Standard insulation materials, such as fiberglass and foam, provide effective thermal resistance at a lower upfront cost but often require greater thickness to achieve desired R-values. Aerogel insulation offers superior thermal performance with minimal thickness due to its low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for space-constrained applications and energy-efficient buildings. Despite higher initial expenses, aerogel insulation reduces heat loss more effectively, leading to long-term energy savings and enhanced sustainability in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
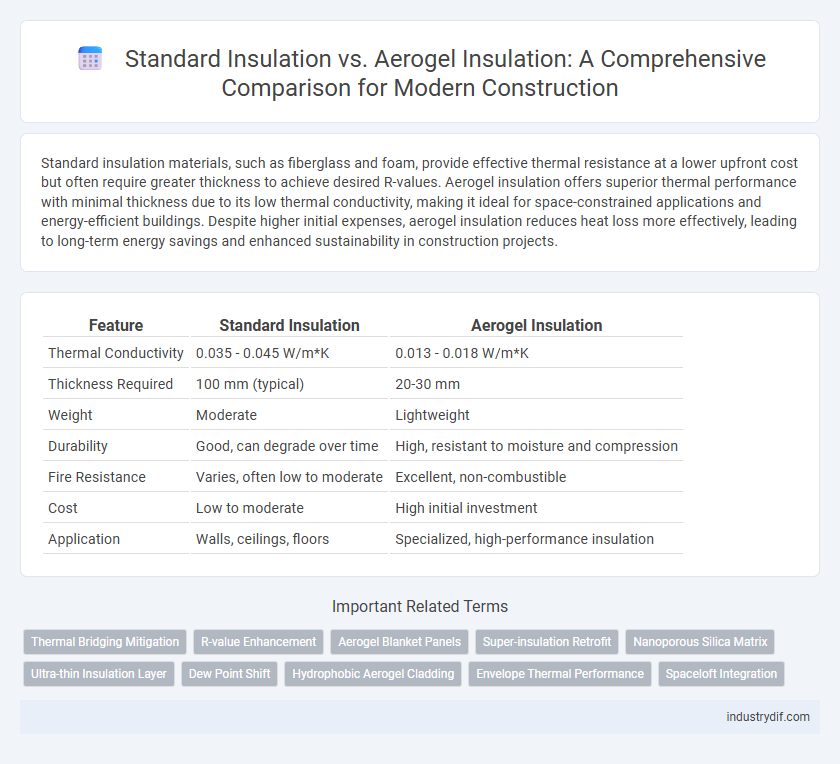
| Feature | Standard Insulation | Aerogel Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.035 - 0.045 W/m*K | 0.013 - 0.018 W/m*K |
| Thickness Required | 100 mm (typical) | 20-30 mm |
| Weight | Moderate | Lightweight |
| Durability | Good, can degrade over time | High, resistant to moisture and compression |
| Fire Resistance | Varies, often low to moderate | Excellent, non-combustible |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High initial investment |
| Application | Walls, ceilings, floors | Specialized, high-performance insulation |
Introduction to Insulation in Construction
Standard insulation materials like fiberglass and foam board provide effective thermal resistance with R-values typically ranging from R-3 to R-6 per inch, making them common choices in residential and commercial construction. Aerogel insulation, known for its ultra-low thermal conductivity and R-values up to R-10 per inch, offers superior energy efficiency and space-saving benefits, especially in environments with strict thermal requirements. Selecting the appropriate insulation type significantly impacts building energy performance, moisture control, and overall sustainability in construction projects.
Overview of Standard Insulation Materials
Standard insulation materials commonly used in construction include fiberglass, mineral wool, and foam board, valued for their thermal resistance and cost-effectiveness. Fiberglass insulation consists of fine glass fibers that trap heat, making it a popular choice for walls, attics, and crawl spaces. Mineral wool offers fire resistance and soundproofing properties, while foam board provides a rigid insulating layer with high R-values per inch, suitable for exterior walls and roofs.
Understanding Aerogel Insulation Technology
Aerogel insulation technology utilizes a nanoporous structure that provides superior thermal resistance compared to standard insulation materials such as fiberglass or mineral wool. With thermal conductivity values as low as 0.013 W/m*K, aerogel significantly reduces heat transfer, making it highly effective for energy-efficient building envelopes and extreme temperature environments. Its lightweight, hydrophobic properties and durability also enhance long-term performance in construction applications where space and weight constraints are critical.
Thermal Performance: Standard vs Aerogel
Aerogel insulation offers significantly superior thermal performance compared to standard insulation materials, boasting up to five times higher R-values per inch. Standard insulation, such as fiberglass or foam boards, typically provides adequate thermal resistance but requires greater thickness to achieve desired energy efficiency. Aerogel's nanostructured composition allows for excellent heat retention in thinner layers, enhancing overall building energy performance while minimizing space requirements.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Standard insulation materials like fiberglass and foam board provide baseline thermal resistance with R-values typically ranging from 3 to 7 per inch, reducing heat transfer but necessitating thicker layers for optimal energy efficiency. Aerogel insulation delivers superior thermal performance with R-values between 9 and 10 per inch due to its nanoporous structure, enabling significant energy savings and space optimization in building envelopes. Enhanced energy efficiency from aerogel insulation minimizes heating and cooling loads, leading to lower utility costs and reduced carbon emissions in construction applications.
Installation Methods and Challenges
Standard insulation materials typically require bulkier installation spaces and may involve stapling or friction-fitting, which can lead to air gaps and reduced thermal performance. Aerogel insulation, known for its ultra-thin profile and high R-value, often demands precise application techniques such as adhesive bonding or encapsulation to maintain integrity and avoid damage during handling. Challenges with aerogel include its higher cost and fragility, necessitating skilled labor and careful protective measures during installation to ensure optimal performance and durability on construction sites.
Material Durability and Lifespan
Standard insulation materials such as fiberglass or foam tend to degrade faster due to moisture absorption and environmental stress, often requiring replacement every 15-20 years. Aerogel insulation offers superior material durability, maintaining thermal performance and structural integrity for over 25 years even in harsh conditions. Its hydrophobic properties and resistance to compression significantly extend lifespan, reducing maintenance needs in construction applications.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term
Standard insulation typically involves lower initial costs, with material prices ranging from $0.50 to $2.00 per square foot, making it a budget-friendly choice for conventional projects. Aerogel insulation, despite an initial cost of $10 to $20 per square foot, offers superior thermal resistance, leading to significant energy savings and reduced HVAC expenses over the building's lifespan. Long-term cost analysis reveals that aerogel's high R-value and durability can offset the higher upfront investment through lower energy consumption and maintenance costs in commercial and industrial construction.
Fire Resistance and Safety Standards
Standard insulation materials such as fiberglass and mineral wool offer moderate fire resistance, typically meeting the ASTM E84 Class A standard, which classifies materials based on flame spread and smoke development. Aerogel insulation outperforms traditional options with superior fire resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1,200degF, and complying with stringent safety standards including NFPA 285 for exterior wall assemblies. Its low thermal conductivity and hydrophobic properties enhance fire safety by reducing heat transfer and preventing moisture-related deterioration, making it a preferred choice for high-risk construction projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Standard insulation materials, such as fiberglass and foam, often have higher embodied energy and contribute to landfill waste due to their limited recyclability. Aerogel insulation offers superior thermal performance with significantly reduced material thickness, lowering energy consumption for heating and cooling and minimizing carbon emissions over the building lifecycle. Its non-toxic composition and potential for reuse enhance sustainability, making aerogel a more environmentally responsible choice in modern construction projects.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Bridging Mitigation
Standard insulation materials such as fiberglass and foam boards often allow thermal bridging due to their lower resistance to heat flow at structural junctions, leading to increased energy loss. Aerogel insulation, with its ultra-low thermal conductivity and conformable nature, effectively minimizes thermal bridging by filling gaps and providing continuous thermal barriers in complex building assemblies.
R-value Enhancement
Aerogel insulation offers an R-value up to five times higher per inch compared to standard fiberglass or foam insulation, significantly improving thermal resistance in building envelopes. This enhanced R-value reduces heat transfer, leading to better energy efficiency and lower heating and cooling costs in construction projects.
Aerogel Blanket Panels
Aerogel blanket panels offer superior thermal insulation performance with R-values up to 10 per inch, significantly outperforming standard insulation materials like fiberglass or foam boards. Their lightweight, hydrophobic properties combined with exceptional vapor permeability make aerogel blankets ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes and condensation control in modern construction projects.
Super-insulation Retrofit
Standard insulation materials like fiberglass and foam board offer moderate thermal resistance with R-values typically ranging from R-3 to R-6 per inch, but aerogel insulation provides superior super-insulation performance with R-values up to R-10 per inch, making it ideal for retrofit projects requiring minimal thickness and maximum energy efficiency. Aerogel's nanoporous structure significantly reduces thermal bridging and air infiltration, resulting in enhanced building envelope performance and lower heating and cooling costs compared to conventional insulation.
Nanoporous Silica Matrix
Standard insulation materials such as fiberglass and foam primarily rely on trapped air pockets to reduce heat transfer, whereas aerogel insulation leverages a nanoporous silica matrix with over 90% air content, providing superior thermal resistance and minimal heat conduction. This nanoporous structure dramatically decreases thermal conductivity to as low as 0.013 W/m*K, making aerogel insulation highly efficient for energy-saving applications in modern construction.
Ultra-thin Insulation Layer
Ultra-thin aerogel insulation layers provide superior thermal resistance with significantly reduced thickness compared to standard insulation materials, enabling space-saving applications without compromising energy efficiency. This advanced material exhibits low thermal conductivity around 0.013 W/m*K, making it ideal for high-performance building envelopes where maximizing interior space is critical.
Dew Point Shift
Aerogel insulation significantly shifts the dew point further into the wall assembly compared to standard insulation, reducing the risk of condensation and moisture damage. This enhanced moisture control improves durability and energy efficiency in building envelopes by maintaining structural integrity and preventing mold growth.
Hydrophobic Aerogel Cladding
Standard insulation materials like fiberglass and foam provide basic thermal resistance but often fall short in moisture control, leading to mold and energy loss over time. Hydrophobic aerogel cladding offers superior insulation with extremely low thermal conductivity and exceptional water repellency, ensuring long-term durability and enhanced energy efficiency in construction.
Envelope Thermal Performance
Standard insulation materials like fiberglass and foam boards provide effective thermal resistance with R-values typically ranging from R-3 to R-6 per inch, reducing heat transfer through building envelopes to improve energy efficiency. Aerogel insulation offers superior envelope thermal performance with R-values up to R-10 per inch, significantly enhancing heat retention and minimizing thermal bridging in high-performance building envelopes.
Spaceloft Integration
Standard insulation materials, such as fiberglass and foam boards, offer effective thermal resistance but often require thicker layers to achieve desired R-values, limiting space efficiency in construction projects. Aerogel insulation like Spaceloft provides superior thermal performance with ultra-thin profiles, enhancing energy efficiency while maximizing usable interior space and reducing installation complexity.
Standard Insulation vs Aerogel Insulation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com