Hand tools offer precision and control for detailed construction tasks, making them ideal for small-scale projects and finishing work. Robotic construction tools enhance efficiency and consistency, especially in repetitive or large-scale operations, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error. Integrating both methods can optimize workflow by balancing craftsmanship with automation.
Table of Comparison
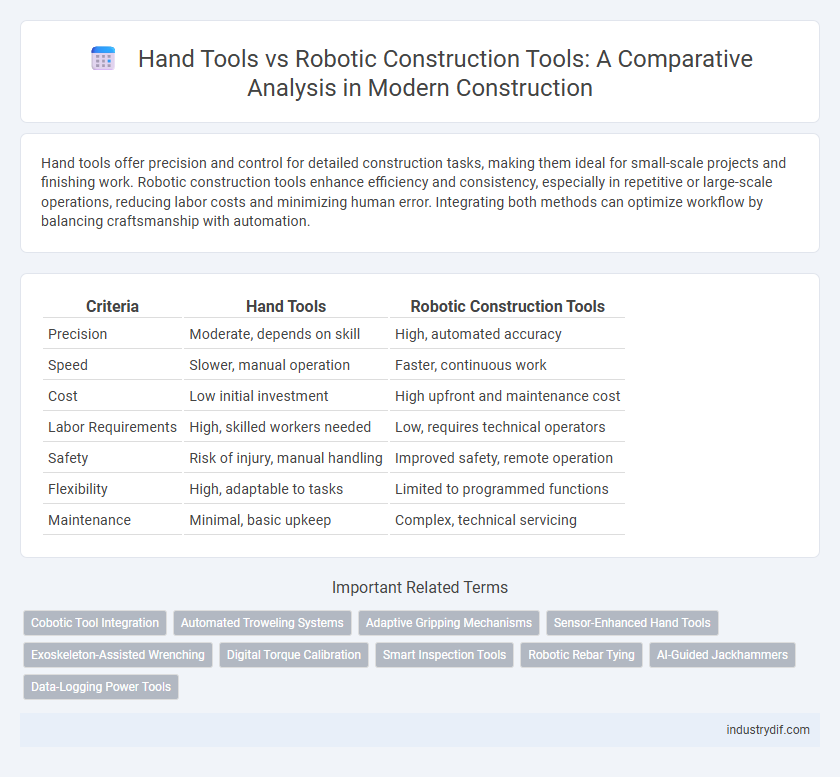
| Criteria | Hand Tools | Robotic Construction Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Moderate, depends on skill | High, automated accuracy |
| Speed | Slower, manual operation | Faster, continuous work |
| Cost | Low initial investment | High upfront and maintenance cost |
| Labor Requirements | High, skilled workers needed | Low, requires technical operators |
| Safety | Risk of injury, manual handling | Improved safety, remote operation |
| Flexibility | High, adaptable to tasks | Limited to programmed functions |
| Maintenance | Minimal, basic upkeep | Complex, technical servicing |
Overview: Hand Tools and Robotic Construction Tools
Hand tools in construction provide precise manual control, essential for detailed tasks such as measuring, cutting, and assembling materials. Robotic construction tools automate repetitive and labor-intensive jobs like bricklaying, welding, and site surveying, significantly increasing efficiency and safety. The integration of both technologies enables a balanced approach, combining human skill with advanced automation for optimized project execution.
Historical Evolution of Construction Tools
Hand tools have been the foundation of construction for millennia, with simple implements like hammers, chisels, and saws enabling early builders to shape materials manually. The historical evolution accelerated with the Industrial Revolution, introducing mechanized tools that increased precision and efficiency, paving the way for modern robotic construction technologies. Today, robotic construction tools integrate advanced sensors, automation, and AI, transforming traditional craftsmanship into highly accurate, scalable, and safer building processes.
Core Differences: Manual vs Automated Tools
Hand tools in construction rely on manual operation, requiring physical labor and human skill for tasks such as measuring, cutting, and assembling materials. Robotic construction tools operate through automation, utilizing programmed systems and sensors to perform precise and repetitive tasks with reduced human intervention. The core differences lie in efficiency, accuracy, and labor intensity, where manual tools offer flexibility but demand time and effort, while robotic tools enhance productivity and consistency by leveraging technology.
Efficiency and Productivity Comparison
Hand tools in construction offer precision and control for detailed tasks but often result in slower project completion and higher labor costs. Robotic construction tools significantly increase efficiency by automating repetitive processes, reducing human error, and accelerating timelines through continuous operation. Companies integrating robotic technologies report productivity improvements of up to 50%, enhanced safety, and consistent quality outcomes compared to traditional hand tool usage.
Safety Implications in Tool Usage
Hand tools require direct human operation, increasing the risk of repetitive strain injuries and accidental cuts, while robotic construction tools minimize physical strain and improve overall site safety by automating hazardous tasks. The precision and consistency of robotic tools reduce human error, lowering the chances of accidents caused by mishandling or fatigue. Implementing robotic construction technologies enhances workplace safety protocols by limiting workers' exposure to dangerous environments and heavy machinery.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Hand tools require minimal initial investment and low maintenance costs, making them cost-effective for small-scale construction projects. Robotic construction tools involve a substantial upfront cost due to advanced technology and specialized components, but they can reduce labor expenses and improve efficiency over time. Maintenance for robotic tools is more complex and costly, often requiring trained technicians and regular software updates, whereas hand tools demand simple upkeep such as sharpening and cleaning.
Skill Requirements and Workforce Adaptation
Hand tools in construction demand manual dexterity, craftsmanship, and years of trade-specific experience, emphasizing hands-on skills and physical labor. Robotic construction tools require workers to acquire technical proficiency in programming, operating advanced machinery, and maintaining automation systems, highlighting a shift toward digital literacy and engineering knowledge. Workforce adaptation involves comprehensive training programs to bridge traditional skills with technological expertise, ensuring seamless integration of robotics without displacing skilled labor.
Impact on Project Timelines and Deadlines
Hand tools require significant manual labor, often leading to extended project timelines due to slower task completion and increased human fatigue. Robotic construction tools enhance precision and speed, reducing the likelihood of errors and rework, which directly accelerates project deadlines. Integration of robotics in construction projects results in more consistent work progress and improved adherence to tight schedules, minimizing costly delays.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Hand tools in construction consume no energy and produce zero emissions, making them inherently sustainable for small-scale or precision tasks. Robotic construction tools, while energy-dependent, can optimize material use and reduce waste through precise operations, significantly lowering the overall environmental footprint on large projects. Integrating renewable energy sources to power robotic tools further enhances eco-friendly construction practices by minimizing reliance on fossil fuels.
Future Trends in Construction Tool Technology
Emerging trends in construction tool technology emphasize the integration of robotic tools for enhanced precision, efficiency, and safety on job sites. Smart hand tools equipped with IoT sensors are improving real-time data collection and operator feedback, bridging traditional methods with digital advancements. The future landscape prioritizes automation, AI-driven diagnostics, and collaborative human-robot interactions to transform construction workflows and productivity.
Related Important Terms
Cobotic Tool Integration
Cobotic tool integration in construction combines the precision and strength of robotic tools with the adaptability of human-operated hand tools, enhancing efficiency and reducing fatigue on complex projects. This synergy enables real-time collaboration between workers and cobots, improving accuracy, safety, and productivity on-site.
Automated Troweling Systems
Automated troweling systems enhance construction efficiency by delivering consistent concrete finishing with reduced labor costs and increased surface quality compared to traditional hand tools. These robotic tools integrate advanced sensors and programmable controls to optimize troweling speed and pressure, ensuring uniform results across large-scale concrete slabs.
Adaptive Gripping Mechanisms
Adaptive gripping mechanisms in hand tools rely on ergonomic designs and manual dexterity for precision, while robotic construction tools utilize advanced sensors and AI-driven actuators to automatically adjust grip strength and shape for varying materials and complex tasks. The integration of force feedback and real-time environmental data enables robotic systems to outperform traditional hand tools in efficiency, consistency, and safety on construction sites.
Sensor-Enhanced Hand Tools
Sensor-enhanced hand tools integrate advanced technologies such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and pressure sensors to improve precision and reduce human error in construction tasks. These tools provide real-time feedback and data analytics, enhancing safety and productivity compared to traditional hand tools while offering greater flexibility and ease of use than fully robotic construction systems.
Exoskeleton-Assisted Wrenching
Exoskeleton-assisted wrenching enhances precision and reduces worker fatigue by integrating robotic support with traditional hand tools, increasing efficiency on construction sites. This technology boosts torque application and minimizes repetitive strain injuries, offering a significant advantage over manual wrenching methods.
Digital Torque Calibration
Digital torque calibration enhances precision in robotic construction tools by ensuring accurate torque application for fasteners, reducing human error and increasing consistency compared to traditional hand tools. This technology enables real-time monitoring and adjustment of torque levels, optimizing structural integrity and improving overall project quality.
Smart Inspection Tools
Smart inspection tools in construction leverage AI-powered sensors and real-time data analysis to detect structural issues with high precision, surpassing traditional hand tools in speed and accuracy. These robotic systems enhance safety and efficiency by enabling non-invasive evaluations and continuous monitoring, reducing human error and costly delays on job sites.
Robotic Rebar Tying
Robotic rebar tying systems significantly increase efficiency and precision on construction sites by automating the repetitive task of securing steel reinforcement bars, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error. These advanced robotic tools integrate with Building Information Modeling (BIM) to ensure accurate placement and improved safety standards compared to traditional hand tools.
AI-Guided Jackhammers
AI-guided jackhammers integrate advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms to enhance precision and reduce operator fatigue, outperforming traditional hand tools in efficiency and safety on construction sites. These robotic construction tools enable real-time data analysis for adaptive drilling, minimizing structural damage while maximizing productivity and cost-effectiveness.
Data-Logging Power Tools
Data-logging power tools in robotic construction enhance precision and efficiency by automatically recording usage metrics, reducing human error and improving project management accuracy. Compared to traditional hand tools, these advanced tools enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, streamlining workflows and minimizing downtime on construction sites.
Hand Tools vs Robotic Construction Tools Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com