefab emphasizing rapid assembly and mass timber offering structural strength combined with environmental benefits.
Future Trends in Prefab and Mass Timber Construction
Prefab and mass timber construction are transforming the building industry with innovations that emphasize sustainability, efficiency, and scalability. Advances in digital design, robotics, and modular assembly are driving faster project delivery, reduced waste, and lower carbon footprints in urban development. Emerging trends highlight the integration of mass timber with prefab technologies, promoting resilient structures and meeting escalating demands for eco-friendly high-rise and mixed-use buildings.
Related Important Terms
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and sustainability compared to traditional prefab materials, enabling faster assembly and reduced onsite labor costs in construction projects. Prefabricated CLT panels provide enhanced dimensional stability and fire resistance, making them ideal for mid-rise buildings and eco-friendly urban developments.
Volumetric Modular Prefab
Volumetric modular prefab construction offers accelerated build times and precise factory-controlled quality, reducing onsite labor and waste compared to mass timber systems that rely on assembling large solid wood panels. Prefabricated volumetric modules deliver enhanced design flexibility and improved structural performance by integrating mechanical, electrical, and plumbing components before delivery, optimizing project efficiency in commercial and residential buildings.
Hybrid Mass Timber Systems
Hybrid mass timber systems combine the precision and speed of prefabricated components with the structural strength and sustainability of mass timber, reducing construction time and waste. These systems enhance architectural flexibility while delivering improved seismic performance and thermal efficiency compared to traditional prefab or pure mass timber approaches.
Panelized Offsite Construction
Panelized offsite construction offers precise quality control and accelerated timelines by manufacturing building components like walls and floors in a factory setting. Compared to mass timber, prefab panels integrate diverse materials for enhanced design flexibility and efficient on-site assembly, reducing labor costs and waste.
Glulam (Glued Laminated Timber)
Glulam (Glued Laminated Timber) offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and design flexibility compared to traditional prefab materials, enabling faster assembly and reduced construction time. Its engineered composition ensures durability, sustainability, and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for large-span structures and environmentally conscious buildings.
DfMA (Design for Manufacture and Assembly)
DfMA principles enhance prefab construction by streamlining off-site manufacturing processes, reducing on-site labor, and improving quality control; in contrast, mass timber benefits from DfMA through precise digital fabrication and modular assembly, enabling faster construction timelines and sustainable building performance. Incorporating DfMA in both prefab and mass timber projects optimizes resource efficiency, minimizes waste, and accelerates project delivery in modern construction.
Passive House Timber Modules
Passive House timber modules prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability by using mass timber for superior thermal insulation and airtightness compared to traditional prefab systems. Mass timber's natural properties enhance indoor air quality and reduce carbon footprint, making it the preferred choice in high-performance passive house construction.
Digital Twin Fabrication
Digital twin fabrication enables precise simulation and monitoring of prefab and mass timber construction processes, enhancing accuracy and reducing waste. Integrating digital twins with mass timber techniques streamlines assembly and quality control compared to traditional prefab methods.
Biophilic Structural Elements
Prefabricated construction integrates mass timber components that emphasize biophilic design principles, enhancing indoor air quality and natural aesthetics through the use of renewable wood materials. Mass timber panels and beams, prefabricated off-site, promote efficient assembly while supporting occupant well-being by maximizing natural light and connection to nature in structural frameworks.
Carbon Sequestering Structures
Mass timber structures sequester significantly more carbon dioxide during their lifecycle compared to traditional prefab concrete systems, storing carbon within the wood fibers and reducing embodied carbon emissions. The renewable nature of mass timber supports sustainable construction by lowering environmental impact while prefab systems often rely on high-carbon materials with limited carbon storage capacity.
Prefab vs Mass Timber Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com