Value Engineering focuses on optimizing project value by analyzing functions to reduce costs without compromising quality, while Lean Construction emphasizes eliminating waste and improving workflow efficiency throughout the project lifecycle. Both approaches aim to enhance overall project performance, but Value Engineering targets cost-effectiveness during design and planning, whereas Lean Construction drives continuous improvement during execution. Integrating both methods can lead to cost savings, faster delivery, and higher quality in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
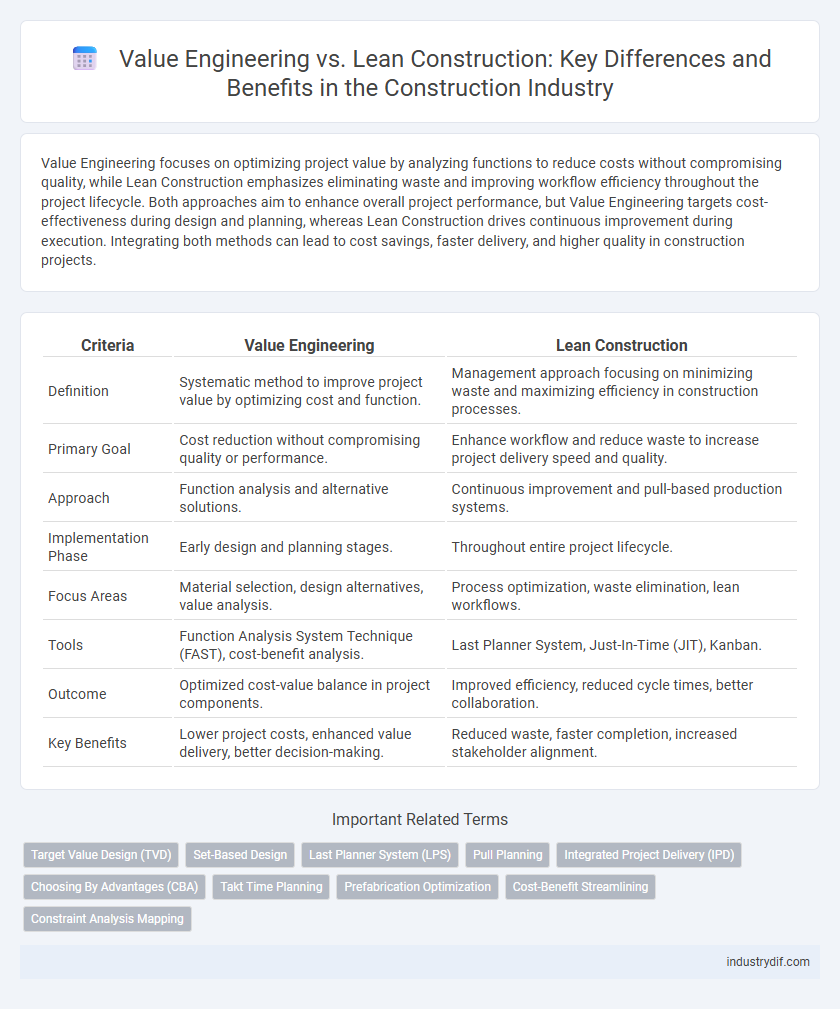
| Criteria | Value Engineering | Lean Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic method to improve project value by optimizing cost and function. | Management approach focusing on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency in construction processes. |
| Primary Goal | Cost reduction without compromising quality or performance. | Enhance workflow and reduce waste to increase project delivery speed and quality. |
| Approach | Function analysis and alternative solutions. | Continuous improvement and pull-based production systems. |
| Implementation Phase | Early design and planning stages. | Throughout entire project lifecycle. |
| Focus Areas | Material selection, design alternatives, value analysis. | Process optimization, waste elimination, lean workflows. |
| Tools | Function Analysis System Technique (FAST), cost-benefit analysis. | Last Planner System, Just-In-Time (JIT), Kanban. |
| Outcome | Optimized cost-value balance in project components. | Improved efficiency, reduced cycle times, better collaboration. |
| Key Benefits | Lower project costs, enhanced value delivery, better decision-making. | Reduced waste, faster completion, increased stakeholder alignment. |
Introduction to Value Engineering and Lean Construction
Value Engineering in construction emphasizes systematic analysis to improve project value by identifying cost-saving opportunities without compromising quality or function. Lean Construction targets waste reduction and enhances efficiency through collaborative processes and continuous improvement, aiming to optimize resource utilization and project delivery time. Both methodologies prioritize maximizing value but apply distinct approaches to achieve sustainable, cost-effective outcomes.
Core Principles of Value Engineering
Value Engineering centers on maximizing project value by systematically analyzing functions to reduce costs without sacrificing quality or performance, emphasizing functional purpose and cost-effective alternatives. Core principles include function analysis, creativity in solution development, multidisciplinary teamwork, and rigorous evaluation of alternatives to improve overall project value. This approach contrasts with Lean Construction, which focuses more on waste elimination and workflow efficiency throughout the construction process.
Key Foundations of Lean Construction
Lean Construction is founded on principles such as continuous improvement, waste minimization, and enhanced collaboration among project stakeholders to optimize productivity and reduce costs. Unlike Value Engineering, which targets cost reduction through design modifications, Lean Construction emphasizes synchronized workflows and real-time communication to improve overall project efficiency. Key pillars include Just-In-Time delivery, integrated project delivery methods, and a strong focus on stakeholder alignment and transparency throughout the construction process.
Historical Development and Industry Adoption
Value Engineering emerged in the 1940s as a systematic method to improve project value by analyzing functions and cost, gaining rapid adoption during post-World War II reconstruction. Lean Construction developed later, rooted in the Toyota Production System of the 1950s, emphasizing waste reduction and continuous improvement within construction workflows, gaining momentum in the 1990s. The construction industry has increasingly integrated both approaches to optimize resources, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs across complex projects globally.
Goals and Outcomes of Each Approach
Value Engineering aims to optimize project costs and functionality by systematically evaluating materials, designs, and processes to achieve the best value without compromising quality. Lean Construction focuses on minimizing waste, enhancing workflow efficiency, and improving collaboration among stakeholders to deliver projects faster and with reduced costs. Both approaches target cost reduction and improved performance but differ in methodology: Value Engineering emphasizes cost-effective alternatives, while Lean Construction centers on process optimization and continuous improvement.
Comparison of Processes and Workflows
Value Engineering focuses on systematically analyzing project components to optimize cost, functionality, and quality through collaborative workshops early in the design phase. Lean Construction emphasizes eliminating waste and enhancing workflow efficiency by implementing continuous improvement techniques such as Last Planner System and Just-In-Time delivery throughout the project lifecycle. Both methodologies aim to improve project outcomes but differ in approach: Value Engineering targets design optimization, while Lean Construction optimizes operational processes and production flow.
Impact on Project Cost and Efficiency
Value Engineering focuses on systematically analyzing project functions to reduce costs and improve value without sacrificing quality, leading to significant cost savings in construction budgets. Lean Construction emphasizes minimizing waste and enhancing workflow efficiency through continuous improvement and collaborative practices, which accelerates project timelines and reduces operational costs. Both methodologies drive down project expenses but differ in approach: Value Engineering targets design and material optimization, while Lean Construction optimizes process and resource utilization.
Collaboration and Stakeholder Involvement
Value Engineering enhances project outcomes by systematically evaluating functions and costs through active collaboration among designers, contractors, and clients to optimize resource allocation without compromising quality. Lean Construction emphasizes continuous stakeholder involvement to eliminate waste, improve workflow efficiency, and deliver value by fostering transparent communication and integrated team decision-making throughout all project phases. Both methodologies prioritize collaborative stakeholder engagement to drive innovation, cost savings, and schedule adherence in construction projects.
Challenges and Limitations
Value Engineering faces challenges such as potential underestimation of long-term costs and conflicts between cost reduction and quality goals, limiting its effectiveness in complex projects. Lean Construction struggles with cultural resistance and requires significant process changes, making implementation difficult in traditional construction environments. Both methodologies may encounter limitations in scalability and stakeholder alignment, impacting overall project success.
Integrating Value Engineering and Lean Practices in Construction
Integrating Value Engineering and Lean Construction practices enhances project efficiency by systematically eliminating waste while maximizing function and value for the client. Combining Value Engineering's cost optimization with Lean's focus on process improvement leads to streamlined workflows, reduced project timelines, and improved resource allocation. Construction projects experience higher quality outcomes and increased stakeholder satisfaction through this synergistic approach.
Related Important Terms
Target Value Design (TVD)
Target Value Design (TVD) is a collaborative approach within Lean Construction that prioritizes meeting project cost targets without compromising quality or function, integrating continuous stakeholder engagement to optimize value. Value Engineering typically focuses on cost reduction through design modifications post-design phase, whereas TVD drives cost control from project inception by aligning design decisions with budget constraints and client objectives.
Set-Based Design
Value Engineering focuses on cost reduction by evaluating alternative design options after initial decisions, while Lean Construction emphasizes waste elimination through collaborative workflows and continuous improvement. Set-Based Design in Lean Construction promotes exploring multiple design alternatives simultaneously, enabling flexible decision-making and optimizing project value without compromising schedule or quality.
Last Planner System (LPS)
Value Engineering emphasizes cost reduction and function optimization during design phases, while Lean Construction utilizes the Last Planner System (LPS) to enhance workflow reliability and collaboration on-site. LPS improves project delivery by enabling better planning, reducing variability, and fostering continuous feedback among all stakeholders in construction projects.
Pull Planning
Value Engineering emphasizes cost reduction and function optimization by analyzing project components, while Lean Construction focuses on minimizing waste through collaborative workflows and continuous improvement; Pull Planning, a key Lean tool, schedules tasks based on downstream constraints to enhance workflow efficiency and reduce delays in the construction process. Employing Pull Planning facilitates better resource allocation, improves team communication, and accelerates project delivery compared to traditional Value Engineering methods.
Integrated Project Delivery (IPD)
Value Engineering systematically analyzes project functions to minimize costs without compromising quality, while Lean Construction emphasizes waste reduction and continuous flow in the building process; Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) combines these methodologies by fostering collaboration among owners, designers, and contractors to optimize project outcomes, enhance efficiency, and share risks and rewards. IPD's emphasis on early stakeholder involvement and transparent communication bridges the cost efficiency of Value Engineering with the process improvements of Lean Construction, leading to improved project performance and value.
Choosing By Advantages (CBA)
Choosing By Advantages (CBA) integrates value engineering principles with lean construction by systematically quantifying project options based on cost and functional benefits, enabling more objective and transparent decision-making. This method improves resource allocation and minimizes waste by prioritizing choices that maximize value and efficiency throughout the construction lifecycle.
Takt Time Planning
Value Engineering emphasizes cost reduction and function optimization by analyzing project components, while Lean Construction prioritizes workflow efficiency and continuous improvement through techniques such as Takt Time Planning, which schedules production in predictable, consistent intervals to enhance coordination. Implementing Takt Time Planning in Lean Construction reduces waste, minimizes variability, and aligns labor and resources with project milestones to achieve faster, more reliable project delivery.
Prefabrication Optimization
Value Engineering enhances prefabrication optimization by identifying cost-effective materials and design modifications that reduce waste and improve structural efficiency without compromising quality. Lean Construction streamlines prefabrication processes through just-in-time delivery and process standardization, minimizing inventory and labor costs while accelerating project timelines.
Cost-Benefit Streamlining
Value Engineering systematically analyzes project functions to identify cost-reduction opportunities without sacrificing quality, maximizing return on investment through targeted improvements. Lean Construction eliminates waste by optimizing workflows and resource use, enhancing overall efficiency and delivering greater value across the project lifecycle.
Constraint Analysis Mapping
Value Engineering emphasizes systematic Constraint Analysis Mapping to identify cost-saving opportunities by evaluating design functions and eliminating unnecessary expenses, whereas Lean Construction integrates Constraint Analysis Mapping to streamline workflows, minimize waste, and enhance project delivery efficiency through continuous process improvement. Constraint Analysis Mapping in Value Engineering targets functional cost optimization, while in Lean Construction it focuses on synchronizing constraints to improve overall project value and time performance.
Value Engineering vs Lean Construction Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com