Scaffolding provides traditional support for workers and materials, offering flexibility and reusability across various construction projects. 3D printed formwork enables precise, customizable molds that reduce labor time and material waste while enhancing structural complexity. Choosing between scaffolding and 3D printed formwork depends on project scale, design requirements, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
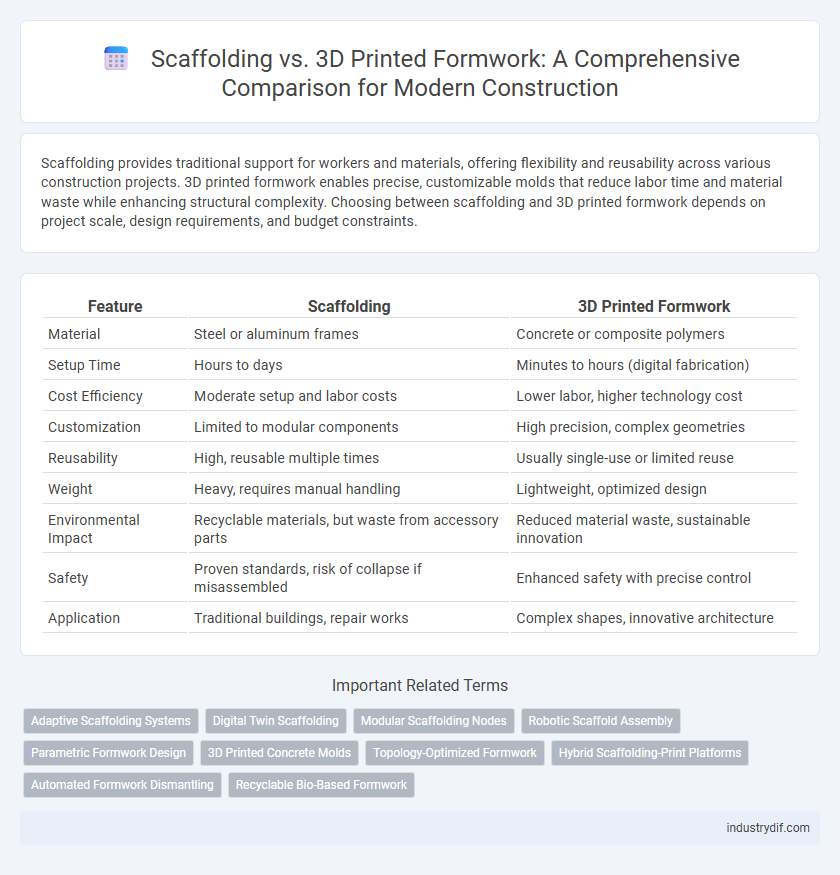
| Feature | Scaffolding | 3D Printed Formwork |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel or aluminum frames | Concrete or composite polymers |
| Setup Time | Hours to days | Minutes to hours (digital fabrication) |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate setup and labor costs | Lower labor, higher technology cost |
| Customization | Limited to modular components | High precision, complex geometries |
| Reusability | High, reusable multiple times | Usually single-use or limited reuse |
| Weight | Heavy, requires manual handling | Lightweight, optimized design |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable materials, but waste from accessory parts | Reduced material waste, sustainable innovation |
| Safety | Proven standards, risk of collapse if misassembled | Enhanced safety with precise control |
| Application | Traditional buildings, repair works | Complex shapes, innovative architecture |
Introduction to Scaffolding and 3D Printed Formwork
Scaffolding is a temporary structure commonly used in construction to support workers and materials during building or repair tasks, offering flexibility and ease of assembly. 3D printed formwork utilizes additive manufacturing to create precise molds for concrete casting, enhancing design complexity and reducing material waste. Both methods significantly impact construction efficiency, with scaffolding emphasizing accessibility and 3D printed formwork focusing on innovation and precision.
Key Differences in Construction Applications
Scaffolding provides temporary support and access for workers during construction, emphasizing versatility and reusability in various building phases. In contrast, 3D printed formwork offers precise, custom-shaped molds that enhance concrete shaping efficiency and reduce material waste. The key differences lie in scaffolding's adaptability and dismantling ease versus 3D printed formwork's ability to streamline complex designs and improve structural accuracy.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Scaffolding typically uses steel or aluminum, known for durability and reusability, but requires extensive maintenance and raw material extraction, impacting sustainability. 3D printed formwork employs biodegradable or recyclable polymers and concrete composites, reducing waste and allowing precise material use, which enhances eco-friendliness. The shift to 3D printed formwork supports sustainable construction by minimizing resource consumption and lowering carbon footprints compared to traditional metal scaffolding.
Installation Speed and Labor Requirements
Scaffolding typically requires extensive labor and longer installation times due to manual assembly and multiple components, while 3D printed formwork significantly reduces installation speed by producing custom, ready-to-use molds with minimal worker intervention. Labor needs for scaffolding are higher because of the need for skilled personnel in erecting and dismantling structures, whereas 3D printed formwork demands fewer workers, lowering overall labor costs and enhancing project efficiency. The adoption of 3D printed formwork accelerates construction schedules by streamlining formwork installation and reducing on-site complexities compared to traditional scaffolding methods.
Structural Flexibility and Design Capabilities
Scaffolding provides basic structural support with limited design flexibility, making it suitable for repetitive, standardized forms but less adaptable to complex geometries. 3D printed formwork offers advanced structural flexibility and enables intricate, customized designs that traditional scaffolding cannot achieve. The ability to create precise, multifunctional forms improves construction efficiency and material optimization in innovative architectural projects.
Cost Analysis: Traditional vs. Advanced Methods
Scaffolding systems typically involve recurring labor and material costs that fluctuate with project scale and complexity, while 3D printed formwork demands higher initial investment in technology and software but reduces labor and material waste significantly. Cost analysis reveals that advanced 3D printed formwork minimizes long-term expenses through faster setup, less material use, and improved precision, contrasting with traditional scaffolding's ongoing maintenance and storage costs. Projects with stringent architectural customization and tight timelines benefit from the scalability and cost efficiency of 3D printed solutions despite upfront expenses.
Safety Considerations in On-site Usage
Scaffolding provides reliable structural support with proven safety standards, allowing workers to maneuver securely at various heights, but requires regular inspection to prevent accidents from wear or improper assembly. 3D printed formwork reduces on-site labor risks by minimizing manual handling and repetitive setup tasks, though its safety depends heavily on material integrity and precision in the printing process to avoid failures. Integrating both methods requires strict adherence to safety protocols, ensuring site stability and worker protection through continuous monitoring and compliance with industry regulations.
Impact on Project Timelines
Scaffolding often requires extensive manual assembly and disassembly, which can extend project timelines due to labor-intensive processes and coordination efforts. In contrast, 3D printed formwork significantly reduces construction time by enabling rapid production of complex shapes with minimal on-site adjustments. This advancement in formwork technology streamlines workflow, potentially accelerating project completion and improving scheduling accuracy.
Modern Innovations in Formwork Technology
Modern innovations in formwork technology increasingly favor 3D printed formwork due to its precision, customization, and material efficiency compared to traditional scaffolding. 3D printed formwork reduces labor costs and construction time by enabling complex geometries and reducing the need for extensive manual assembly. This advanced technique supports sustainable construction practices by minimizing waste and enhancing structural performance in various building projects.
Future Trends in Construction Formwork Solutions
Advancements in construction formwork solutions highlight a transition from traditional scaffolding to 3D printed formwork, offering enhanced precision and customization for complex geometries. 3D printed formwork reduces material waste and accelerates project timelines by enabling on-site fabrication with improved structural performance. Integration of smart sensors in both scaffolding and 3D printed systems is expected to optimize safety monitoring and real-time adjustments in future construction sites.
Related Important Terms
Adaptive Scaffolding Systems
Adaptive scaffolding systems enhance construction efficiency by providing modular, customizable support that adjusts to complex architectural designs, unlike traditional scaffolding. These systems integrate with 3D printed formwork technologies to optimize material use, reduce labor costs, and improve safety on job sites.
Digital Twin Scaffolding
Digital twin scaffolding integrates real-time data and 3D modeling to enhance safety, monitoring, and efficiency compared to traditional scaffolding and 3D printed formwork. This digital innovation allows precise structural analysis and predictive maintenance, optimizing construction workflows and reducing risks on complex building sites.
Modular Scaffolding Nodes
Modular scaffolding nodes offer versatile, reusable connection points that enhance structural stability and assembly efficiency in construction projects compared to the fixed geometry of 3D printed formwork. These nodes facilitate rapid configuration adjustments, reducing labor time and improving safety while supporting complex scaffolding frameworks in diverse site conditions.
Robotic Scaffold Assembly
Robotic scaffold assembly enhances construction efficiency by automating the precise erection of scaffolding structures, reducing labor costs and improving safety compared to traditional manual methods. In contrast, 3D printed formwork offers customized, rapid fabrication of complex concrete molds but lacks the scalability and flexibility that robotic scaffolding provides for large-scale building projects.
Parametric Formwork Design
Parametric formwork design in 3D printed formwork enables precise customization of complex geometries, reducing material waste and construction time compared to traditional scaffolding methods. This digital approach integrates advanced algorithms to optimize structural efficiency and enhance on-site adaptability, transforming conventional concrete casting processes.
3D Printed Concrete Molds
3D printed concrete molds revolutionize construction by enabling precise, complex shapes unattainable with traditional scaffolding, reducing material waste and labor costs. These molds enhance structural integrity through customizable designs and accelerate project timelines by streamlining formwork production.
Topology-Optimized Formwork
Topology-optimized formwork in 3D printing significantly reduces material usage and enhances structural performance compared to traditional scaffolding methods. By precisely distributing material only where needed, this approach minimizes waste and accelerates construction processes while maintaining high safety standards.
Hybrid Scaffolding-Print Platforms
Hybrid scaffolding-print platforms combine traditional scaffolding frameworks with advanced 3D printed formwork, enhancing construction speed and precision by providing customizable, reusable support structures tailored to complex architectural designs. This integration reduces material waste and labor costs while increasing structural safety and adaptability on dynamic sites.
Automated Formwork Dismantling
Automated formwork dismantling in 3D printed formwork significantly reduces labor costs and enhances safety by minimizing manual intervention compared to traditional scaffolding methods. This technology accelerates project timelines through precise, mechanized removal processes that optimize workflow efficiency on construction sites.
Recyclable Bio-Based Formwork
Recyclable bio-based formwork offers a sustainable alternative to traditional scaffolding and 3D printed formwork by utilizing biodegradable materials such as bamboo and mycelium that significantly reduce environmental impact. These eco-friendly formworks not only provide robust structural support but also facilitate circular construction practices through their ease of reuse and decomposition, enhancing green building initiatives in the construction industry.
Scaffolding vs 3D Printed Formwork Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com