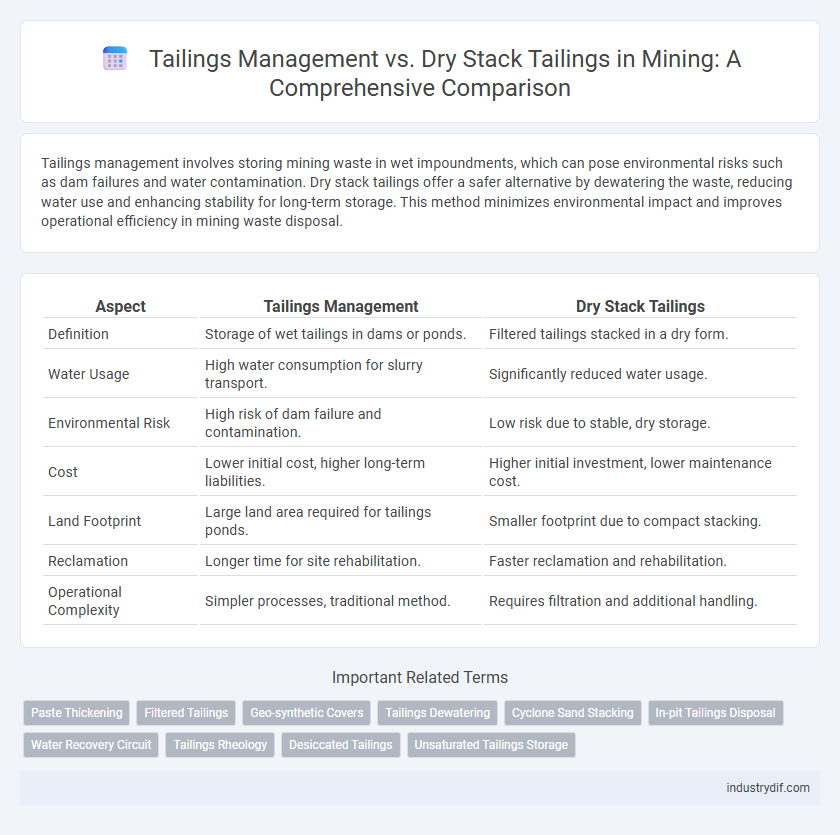
Tailings management involves storing mining waste in wet impoundments, which can pose environmental risks such as dam failures and water contamination. Dry stack tailings offer a safer alternative by dewatering the waste, reducing water use and enhancing stability for long-term storage. This method minimizes environmental impact and improves operational efficiency in mining waste disposal.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tailings Management | Dry Stack Tailings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Storage of wet tailings in dams or ponds. | Filtered tailings stacked in a dry form. |
| Water Usage | High water consumption for slurry transport. | Significantly reduced water usage. |
| Environmental Risk | High risk of dam failure and contamination. | Low risk due to stable, dry storage. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher long-term liabilities. | Higher initial investment, lower maintenance cost. |
| Land Footprint | Large land area required for tailings ponds. | Smaller footprint due to compact stacking. |
| Reclamation | Longer time for site rehabilitation. | Faster reclamation and rehabilitation. |
| Operational Complexity | Simpler processes, traditional method. | Requires filtration and additional handling. |
Introduction to Tailings Management
Tailings management involves the safe containment and disposal of mine waste materials, primarily slurry composed of water and finely ground rock particles. Dry stack tailings represent an advanced technique where dewatered tailings are compacted into a solid form, significantly reducing environmental risks such as dam failures and water contamination. Effective tailings management is critical for minimizing ecological impact, improving operational safety, and ensuring regulatory compliance in mining operations.
What Are Dry Stack Tailings?
Dry stack tailings are a method of tailings management where processed mine waste is dewatered to a low moisture content, creating a stackable, stable material that reduces the risk of dam failures. Unlike conventional tailings stored in slurry form behind dams, dry stack tailings significantly minimize water usage, environmental impact, and potential seepage or contamination of surrounding ecosystems. This technique enhances operational safety, lowers long-term monitoring costs, and supports sustainable mining practices by promoting more effective tailings disposal and reclamation.
Conventional Tailings Disposal Methods
Conventional tailings disposal methods primarily involve slurry pipelines transporting tailings to large containment ponds or impoundments, where water is retained, and solids settle. These methods require extensive water management systems to prevent seepage, dam failures, and environmental contamination, posing significant risks and long-term liabilities. In contrast, dry stack tailings reduce water usage by dewatering tailings into a stackable, semi-solid form, enhancing stability and minimizing environmental impact.
Environmental Impacts of Tailings Storage
Tailings management through conventional storage methods often results in significant environmental risks such as groundwater contamination, tailings dam failures, and long-term landscape disruption. Dry stack tailings technology reduces water usage and minimizes the potential for dam breaches, thereby lowering the chances of toxic leaks and soil contamination. This approach enhances environmental safety by stabilizing tailings in a solid form, promoting better reclamation and reducing the footprint of mine waste storage.
Water Conservation in Dry Stack Tailings
Dry stack tailings significantly enhance water conservation by enabling the dewatering of tailings, reducing the need for large tailings ponds and minimizing water loss through evaporation and seepage. This method promotes the recycling of process water, lowering freshwater consumption and mitigating environmental risks associated with traditional wet tailings disposal. Implementation of dry stacking in mining operations results in improved water management, critical in arid regions facing water scarcity challenges.
Safety and Stability Concerns
Tailings management with conventional wet impoundments poses significant safety risks due to potential dam failures and seepage, threatening nearby communities and ecosystems. Dry stack tailings offer enhanced stability by reducing the risk of liquefaction and minimizing water-related hazards, making them a safer alternative for long-term storage. Implementing dry stacking technology also improves environmental protection by limiting tailings pore water and reducing the footprint of tailings storage facilities.
Regulatory Requirements for Tailings Management
Regulatory requirements for tailings management emphasize strict monitoring, environmental protection, and the prevention of catastrophic failures, mandating comprehensive risk assessments and engineered containment solutions. Dry stack tailings systems often meet or exceed these regulations by reducing water use, lowering dam stability risks, and facilitating more controlled storage to comply with stringent environmental standards. Regulatory frameworks increasingly favor dry stack tailings due to their enhanced safety profile and reduced potential for environmental contamination compared to conventional wet tailings storage facilities.
Cost Considerations: Wet vs Dry Disposal
Wet tailings disposal involves slurry pipelines and large tailings ponds, leading to higher costs in water treatment, dam construction, and long-term environmental monitoring. Dry stack tailings reduce water usage and eliminate the need for tailings dams, resulting in lower operational expenses and minimized environmental liability. Initial capital investment for dry stacking may be higher, but life-cycle costs often prove more economical compared to wet disposal.
Technology Innovations in Tailings Management
Innovations in tailings management technology prioritize environmental safety and operational efficiency, with dry stack tailings emerging as a key solution to reduce water usage and minimize tailings dam risks. Advanced dewatering techniques and real-time monitoring systems enhance the stability and dryness of tailings, enabling safer storage and facilitating reclamation efforts. These technological advancements offer significant improvements over traditional tailings management by reducing potential leakage and ecological impact in mining operations.
Future Trends in Tailings Storage Solutions
Future trends in tailings storage solutions emphasize the shift from conventional wet tailings management to dry stack tailings, driven by environmental safety and regulatory pressures. Innovations in dewatering technologies and improved geotechnical stability of dry stacks reduce the risk of dam failures and minimize water usage. Industry adoption of smart monitoring systems and sustainable reclamation practices further enhances the durability and ecological compatibility of tailings storage facilities.
Related Important Terms
Paste Thickening
Paste thickening enhances tailings management by reducing water content to create a dense, pumpable slurry that minimizes environmental impact and storage footprint. Compared to dry stack tailings, paste thickened tailings improve stability and inertness, lowering risks of dam failures and enabling efficient reclamation.
Filtered Tailings
Filtered tailings, a key component of dry stack tailings technology, significantly reduce water usage and environmental risks by dewatering mining waste to a paste-like consistency for safer storage and easier reclamation. Compared to conventional tailings management, filtered tailings minimize the potential for dam failures, lower the footprint of tailings storage facilities, and enhance long-term stability and sustainability in mining operations.
Geo-synthetic Covers
Geo-synthetic covers are critical in tailings management, providing effective containment and minimizing environmental contamination by preventing water infiltration and dust dispersion. Dry stack tailings benefit significantly from geo-synthetic covers, enhancing stability and reducing seepage risks compared to conventional wet tailings storage facilities.
Tailings Dewatering
Tailings dewatering is a critical process in tailings management that enhances the stability and environmental safety of mine waste by reducing moisture content before disposal. Dry stack tailings, achieved through efficient dewatering techniques, offer improved water recovery, lower risk of dam failure, and minimized environmental impact compared to conventional wet tailings storage.
Cyclone Sand Stacking
Tailings management techniques such as Cyclone Sand Stacking optimize dry stack tailings by improving dewatering efficiency and reducing water usage, enabling safer, more stable tailings storage with minimal environmental impact. This method separates coarse solids for dry stacking, enhancing storage density and reducing potential acid mine drainage compared to conventional wet tailings disposal.
In-pit Tailings Disposal
In-pit tailings disposal integrates tailings back into the mined-out pit, reducing surface footprint and minimizing environmental impact compared to conventional tailings management methods. Dry stack tailings, characterized by filtered, low-moisture content, offer enhanced stability and reduced risk of dam failure, but in-pit deposition allows for cost-effective containment within existing mine voids.
Water Recovery Circuit
Tailings management using Dry Stack Tailings significantly enhances water recovery by minimizing water usage and promoting efficient dewatering processes, which reduces environmental risks associated with liquid tailings storage facilities. Advanced water recovery circuits in dry stacking systems enable up to 90% water reclamation, lowering operational costs and supporting sustainable mining practices.
Tailings Rheology
Tailings rheology plays a critical role in optimizing both conventional tailings management and dry stack tailings, influencing flow behavior, stability, and water recovery efficiency. Improved rheological control reduces the risk of dam failures in wet tailings, while enabling better compaction and reduced moisture content in dry stack tailings for safer long-term storage.
Desiccated Tailings
Desiccated tailings, a form of dry stack tailings, offer enhanced stability and reduced environmental risks by minimizing water content and preventing seepage compared to conventional tailings management. This method significantly decreases the likelihood of tailings dam failures and supports sustainable mining practices through improved site reclamation and water conservation.
Unsaturated Tailings Storage
Unsaturated tailings storage in dry stack tailings systems significantly reduces environmental risks by minimizing water content, enhancing stability, and preventing acid mine drainage compared to conventional tailings management methods. This approach improves site water balance, lowers the potential for catastrophic dam failures, and supports more sustainable mine closure practices.
Tailings management vs Dry stack tailings Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com