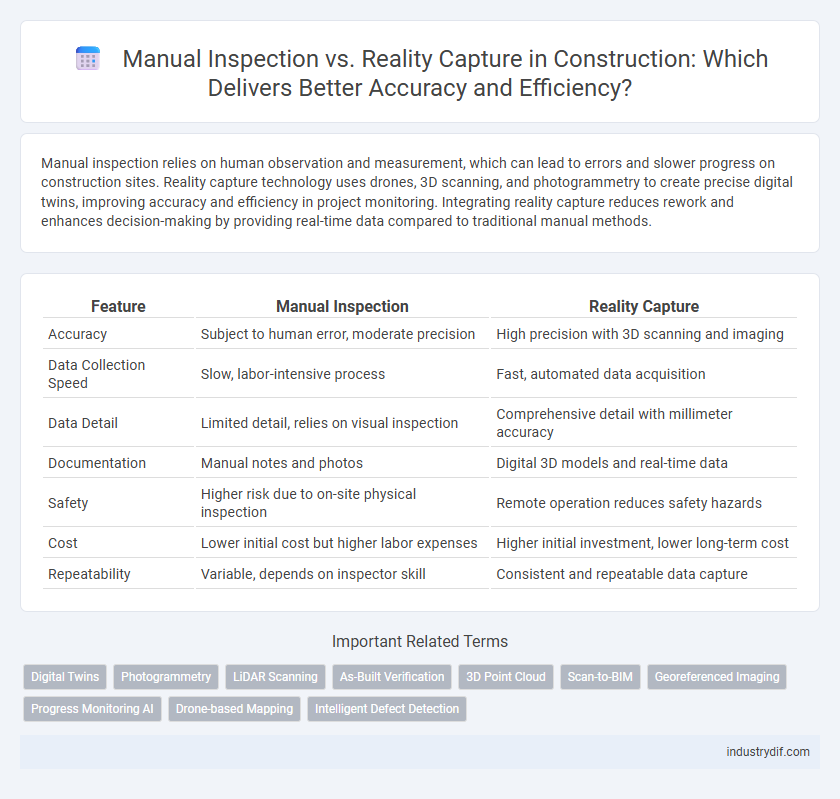
Manual inspection relies on human observation and measurement, which can lead to errors and slower progress on construction sites. Reality capture technology uses drones, 3D scanning, and photogrammetry to create precise digital twins, improving accuracy and efficiency in project monitoring. Integrating reality capture reduces rework and enhances decision-making by providing real-time data compared to traditional manual methods.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Inspection | Reality Capture |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Subject to human error, moderate precision | High precision with 3D scanning and imaging |
| Data Collection Speed | Slow, labor-intensive process | Fast, automated data acquisition |
| Data Detail | Limited detail, relies on visual inspection | Comprehensive detail with millimeter accuracy |
| Documentation | Manual notes and photos | Digital 3D models and real-time data |
| Safety | Higher risk due to on-site physical inspection | Remote operation reduces safety hazards |
| Cost | Lower initial cost but higher labor expenses | Higher initial investment, lower long-term cost |
| Repeatability | Variable, depends on inspector skill | Consistent and repeatable data capture |
Introduction to Manual Inspection and Reality Capture in Construction
Manual inspection in construction involves hands-on evaluation of structures, relying on skilled personnel to identify defects, ensure compliance, and verify workmanship quality through visual and tactile assessment. Reality capture employs advanced technologies like 3D laser scanning, drones, and photogrammetry to digitally document construction sites and elements with high precision and comprehensive spatial data. Integrating reality capture with manual inspection enhances accuracy, reduces human error, and provides a robust dataset for monitoring project progress and quality control.
Core Differences Between Manual Inspection and Reality Capture
Manual inspection in construction relies on human observation and physical measurements, often leading to subjective data and potential errors. Reality capture utilizes advanced technologies such as 3D laser scanning, drones, and photogrammetry to generate precise, objective digital models and measurements. The core difference lies in manual inspection's dependence on human input versus reality capture's data-driven automation, resulting in enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and comprehensive site documentation.
Accuracy and Reliability: Manual Inspection vs Reality Capture
Reality capture technologies such as 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry provide significantly higher accuracy and reliability compared to traditional manual inspections by minimizing human error and capturing comprehensive site data. Manual inspections often rely on subjective measurements and visual assessments, which can result in inconsistencies and lower precision. Integrating reality capture ensures precise, repeatable data collection, enhancing construction quality control and project documentation.
Time and Cost Efficiency in Construction Inspections
Manual inspection in construction often requires significant time and labor costs, increasing overall project expenses. Reality capture technology, such as 3D laser scanning and drones, accelerates data collection and reduces labor, enhancing both time and cost efficiency. Implementing reality capture enables more accurate inspections with fewer on-site visits, minimizing project delays and budget overruns.
Safety Considerations in Both Inspection Methods
Manual inspection in construction involves physical presence, increasing the risk of falls, exposure to hazardous materials, and accidents, necessitating strict safety protocols and personal protective equipment (PPE). Reality capture technologies like drones and 3D scanners minimize worker exposure to dangerous sites by remotely collecting accurate data, thereby enhancing safety but requiring specialized training and compliance with regulatory standards for operation. Both methods demand rigorous safety considerations, but reality capture offers significant risk reduction while maintaining inspection quality and efficiency.
Technology Integration and Digital Workflows
Manual inspection in construction relies heavily on visual assessments and physical measurements, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Reality capture technologies, such as 3D laser scanning and drones, integrate seamlessly with digital workflows to provide precise, real-time data for building information modeling (BIM) and project management. The integration of these technologies enhances accuracy, improves collaboration across teams, and accelerates decision-making processes on construction sites.
Common Use Cases for Manual and Reality Capture Inspections
Manual inspections are commonly used for detailed visual assessments, quality control, and safety checks that require human judgment and experience on construction sites. Reality capture inspections, utilizing technologies such as 3D laser scanning, drones, and photogrammetry, are ideal for creating accurate as-built documentation, progress tracking, and identifying discrepancies between design models and actual conditions. Both methods complement each other by addressing different inspection needs, with manual inspections excelling in nuanced evaluations and reality capture providing comprehensive, data-rich overviews.
Challenges and Limitations Faced by Each Approach
Manual inspection in construction often encounters challenges such as human error, limited access to complex structures, and time-consuming processes, which can result in incomplete or inaccurate data. Reality capture methods like 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry offer higher precision and comprehensive documentation but face limitations including high equipment costs, data processing complexity, and dependence on environmental conditions. Balancing these approaches requires addressing the trade-offs between affordability, accuracy, and operational feasibility on construction sites.
Impact on Project Documentation and Reporting
Manual inspection in construction often leads to incomplete or delayed project documentation due to human error and limited data capture. Reality capture technologies like 3D scanning and drones provide accurate, real-time data that enhances the precision and comprehensiveness of reports. This improvement in documentation quality accelerates decision-making and reduces project risks.
Future Trends: Evolving Roles of Manual Inspection and Reality Capture
Future trends in construction highlight the evolving roles of manual inspection and reality capture, with increasing integration of advanced technologies like drones, LiDAR, and AI-driven analytics enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Manual inspection remains crucial for nuanced problem-solving and complex decision-making, while reality capture enables comprehensive digital twins and real-time data visualization. The synergy between human expertise and automated data collection is driving improved project outcomes and reduced rework in construction workflows.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twins
Manual inspection in construction often leads to incomplete data and human errors, whereas reality capture technologies like 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry provide precise, comprehensive datasets essential for creating accurate digital twins. Digital twins enhance project monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time decision-making by integrating high-fidelity reality capture data with BIM models, driving efficiency and reducing rework.
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry enhances construction quality control by producing accurate 3D models from images, enabling detailed reality capture that surpasses the limitations of manual inspection. This technology accelerates progress tracking and defect detection, providing precise spatial data that manual methods often miss.
LiDAR Scanning
LiDAR scanning significantly enhances construction project accuracy by creating precise 3D models that surpass the limitations of manual inspections, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. While manual inspections rely on visual assessments and measurements, LiDAR technology captures millions of data points to detect structural inconsistencies and progress deviations in real-time.
As-Built Verification
Manual inspection for As-Built verification involves labor-intensive measurements prone to human error, whereas reality capture technologies like 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry provide precise, comprehensive digital models accelerating discrepancy identification and improving construction accuracy. Integrating reality capture significantly enhances verification workflows, ensuring compliance with design specifications and reducing costly rework.
3D Point Cloud
Manual inspection in construction relies on visual assessments and physical measurements, which can miss critical details and introduce human error, whereas reality capture technology generates highly accurate 3D point clouds that provide comprehensive spatial data for precise analysis and decision-making. Leveraging 3D point cloud data improves project quality control, reduces rework, and accelerates progress tracking by creating detailed digital twins of construction sites.
Scan-to-BIM
Manual inspection in construction relies heavily on subjective measurements and is time-consuming, often leading to inaccuracies in as-built documentation. Scan-to-BIM technology leverages reality capture methods like laser scanning to produce precise, up-to-date 3D models, significantly improving accuracy and efficiency in project planning and execution.
Georeferenced Imaging
Manual inspection often lacks the spatial accuracy and efficiency provided by georeferenced imaging in reality capture, which enables precise mapping and documentation of construction sites. Georeferenced imaging integrates GPS coordinates with visual data, offering enhanced quality control, progress tracking, and risk mitigation compared to traditional manual methods.
Progress Monitoring AI
Manual inspection in construction progress monitoring relies heavily on human observation and subjective reporting, often causing delays and inaccuracies. Reality capture technologies combined with AI deliver precise, real-time data through drones and 3D scanning, enabling automated progress tracking and early detection of deviations from project schedules.
Drone-based Mapping
Drone-based mapping revolutionizes manual inspection by delivering precise, high-resolution aerial data that enhances construction site monitoring and progress tracking. This technology reduces human error and safety risks while accelerating project timelines through rapid, comprehensive reality capture.
Intelligent Defect Detection
Manual inspection in construction often leads to missed defects and subjective assessments, whereas reality capture technologies leverage AI-powered intelligent defect detection to identify issues with higher accuracy and consistency. This advanced approach accelerates project timelines by enabling real-time analysis of 3D scans and imagery, reducing human error and enhancing quality control.
Manual Inspection vs Reality Capture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com