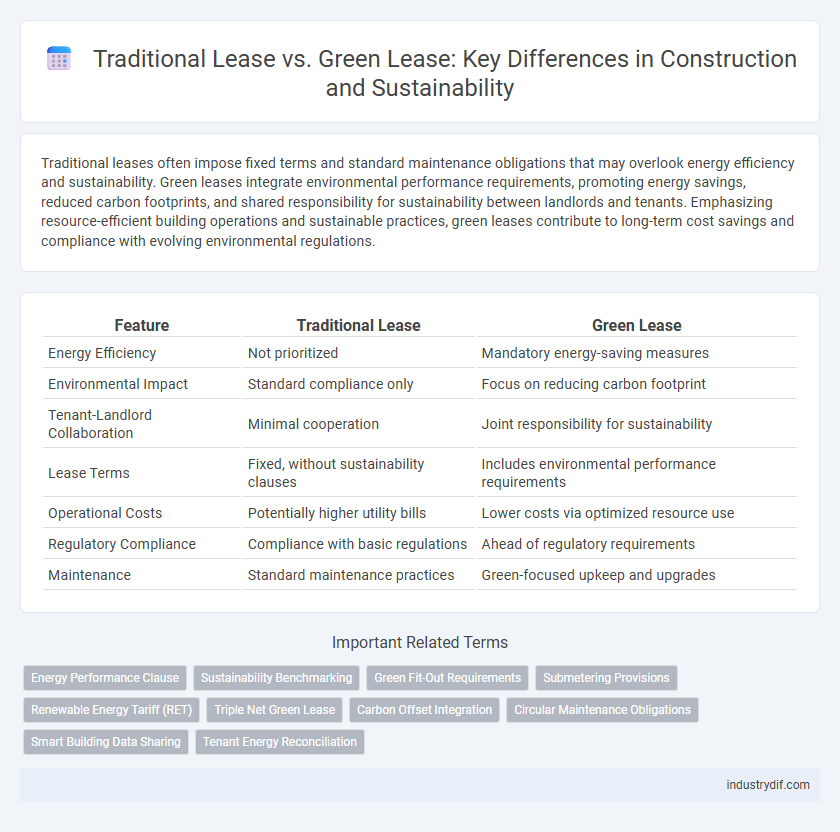
Traditional leases often impose fixed terms and standard maintenance obligations that may overlook energy efficiency and sustainability. Green leases integrate environmental performance requirements, promoting energy savings, reduced carbon footprints, and shared responsibility for sustainability between landlords and tenants. Emphasizing resource-efficient building operations and sustainable practices, green leases contribute to long-term cost savings and compliance with evolving environmental regulations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Lease | Green Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Not prioritized | Mandatory energy-saving measures |
| Environmental Impact | Standard compliance only | Focus on reducing carbon footprint |
| Tenant-Landlord Collaboration | Minimal cooperation | Joint responsibility for sustainability |
| Lease Terms | Fixed, without sustainability clauses | Includes environmental performance requirements |
| Operational Costs | Potentially higher utility bills | Lower costs via optimized resource use |
| Regulatory Compliance | Compliance with basic regulations | Ahead of regulatory requirements |
| Maintenance | Standard maintenance practices | Green-focused upkeep and upgrades |
Introduction to Lease Types in Construction
Traditional leases in construction typically involve fixed rental agreements where tenants are responsible for maintenance and utility costs. Green leases integrate sustainable building practices by including clauses that promote energy efficiency, waste reduction, and shared environmental responsibilities between landlords and tenants. This emerging lease type supports compliance with green building certifications and enhances long-term operational savings.
Defining Traditional Leases
Traditional leases in construction typically establish fixed rental terms without accounting for sustainability or energy efficiency measures, often leading to inefficient resource use and higher operational costs. These leases delegate maintenance and utility responsibilities inconsistently, potentially causing disputes over expenses between landlords and tenants. Unlike green leases, traditional agreements rarely incentivize or require environmentally friendly building practices, limiting opportunities for reducing carbon footprints in property management.
What Is a Green Lease?
A green lease is a contractual agreement between landlords and tenants that incorporates sustainable building practices and energy-efficient operations to reduce environmental impact. It outlines responsibilities for maintaining eco-friendly systems such as energy use, water conservation, and waste management within the leased property. This approach promotes long-term cost savings, regulatory compliance, and the pursuit of environmental certification standards like LEED or BREEAM.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Green Leases
Traditional leases primarily focus on basic rental terms and maintenance responsibilities, often neglecting environmental performance and energy efficiency standards. Green leases incorporate sustainability clauses, requiring tenants and landlords to cooperate on energy-saving measures, waste reduction, and the use of eco-friendly materials in construction and operation. These key differences influence building performance, operational costs, and compliance with green building certifications such as LEED and BREEAM.
Energy Efficiency Standards in Green Leases
Green leases incorporate stringent energy efficiency standards that mandate reduced energy consumption through the use of advanced HVAC systems, LED lighting, and high-performance insulation materials. Unlike traditional leases, green leases often require tenants and landlords to collaborate on sustainability initiatives such as regular energy audits and shared utility benchmarking. These provisions drive significant cost savings and contribute to lower carbon footprints across leased commercial properties.
Impact on Operating Costs
Traditional leases often result in higher operating costs due to fixed terms that disregard energy efficiency and sustainability improvements. Green leases incorporate clauses that promote energy-saving measures, reducing utility expenses and maintenance costs over time. This alignment of tenant and landlord incentives leads to significant reductions in overall operational expenses within sustainable buildings.
Environmental Compliance and Regulations
Green leases incorporate environmental compliance and regulations by requiring tenants and landlords to adhere to sustainability criteria, energy efficiency standards, and waste reduction practices, promoting reduced carbon footprints in building operations. Traditional leases often lack explicit clauses for environmental performance, resulting in limited accountability for regulatory compliance related to green building certifications such as LEED or BREEAM. Implementing green lease provisions supports compliance with increasingly stringent environmental laws and incentives targeting sustainable construction and occupancy practices.
Tenant and Landlord Responsibilities
Traditional leases typically place maintenance and repair responsibilities primarily on landlords, while tenants focus on rent payments and internal upkeep. Green leases incorporate environmental performance clauses, requiring tenants and landlords to collaboratively manage energy efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable resource use. These agreements promote shared accountability for achieving sustainability goals within building operations.
Long-Term Value and Investment Return
Traditional leases often emphasize short-term rental income without incentivizing energy efficiency, leading to higher operational costs and limited asset value growth. Green leases, by integrating sustainability clauses and shared energy-saving responsibilities, enhance long-term property performance and reduce utility expenses, directly boosting net operating income. Investors benefit from increased asset valuation, lower vacancy rates, and stronger tenant retention, which collectively improve long-term investment returns in the construction and real estate sectors.
Future Trends in Construction Leasing
Future trends in construction leasing emphasize the shift from traditional leases towards green leases, integrating sustainability clauses that encourage energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprints in building operations. Green leases align tenant and landlord incentives by incorporating environmental performance metrics, renewable energy requirements, and waste reduction targets, fostering long-term cost savings and regulatory compliance. The increasing demand for LEED-certified and net-zero buildings drives the adoption of green lease frameworks as a strategic approach to enhance property value and meet evolving market and climate goals.
Related Important Terms
Energy Performance Clause
Traditional leases often lack specific Energy Performance Clauses, resulting in limited accountability for energy consumption and sustainability improvements throughout the lease term. Green leases incorporate detailed Energy Performance Clauses that mandate energy efficiency targets, data sharing, and collaboration between landlords and tenants to reduce environmental impact and operating costs.
Sustainability Benchmarking
Traditional leases often overlook energy efficiency and environmental impact, leading to higher operational costs and carbon footprints, while green leases incorporate sustainability benchmarking by setting measurable targets for energy use, waste reduction, and indoor air quality. These benchmarks enable building owners and tenants to collaborate on achieving environmental certifications such as LEED or BREEAM, promoting long-term sustainability and regulatory compliance in the construction sector.
Green Fit-Out Requirements
Green lease fit-out requirements mandate the use of sustainable materials, energy-efficient systems, and waste reduction practices to minimize environmental impact during tenant improvements. Unlike traditional leases, green leases incorporate specific clauses that enforce compliance with environmental standards such as LEED or BREEAM certifications, promoting long-term sustainability in building operations.
Submetering Provisions
Traditional leases often lack detailed submetering provisions, resulting in landlords bearing utility costs, while green leases incorporate specific submetering clauses to promote energy efficiency and transparent utility consumption tracking. Submetering in green leases encourages tenant accountability and supports sustainability by enabling precise measurement of individual energy and water usage within leased spaces.
Renewable Energy Tariff (RET)
Traditional leases often lack provisions for Renewable Energy Tariffs (RET), resulting in higher operational costs due to reliance on conventional energy sources. Green leases integrate RET clauses that enable tenants and landlords to share benefits from renewable energy use, reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainable building practices.
Triple Net Green Lease
Triple Net Green Leases integrate environmental commitments into traditional triple net leases by requiring tenants to cover property taxes, insurance, and maintenance while adhering to sustainability practices such as energy efficiency, waste reduction, and water conservation. This lease structure promotes reduced operational costs and lower carbon footprints, aligning landlord and tenant incentives for sustainable building management.
Carbon Offset Integration
Traditional leases typically lack provisions for carbon offset integration, resulting in limited environmental accountability within property agreements. Green leases incorporate specific clauses that mandate carbon offset measures, promoting sustainable construction practices and reducing the building's overall carbon footprint.
Circular Maintenance Obligations
Traditional leases typically impose fixed maintenance obligations that often lead to linear resource use and waste accumulation, whereas green leases emphasize circular maintenance responsibilities designed to promote sustainable building operations through repair, reuse, and recycling practices. Circular maintenance obligations in green leases encourage tenants and landlords to collaborate on preserving asset value and minimizing environmental impact by extending the lifecycle of materials and components within the built environment.
Smart Building Data Sharing
Traditional leases typically restrict tenant access to building performance data, limiting opportunities for optimizing energy use and reducing operational costs. Green leases incorporate smart building data sharing clauses that enable real-time monitoring and collaborative energy management, enhancing sustainability and promoting efficient resource consumption.
Tenant Energy Reconciliation
Tenant energy reconciliation in traditional leases often lacks transparency, leading to inefficiencies and disputes over energy costs. Green leases incorporate clear tenant energy reconciliation clauses, promoting accountability and encouraging energy-saving practices that reduce overall consumption and costs.
Traditional Lease vs Green Lease Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com