Tailings storage involves depositing mining waste in large containment areas that minimize environmental impact and prevent contamination. Paste backfill, on the other hand, repurposes tailings mixed with binders as a filling material within mined-out voids, enhancing underground stability and reducing surface disposal needs. Both methods aim to manage tailings sustainably but differ in application, environmental benefits, and operational integration.
Table of Comparison
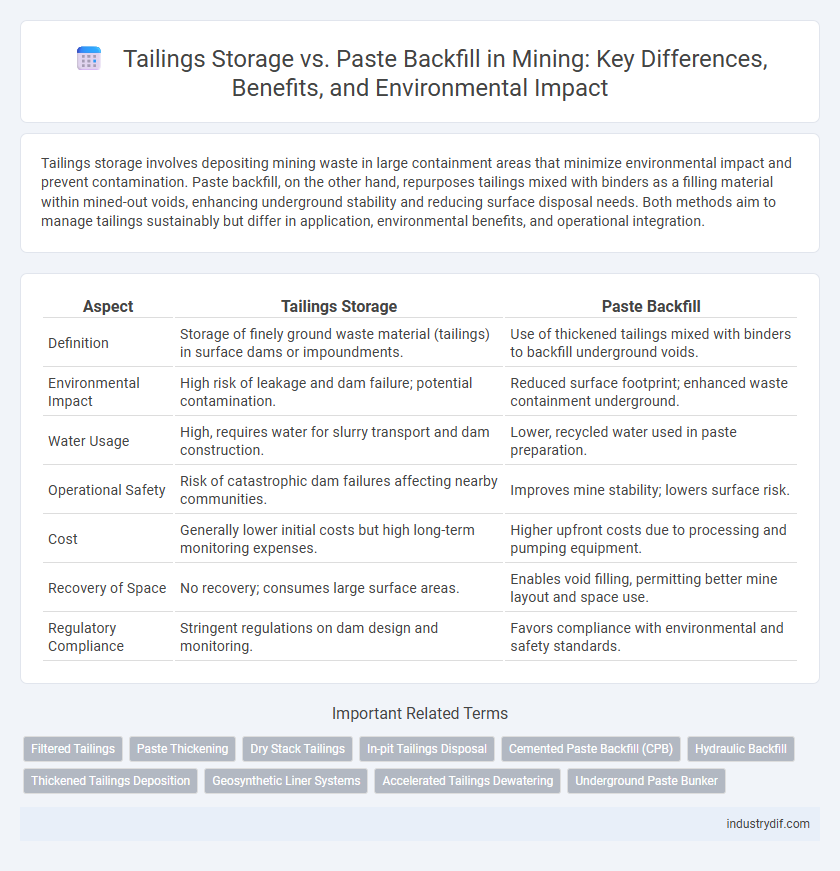
| Aspect | Tailings Storage | Paste Backfill |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Storage of finely ground waste material (tailings) in surface dams or impoundments. | Use of thickened tailings mixed with binders to backfill underground voids. |
| Environmental Impact | High risk of leakage and dam failure; potential contamination. | Reduced surface footprint; enhanced waste containment underground. |
| Water Usage | High, requires water for slurry transport and dam construction. | Lower, recycled water used in paste preparation. |
| Operational Safety | Risk of catastrophic dam failures affecting nearby communities. | Improves mine stability; lowers surface risk. |
| Cost | Generally lower initial costs but high long-term monitoring expenses. | Higher upfront costs due to processing and pumping equipment. |
| Recovery of Space | No recovery; consumes large surface areas. | Enables void filling, permitting better mine layout and space use. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Stringent regulations on dam design and monitoring. | Favors compliance with environmental and safety standards. |
Introduction to Tailings Storage and Paste Backfill
Tailings storage involves the containment of mining byproducts in engineered facilities designed to minimize environmental impact and ensure structural stability. Paste backfill is a method that recycles tailings by mixing them with binders to create a thick, flowable material used to fill mined-out voids underground, enhancing ground support and reducing surface storage needs. Both techniques address tailings management but differ in application, environmental footprint, and operational integration within mining projects.
Definitions: Tailings Storage Explained
Tailings storage refers to the containment of mining byproducts, primarily consisting of finely ground rock and process water, in engineered facilities called tailings dams or impoundments. These structures are designed to safely store and isolate tailings to prevent environmental contamination and ensure stability throughout the mine's lifecycle. Proper tailings management is critical for minimizing risks such as seepage, dam failure, and long-term environmental impacts.
Understanding Paste Backfill Technology
Paste backfill technology involves mixing mining tailings with binders like cement to create a thick, stable paste used to fill underground voids. This method improves mine stability by reducing surface tailings storage requirements and mitigating environmental risks associated with tailings dams. Compared to traditional tailings storage facilities, paste backfill enhances resource recovery and supports safer, more sustainable mining operations.
Key Differences Between Tailings Storage and Paste Backfill
Tailings storage involves the confinement of finely ground mining waste in large surface impoundments, posing risks such as dam failures and environmental contamination. Paste backfill, on the other hand, recycles tailings by mixing them with binders to create a thick, stable material used to fill underground voids, enhancing mine stability and reducing surface disposal. Key differences include environmental impact, safety considerations, water usage, and the potential for reducing the mine's surface footprint through underground applications.
Environmental Impacts of Tailings Storage
Tailings storage facilities pose significant environmental risks, including potential contamination of local water sources through seepage and leaching of heavy metals and toxic chemicals. These structures often occupy large land areas, leading to habitat destruction and soil erosion, while breaches or failures can cause catastrophic ecological damage. Compared to paste backfill, tailings storage generally results in higher potential for environmental pollution and increased challenges in long-term waste management.
Environmental Benefits of Paste Backfill
Paste backfill significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing tailings surface storage and associated risks such as dam failures and groundwater contamination. Its ability to recycle mining residues back into voids limits surface footprint, decreasing dust generation and acid mine drainage potential. This sustainable waste management approach enhances site reclamation and lowers long-term environmental liabilities.
Economic Considerations in Selecting Storage Methods
Tailings storage facilities (TSFs) often involve lower initial capital costs compared to paste backfill systems, but long-term economic risks such as environmental liabilities and regulatory compliance can increase total expenditure. Paste backfill, while more capital intensive and operationally complex, provides economic benefits by allowing underground voids to be filled, reducing ore dilution and increasing resource recovery. Evaluating the trade-offs between upfront costs, operational efficiency, environmental impact, and regulatory requirements is essential for selecting the most cost-effective tailings management solution.
Safety and Risk Management in Tailings and Backfill
Tailings storage facilities pose significant risks including dam failure and environmental contamination, necessitating rigorous monitoring and engineering controls to ensure stability and minimize hazards. Paste backfill, composed of tailings mixed with binders, enhances underground mine safety by reducing surface storage requirements and improving ground support, which lowers the risk of collapses. Effective risk management integrates real-time geotechnical data and adherence to regulatory standards to mitigate safety issues associated with both tailings storage and paste backfill systems.
Regulatory Compliance for Tailings and Backfill Solutions
Tailings storage facilities must adhere to stringent regulatory frameworks, such as the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) standards and local environmental protection laws, to mitigate risks of environmental contamination and structural failure. Paste backfill solutions offer enhanced regulatory compliance by reducing tailings volume, improving underground stability, and minimizing surface storage footprints, thus aligning with sustainable mining practices and reclamation requirements. Implementing paste backfill can facilitate adherence to water discharge limits and reduce the potential for tailings dam breaches under increasingly strict government mandates.
Future Trends in Mine Waste Management
Future trends in mine waste management emphasize the transition from conventional tailings storage facilities to paste backfill techniques due to enhanced environmental safety and improved ground stability. Advances in rheology and binder technology enable paste backfill to reduce water usage and minimize the footprint of tailings deposits, addressing regulatory pressures and community concerns. Integration of smart monitoring systems and real-time data analytics further optimizes paste backfill performance, promoting sustainable mining operations.
Related Important Terms
Filtered Tailings
Filtered tailings significantly reduce water content compared to conventional tailings, enhancing storage stability and minimizing environmental risks in tailings storage facilities (TSFs). Paste backfill uses filtered tailings mixed with binders to fill underground voids, improving ground support and reducing surface disposal volumes, which optimizes resource recovery and tailings management efficiency.
Paste Thickening
Paste thickening enhances tailings management by significantly reducing water content, producing a dense, pumpable paste ideal for backfilling underground voids in mining operations. This method improves ground stability, minimizes surface storage footprint, and promotes sustainable water recycling compared to conventional tailings storage facilities.
Dry Stack Tailings
Dry stack tailings offer enhanced environmental safety by reducing water use and minimizing seepage risks compared to paste backfill, facilitating more stable and space-efficient storage solutions. This method enhances mine closure processes and enables better tailings management in arid regions where water scarcity is critical.
In-pit Tailings Disposal
In-pit tailings disposal offers a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable solution by backfilling mined-out pits with tailings, reducing surface storage requirements and minimizing landscape disturbance. Compared to conventional paste backfill methods, it enhances geotechnical stability and groundwater isolation by utilizing the natural pit geometry, thereby lowering the risk of tailings dam failures and seepage.
Cemented Paste Backfill (CPB)
Cemented Paste Backfill (CPB) offers superior ground support and environmental benefits compared to traditional tailings storage by enhancing mine stability and reducing surface tailings footprint. Utilizing CPB integrates mine waste with cementitious binders, effectively minimizing acid rock drainage risks and optimizing resource recovery.
Hydraulic Backfill
Hydraulic backfill in mining uses a slurry mixture of tailings and water to fill underground voids, enhancing ground support and reducing surface tailings storage footprint. Compared to paste backfill, hydraulic backfill offers lower viscosity for easier pumping but generally provides less strength and consolidation.
Thickened Tailings Deposition
Thickened tailings deposition in tailings storage facilities reduces water content and increases density, improving stability and minimizing environmental risks compared to conventional tailings storage methods. Paste backfill offers a method to reuse thickened tailings underground, enhancing mine backfill strength and reducing surface disposal footprint.
Geosynthetic Liner Systems
Geosynthetic liner systems in tailings storage facilities provide essential impermeable barriers to prevent environmental contamination, enhancing containment of heavy metals and acidic drainage. In paste backfill applications, these liners support structural stability by minimizing seepage and reinforcing backfill integrity, reducing risks of ground subsidence and ensuring safer mine void management.
Accelerated Tailings Dewatering
Accelerated tailings dewatering enhances solid-liquid separation efficiency, reducing moisture content and allowing safer, more stable tailings storage facility operation compared to conventional tailings disposal. Paste backfill utilizes dewatered tailings blended with binders to fill underground voids, improving ground support and minimizing surface storage risks while optimizing waste material reuse.
Underground Paste Bunker
Underground paste bunkers provide a reliable storage solution for paste backfill, ensuring consistent delivery for underground mining operations and reducing environmental risks associated with tailings storage facilities. The compact nature of paste backfill minimizes surface footprint and enhances mine stability compared to conventional tailings storage methods.
Tailings Storage vs Paste Backfill Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com