Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and basic tools to collect spatial data, often leading to longer project timelines and potential human errors. Reality capture utilizes advanced technologies such as 3D laser scanning and drone photogrammetry to quickly generate highly accurate, detailed digital models of construction sites. Integrating reality capture into construction workflows improves precision, enhances project monitoring, and reduces rework compared to conventional surveying methods.
Table of Comparison
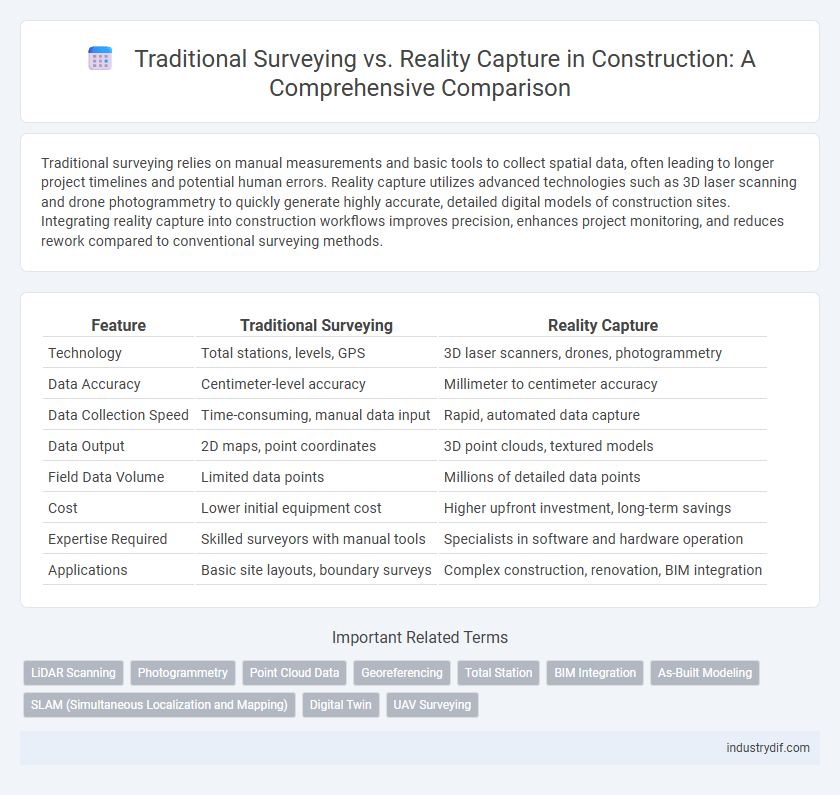
| Feature | Traditional Surveying | Reality Capture |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Total stations, levels, GPS | 3D laser scanners, drones, photogrammetry |
| Data Accuracy | Centimeter-level accuracy | Millimeter to centimeter accuracy |
| Data Collection Speed | Time-consuming, manual data input | Rapid, automated data capture |
| Data Output | 2D maps, point coordinates | 3D point clouds, textured models |
| Field Data Volume | Limited data points | Millions of detailed data points |
| Cost | Lower initial equipment cost | Higher upfront investment, long-term savings |
| Expertise Required | Skilled surveyors with manual tools | Specialists in software and hardware operation |
| Applications | Basic site layouts, boundary surveys | Complex construction, renovation, BIM integration |
Introduction to Surveying in Construction
Traditional surveying in construction involves manual measurement techniques using tools like total stations, theodolites, and measuring tapes to establish accurate site boundaries and elevations. Reality capture utilizes advanced technologies such as laser scanning, drones, and photogrammetry to quickly create detailed 3D models of construction sites, improving precision and reducing human error. These methods provide foundational data essential for project planning, design validation, and progress monitoring.
Defining Traditional Surveying Techniques
Traditional surveying techniques use tools like total stations, theodolites, and GPS to measure land and create accurate maps or plans. These methods rely on manual data collection, including distance, angle, and elevation measurements, which are then processed to define site boundaries and topography. Surveyors often use leveling instruments and optical targets to ensure precision in construction layouts and infrastructure projects.
Overview of Reality Capture Technologies
Reality capture technologies, such as LiDAR scanning, photogrammetry, and drones, offer precise 3D mapping and modeling of construction sites, enhancing data accuracy beyond traditional surveying methods. These technologies enable rapid data collection, real-time progress monitoring, and improved asset management throughout the construction lifecycle. Integrating reality capture accelerates workflows, reduces errors, and supports better decision-making with comprehensive spatial information.
Accuracy Comparison: Traditional vs Reality Capture
Traditional surveying methods rely on manual measurements and optical instruments, which can introduce human error and limit accuracy, especially in complex or large-scale construction sites. Reality capture technologies, such as LiDAR and photogrammetry, provide highly precise, three-dimensional data with accuracy often within millimeters, significantly reducing discrepancies and rework. Integrating reality capture enhances project outcomes by delivering detailed spatial information that surpasses the precision achievable through traditional surveying techniques.
Time and Cost Efficiency
Traditional surveying methods often require extensive manual measurements and fieldwork, leading to longer project timelines and increased labor costs. Reality capture technology uses drones, 3D laser scanning, and photogrammetry to quickly gather precise data, significantly reducing time on site and minimizing errors that can drive up expenses. This integration of advanced digital techniques enhances overall cost efficiency by streamlining workflows and accelerating the decision-making process in construction projects.
Data Output and Visualization
Traditional surveying produces point-based data that often requires manual processing and interpretation, leading to potential delays and inaccuracies in project visualization. Reality capture technologies generate highly detailed 3D models and textured meshes, enabling real-time visualization and immediate data integration for enhanced decision-making. This shift dramatically improves spatial accuracy and accelerates project timelines by providing comprehensive, georeferenced visual outputs.
Integration with BIM and Other Digital Tools
Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and point data collection, which integrates with BIM through converting survey points into digital models, often requiring extensive data manipulation. Reality capture utilizes advanced technologies like laser scanning and photogrammetry to create highly detailed 3D models, enabling seamless integration with BIM software for enhanced accuracy and real-time updates. This integration enhances project coordination, reduces errors, and streamlines workflows by providing comprehensive digital representations that align directly with construction planning and execution.
Skill Requirements and Training Needs
Traditional surveying demands extensive expertise in manual measurement techniques, angle calculations, and the use of classic instruments like theodolites and levels, requiring comprehensive training in fieldwork and geometric principles. Reality capture leverages advanced technologies such as 3D laser scanning, photogrammetry, and drone mapping, necessitating proficiency in software operation, data processing, and interpretation of digital point clouds, which shifts training focus toward technical and software skills. The contrast in skill sets highlights a growing need for hybrid professionals adept in both hands-on surveying methods and cutting-edge digital data acquisition tools to optimize construction accuracy and efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations
Traditional surveying often faces challenges such as limited data density, prolonged project timelines, and susceptibility to human error, which can impact accuracy and efficiency on construction sites. Reality capture technologies, including 3D laser scanning and drone photogrammetry, overcome these limitations by rapidly collecting comprehensive, high-resolution spatial data, though they require significant initial investment and specialized expertise. Both methods are constrained by environmental factors like poor weather or obstructed sightlines, affecting data quality and accessibility during field operations.
Future Trends in Construction Surveying
Future trends in construction surveying emphasize the integration of reality capture technologies such as LiDAR, photogrammetry, and drone-based scanning, which provide highly accurate 3D models and real-time data. Traditional surveying methods face challenges with efficiency and data resolution, promoting a shift toward automated and digital solutions that enhance precision and project timelines. The convergence of BIM (Building Information Modeling) and reality capture is driving smarter construction workflows, enabling proactive decision-making and reducing costs across project lifecycles.
Related Important Terms
LiDAR Scanning
LiDAR scanning revolutionizes traditional surveying by providing high-resolution 3D spatial data with exceptional accuracy and speed, enabling detailed site analysis and reducing human error. Unlike conventional methods relying on manual measurements and sketches, LiDAR captures comprehensive point clouds that support precise modeling, progress tracking, and improved project decision-making in construction.
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry in construction enables precise 3D modeling by capturing high-resolution images from multiple angles, surpassing traditional surveying methods that rely on manual measurements and limited spatial data. This technology accelerates site analysis, improves accuracy in topographic mapping, and enhances project planning with detailed visual documentation.
Point Cloud Data
Point cloud data in traditional surveying relies on manual measurements with total stations and GPS, often resulting in sparse and time-consuming data collection. Reality capture technology uses laser scanning and photogrammetry to generate dense, highly accurate point clouds rapidly, improving precision and efficiency in construction project surveys.
Georeferencing
Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and physical markers to establish georeferencing points, often resulting in slower data acquisition and potential inaccuracies. Reality capture technologies like LiDAR and photogrammetry provide high-precision, digitally georeferenced 3D models that enhance accuracy and efficiency in construction site mapping.
Total Station
Total Station technology enhances traditional surveying by integrating electronic distance measurement and angle calculation, providing precise 3D data crucial for construction site layout and verification. Unlike conventional methods, Total Stations enable faster data collection and improved accuracy, streamlining project workflows and reducing human error in topographic mapping and as-built documentation.
BIM Integration
Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and 2D data collection, which can delay BIM integration and increase potential errors in construction projects. Reality capture techniques, such as 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry, enable precise and real-time data acquisition, streamlining BIM workflows and improving accuracy in model-based project planning and execution.
As-Built Modeling
Traditional surveying relies on manual measurements and 2D drawings, often leading to time-consuming and less accurate as-built models, while reality capture technology uses 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry to create precise, detailed, and efficient as-built building information models (BIM). This advanced approach reduces human error, accelerates project timelines, and enhances collaboration across construction teams by providing real-time, comprehensive spatial data.
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) enhances reality capture in construction by creating precise, real-time 3D maps of job sites, surpassing the limitations of traditional surveying methods reliant on manual measurements and static data. This technology improves accuracy, efficiency, and safety by enabling dynamic environment mapping, reducing human error, and facilitating faster project updates through automated data collection.
Digital Twin
Traditional surveying relies on manual data collection methods that are time-consuming and prone to human error, limiting the accuracy and frequency of site updates. Reality capture technologies, such as LiDAR and photogrammetry, enable the creation of highly detailed Digital Twin models that provide real-time, precise representations of construction sites, improving project monitoring and decision-making.
UAV Surveying
UAV surveying leverages drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and LiDAR sensors to rapidly capture precise topographic data, significantly reducing the time and labor compared to traditional surveying methods that rely on manual measurements and total stations. This reality capture technology enhances accuracy in construction site mapping, enabling real-time progress monitoring and effective project management through detailed 3D models.
Traditional Surveying vs Reality Capture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com