Welded frames provide superior strength and rigidity, making them ideal for heavy-load structural applications in construction. Cold-formed steel offers flexibility and cost-efficiency, allowing for faster fabrication and ease of installation in light to medium-load projects. Selecting between welded frames and cold-formed steel depends on the specific structural requirements and budget constraints of the building project.
Table of Comparison
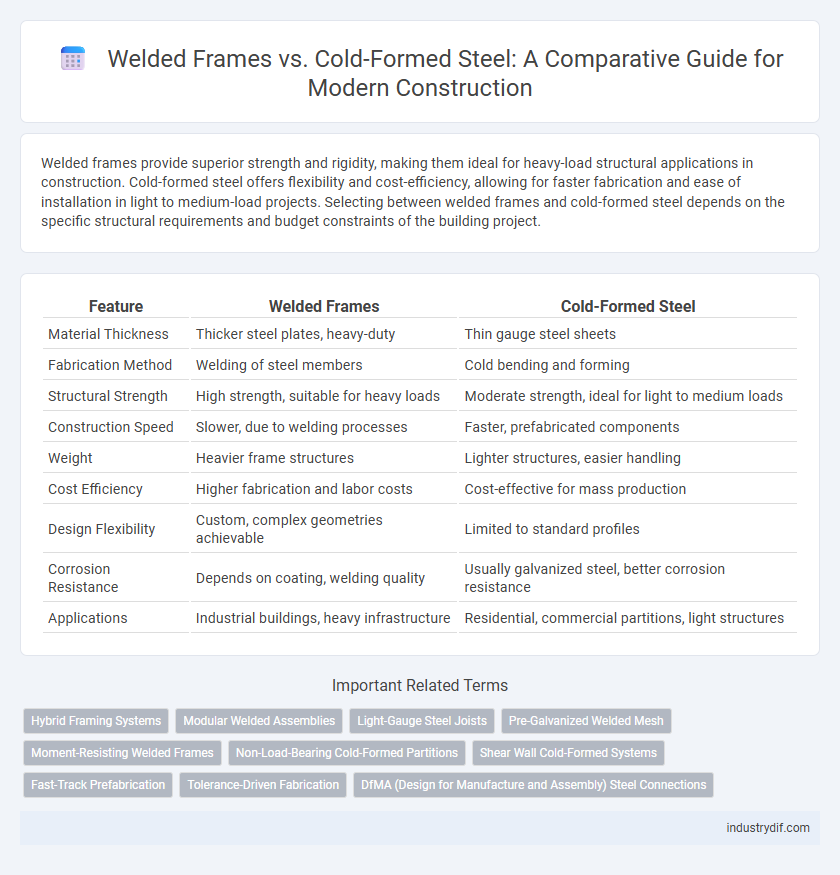
| Feature | Welded Frames | Cold-Formed Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | Thicker steel plates, heavy-duty | Thin gauge steel sheets |
| Fabrication Method | Welding of steel members | Cold bending and forming |
| Structural Strength | High strength, suitable for heavy loads | Moderate strength, ideal for light to medium loads |
| Construction Speed | Slower, due to welding processes | Faster, prefabricated components |
| Weight | Heavier frame structures | Lighter structures, easier handling |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher fabrication and labor costs | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Design Flexibility | Custom, complex geometries achievable | Limited to standard profiles |
| Corrosion Resistance | Depends on coating, welding quality | Usually galvanized steel, better corrosion resistance |
| Applications | Industrial buildings, heavy infrastructure | Residential, commercial partitions, light structures |
Introduction to Welded Frames and Cold-Formed Steel
Welded frames, constructed by fusing steel components through high-heat welding processes, provide strong, rigid structural support often used in large-scale construction projects. Cold-formed steel, produced by bending steel sheets at room temperature without heat, offers lightweight, high-strength framing ideal for non-load bearing walls and partitions. Both materials deliver unique benefits in durability, flexibility, and installation speed, influencing modern construction design choices.
Material Properties Comparison
Welded frames exhibit superior tensile strength and rigidity due to continuous welds, ensuring enhanced load-bearing capacity in structural applications. Cold-formed steel offers greater flexibility and is lighter, allowing for ease of handling and quicker installation but may require additional reinforcement for high-stress areas. The choice between welded frames and cold-formed steel depends on project demands, balancing strength, weight, and fabrication complexity.
Manufacturing Processes
Welded frames are produced by joining steel components through electric arc welding, creating strong, rigid connections ideal for load-bearing applications in construction. Cold-formed steel involves shaping thin steel sheets at room temperature using rollers or presses, resulting in lightweight and precise structural members with high strength-to-weight ratios. Manufacturing welded frames typically requires skilled labor and longer assembly times, while cold-formed steel allows for automated, high-speed production with minimal material waste.
Structural Performance and Strength
Welded frames offer superior structural performance through continuous connections that enhance load-bearing capacity and rigidity in construction applications. Cold-formed steel provides high strength-to-weight ratios and improved flexibility, making it ideal for lightweight framing but may require additional reinforcement for heavy loads. The choice between welded frames and cold-formed steel depends on specific project requirements, including load demands, structural complexity, and design constraints.
Cost Efficiency and Budget Considerations
Welded frames generally incur higher initial costs due to labor-intensive fabrication and specialized welding skills, while cold-formed steel offers cost efficiency through faster production and lighter material usage. Budget considerations favor cold-formed steel in projects requiring mass production or repetitive components, reducing overall expenses and construction timelines. Welded frames, however, provide superior strength and customization potential, which may justify the additional investment in complex or heavy-load structures.
Installation and Construction Techniques
Welded frames offer enhanced structural rigidity through factory-assembled connections, reducing on-site labor time and ensuring precise alignment during installation. Cold-formed steel components are lighter and easier to handle, allowing for faster framing assembly with standard power tools and minimally skilled labor on-site. Installation techniques for welded frames often require specialized equipment for welding, whereas cold-formed steel relies on mechanical fasteners, streamlining construction schedules.
Durability and Longevity
Welded frames offer superior durability in construction due to their seamless joints, providing enhanced strength and resistance to environmental stressors compared to cold-formed steel. Cold-formed steel, while lightweight and easy to fabricate, may be more susceptible to corrosion and fatigue over time if not properly treated or maintained. The longevity of welded frames generally surpasses that of cold-formed steel components, making them ideal for structures requiring long-term resilience and minimal maintenance.
Applications in Modern Construction
Welded frames offer superior strength and rigidity, making them ideal for high-load structural applications such as commercial buildings and industrial facilities. Cold-formed steel is favored in residential and light commercial construction due to its lightweight nature, ease of fabrication, and cost-effectiveness. Both materials contribute to sustainable building practices by enabling faster construction times and reducing material waste.
Compliance with Building Codes and Standards
Welded frames offer robust structural integrity that aligns closely with stringent building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) and American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) standards, ensuring enhanced safety and durability. Cold-formed steel, while lightweight and versatile, requires precise fabrication to meet compliance criteria outlined in standards like AISI S100 to avoid deficiencies in load-bearing capacity and performance. Both materials demand rigorous quality control and certification processes to satisfy regulatory requirements for commercial and residential construction projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Welded frames in construction provide high structural integrity but often involve energy-intensive fabrication processes, contributing to a larger carbon footprint compared to cold-formed steel. Cold-formed steel utilizes thinner gauges and can be produced with recycled materials, leading to reduced raw material consumption and lower emissions throughout its lifecycle. Choosing cold-formed steel supports sustainable building practices by minimizing waste, enhancing recyclability, and improving overall environmental performance in construction projects.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Framing Systems
Hybrid framing systems combine welded frames and cold-formed steel to leverage the strength and rigidity of welded connections with the lightweight, cost-effective benefits of cold-formed steel components. This fusion enhances structural performance, reduces material waste, and accelerates construction timelines in commercial and industrial buildings.
Modular Welded Assemblies
Modular welded assemblies provide superior structural integrity and load-bearing capacity compared to cold-formed steel frames, due to continuous welds that enhance rigidity and reduce deformation under stress. These welded frames optimize precision and assembly speed in modular construction, ensuring consistent quality and simplifying on-site installation processes.
Light-Gauge Steel Joists
Light-gauge steel joists in welded frames provide superior strength and rigidity, enabling longer spans with reduced material usage compared to cold-formed steel equivalents known for their flexibility and ease of fabrication. Efficient load distribution and resistance to deformation make welded frame joists ideal for heavy-duty structural applications, while cold-formed steel joists often suit residential and light commercial construction due to their lighter weight and cost-effectiveness.
Pre-Galvanized Welded Mesh
Pre-galvanized welded mesh offers superior corrosion resistance and structural integrity compared to cold-formed steel, making it ideal for welded frames in construction projects requiring enhanced durability. Its consistent coating thickness and strong weld joints provide extended service life and reduced maintenance costs in both indoor and outdoor applications.
Moment-Resisting Welded Frames
Moment-resisting welded frames provide superior rigidity and load-carrying capacity compared to cold-formed steel structures, making them ideal for withstanding seismic and lateral forces in construction projects. Their continuous welds enhance structural integrity and reduce deflection, offering improved performance in high-stress environments.
Non-Load-Bearing Cold-Formed Partitions
Non-load-bearing cold-formed steel partitions offer superior precision and lightweight installation compared to welded frames, enhancing on-site efficiency and reducing labor costs. These partitions deliver excellent fire resistance and acoustic performance, making them ideal for interior applications where structural support is not required.
Shear Wall Cold-Formed Systems
Shear wall cold-formed steel systems offer enhanced resistance to lateral loads with high strength-to-weight ratios and superior corrosion resistance compared to welded frames. These systems enable faster construction times and precise fabrication while maintaining flexibility in design for seismic and wind load applications.
Fast-Track Prefabrication
Welded frames enable robust, high-strength connections that reduce on-site assembly time, making them ideal for fast-track prefabrication projects. Cold-formed steel offers lightweight, precise components that streamline manufacturing and accelerate construction schedules through efficient modular assembly.
Tolerance-Driven Fabrication
Welded frames offer precise joint alignment and consistent dimensional accuracy due to controlled heat application, enabling tolerance-driven fabrication with minimal deviation. In contrast, cold-formed steel relies on mechanical forming processes that can introduce slight dimensional variances, requiring additional quality checks to maintain fabrication tolerances.
DfMA (Design for Manufacture and Assembly) Steel Connections
Welded frames provide rigidity and strength through permanent joints, optimizing load transfer but requiring skilled labor and controlled environments, whereas cold-formed steel connections in DfMA focus on modularity and ease of assembly with bolted or clipped connections that reduce onsite labor and allow faster construction cycles. Emphasizing DfMA principles, cold-formed steel connections enhance design flexibility, minimize fabrication errors, and improve the speed and accuracy of steel frame assembly compared to traditional welded frames.
Welded Frames vs Cold-Formed Steel Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com