Prefab construction involves manufacturing building components off-site in a controlled environment, allowing for precise quality control and faster on-site assembly. Modular construction takes prefab to the next level by producing fully finished modules that are transported and assembled on-site, significantly reducing construction time and minimizing disruptions. Both methods enhance efficiency and sustainability but differ mainly in the scope and complexity of off-site fabrication.
Table of Comparison
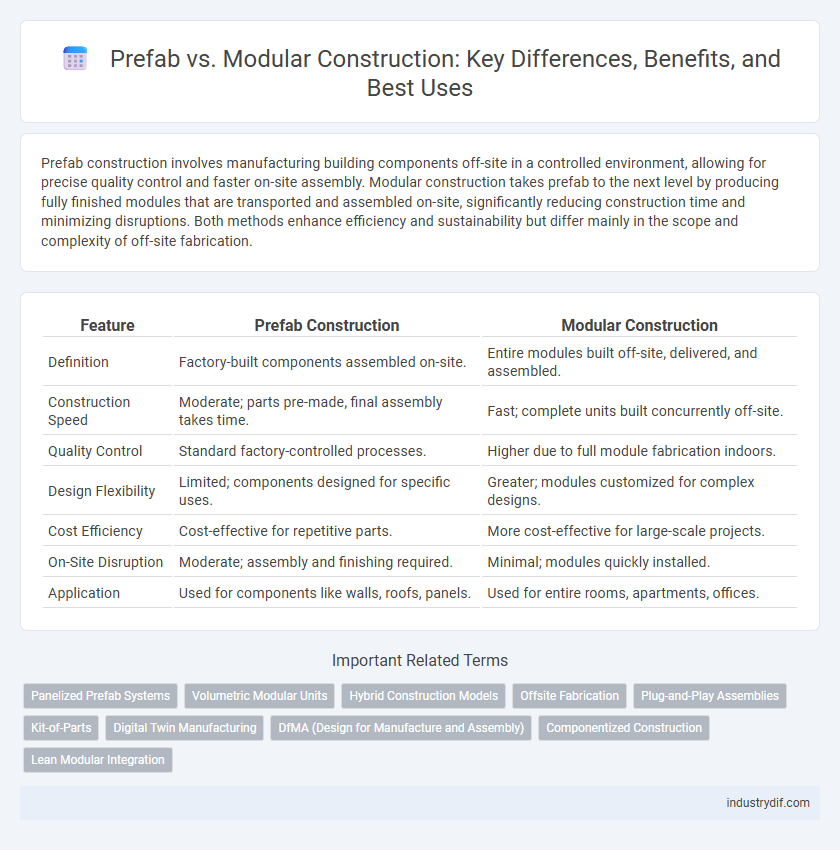
| Feature | Prefab Construction | Modular Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Factory-built components assembled on-site. | Entire modules built off-site, delivered, and assembled. |
| Construction Speed | Moderate; parts pre-made, final assembly takes time. | Fast; complete units built concurrently off-site. |
| Quality Control | Standard factory-controlled processes. | Higher due to full module fabrication indoors. |
| Design Flexibility | Limited; components designed for specific uses. | Greater; modules customized for complex designs. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for repetitive parts. | More cost-effective for large-scale projects. |
| On-Site Disruption | Moderate; assembly and finishing required. | Minimal; modules quickly installed. |
| Application | Used for components like walls, roofs, panels. | Used for entire rooms, apartments, offices. |
Definition of Prefab and Modular Construction
Prefab construction involves manufacturing building components off-site in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the construction site for assembly, enhancing efficiency and reducing on-site labor. Modular construction refers to the process of constructing entire modules or sections of a building off-site, which are then delivered and assembled on-site to create a complete structure faster than traditional methods. Both methods emphasize precision engineering, quality control, and accelerated project timelines compared to conventional construction.
Key Differences Between Prefab and Modular Construction
Prefab construction involves manufacturing building components off-site and assembling them on-site, while modular construction consists of creating entire sections or modules in a factory, allowing for faster on-site assembly and greater design flexibility. Prefab elements typically include panels, trusses, and cabinetry, whereas modular units are fully completed rooms or sections with plumbing, wiring, and finishes pre-installed. Cost efficiency, construction speed, and quality control vary significantly between the two methods, with modular construction often offering more streamlined project timelines and integrated systems.
Advantages of Prefabricated Construction
Prefabricated construction reduces on-site labor costs and shortens project timelines by assembling components in controlled factory environments, ensuring higher precision and quality control. This method minimizes material waste and enhances sustainability through efficient resource management. Prefabrication also mitigates weather-related delays and improves safety by limiting the amount of work performed at construction sites.
Benefits of Modular Construction
Modular construction significantly reduces project timelines by enabling simultaneous site preparation and building fabrication, leading to faster project completion. Factory-controlled environments ensure higher quality and consistency, minimizing material waste and errors compared to traditional prefab methods. Enhanced flexibility in design and scalability allows modular construction to accommodate complex architectural requirements while optimizing cost efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Prefab vs Modular
Prefab construction generally offers lower upfront costs due to standardized production and reduced labor expenses, making it ideal for projects with tight budgets. Modular construction, though initially more expensive because of complex transport and assembly requirements, often results in long-term savings through faster project completion and minimized on-site labor costs. Evaluating total project expenses reveals that modular construction can deliver greater overall value despite higher initial investment.
Project Timelines and Installation Speed
Prefab construction significantly reduces project timelines by fabricating components offsite simultaneously with onsite groundwork, enabling faster overall completion than traditional methods. Modular construction further accelerates installation speed by delivering fully assembled modules ready for immediate assembly, minimizing onsite labor and weather-related delays. Projects employing modular techniques can experience up to 50% shorter construction periods compared to conventional builds, optimizing efficiency and resource management.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Prefab construction reduces waste by manufacturing components in controlled factory settings, leading to precise material usage and minimal site disturbance. Modular construction further enhances sustainability by enabling reuse of modules and promoting energy efficiency through better insulation standards. Both methods significantly lower carbon footprints compared to traditional construction, contributing to greener building practices.
Quality Control in Prefab and Modular Methods
Prefab and modular construction methods both emphasize rigorous quality control through factory-based manufacturing, reducing variability caused by weather and onsite conditions. Prefabrication allows precise standardization of components in controlled environments, ensuring consistent material quality and structural integrity. Modular construction further enhances quality assurance by assembling complete modules under strict protocols before onsite installation, streamlining inspections and reducing defects.
Common Applications in the Construction Industry
Prefab construction is widely applied in residential housing, commercial buildings, and infrastructure projects due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Modular construction is favored for healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and hospitality projects because of its flexibility and rapid on-site assembly. Both methods enhance project timelines and quality control in large-scale construction developments.
Future Trends in Prefab and Modular Construction
Prefab and modular construction are rapidly advancing with the integration of smart technologies and sustainable materials, driving efficiency and reducing environmental impact. The adoption of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and automation is enhancing precision and shortening project timelines in both prefab factories and modular assembly sites. Industry projections indicate a growing market share, fueled by urbanization demands and labor shortages, positioning prefab and modular methods as key solutions in future construction projects.
Related Important Terms
Panelized Prefab Systems
Panelized prefab systems offer precise factory-built wall, floor, and roof panels that allow faster site assembly compared to traditional modular construction modules. These systems optimize material use and reduce on-site labor costs while ensuring high structural quality and design flexibility for residential and commercial buildings.
Volumetric Modular Units
Volumetric modular units in construction offer factory-built, three-dimensional sections that integrate electrical, plumbing, and interior finishes, significantly reducing onsite construction time and labor costs. Compared to traditional prefab components, these volumetric modules provide enhanced quality control, faster assembly, and greater design flexibility, making them ideal for rapid project delivery and scalable building solutions.
Hybrid Construction Models
Hybrid construction models combine prefab and modular construction methods to optimize efficiency, cost, and customization in building projects. Incorporating off-site prefabricated components with on-site modular assembly accelerates timelines and enhances structural quality while maintaining design flexibility.
Offsite Fabrication
Offsite fabrication in prefab construction involves manufacturing building components in a controlled factory environment, enhancing quality control and reducing onsite labor and waste. Modular construction takes this further by assembling entire sections or modules offsite, enabling faster project timelines and improved scalability for large-scale developments.
Plug-and-Play Assemblies
Plug-and-play assemblies in modular construction enable rapid on-site installation by delivering pre-engineered components that seamlessly integrate, reducing labor costs and construction timelines. Prefabricated construction often requires more on-site customization, whereas modular plug-and-play systems enhance quality control and improve project scalability through factory precision.
Kit-of-Parts
Kit-of-parts design in prefab construction involves manufacturing standardized components that are assembled on-site, offering flexibility and cost-efficiency compared to traditional modular construction's larger, pre-assembled units. Prefabricated kit-of-parts systems enable easier customization and scalability, streamlining project timelines while reducing material waste and labor costs.
Digital Twin Manufacturing
Digital Twin Manufacturing enhances modular construction by enabling real-time simulation and monitoring of prefab components, reducing errors and accelerating project timelines. Integrating digital twins in prefab workflows improves quality control and predictive maintenance, offering significant advantages over traditional construction methods.
DfMA (Design for Manufacture and Assembly)
DfMA in prefab construction emphasizes standardizing components for off-site fabrication, enhancing quality control and minimizing on-site labor. Modular construction integrates DfMA principles by assembling complete modules in factories, reducing construction time and improving precision compared to traditional methods.
Componentized Construction
Componentized construction breaks building projects into standardized, factory-made components that are transported and assembled on-site, enhancing efficiency and quality control compared to traditional prefab methods. This approach enables greater customization and flexibility while reducing construction waste and minimizing on-site labor time.
Lean Modular Integration
Lean modular integration in construction streamlines project timelines by combining prefabricated components with on-site assembly, reducing waste and labor costs. This method enhances efficiency and quality control compared to traditional prefab approaches by enabling precise coordination and just-in-time delivery of modular units.
Prefab vs Modular Construction Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com