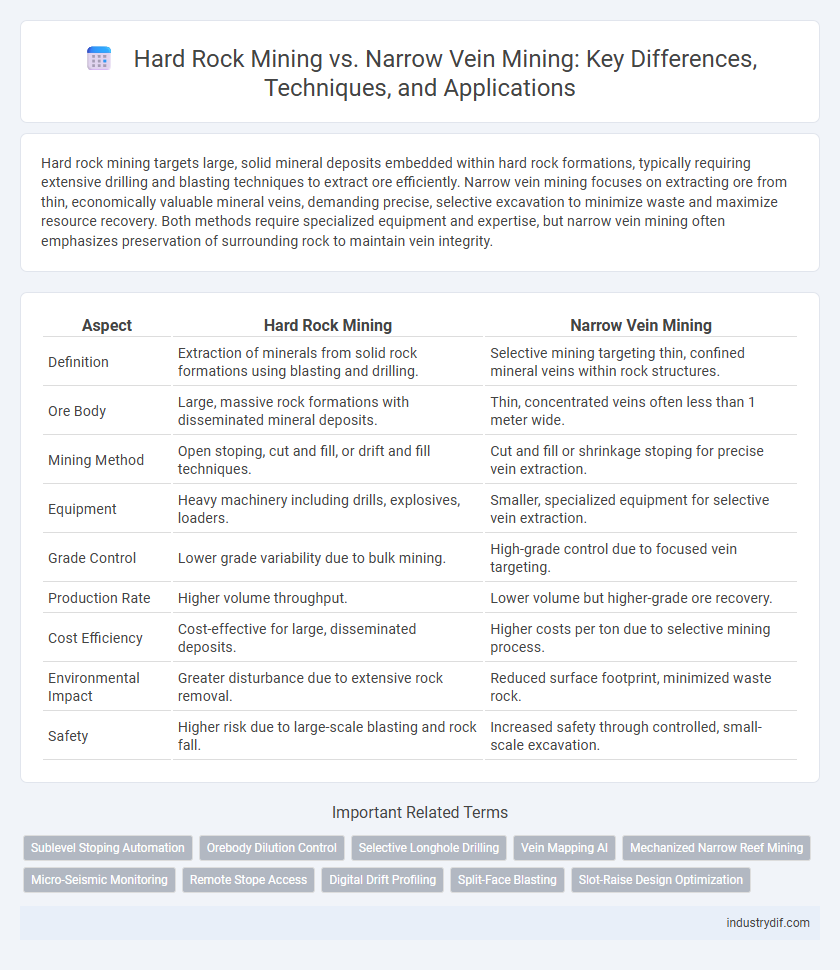
Hard rock mining targets large, solid mineral deposits embedded within hard rock formations, typically requiring extensive drilling and blasting techniques to extract ore efficiently. Narrow vein mining focuses on extracting ore from thin, economically valuable mineral veins, demanding precise, selective excavation to minimize waste and maximize resource recovery. Both methods require specialized equipment and expertise, but narrow vein mining often emphasizes preservation of surrounding rock to maintain vein integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hard Rock Mining | Narrow Vein Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extraction of minerals from solid rock formations using blasting and drilling. | Selective mining targeting thin, confined mineral veins within rock structures. |
| Ore Body | Large, massive rock formations with disseminated mineral deposits. | Thin, concentrated veins often less than 1 meter wide. |
| Mining Method | Open stoping, cut and fill, or drift and fill techniques. | Cut and fill or shrinkage stoping for precise vein extraction. |
| Equipment | Heavy machinery including drills, explosives, loaders. | Smaller, specialized equipment for selective vein extraction. |
| Grade Control | Lower grade variability due to bulk mining. | High-grade control due to focused vein targeting. |
| Production Rate | Higher volume throughput. | Lower volume but higher-grade ore recovery. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large, disseminated deposits. | Higher costs per ton due to selective mining process. |
| Environmental Impact | Greater disturbance due to extensive rock removal. | Reduced surface footprint, minimized waste rock. |
| Safety | Higher risk due to large-scale blasting and rock fall. | Increased safety through controlled, small-scale excavation. |
Overview of Hard Rock Mining
Hard rock mining involves extracting minerals from solid rock formations by drilling, blasting, and hauling ore from underground tunnels or open pits. This method targets valuable metals such as gold, copper, and iron embedded in hard, consolidated rock masses often found at significant depths. Advanced technologies like mechanized drilling, explosives, and ore processing optimize recovery rates and enhance operational efficiency in hard rock mining.
Definition and Characteristics of Narrow Vein Mining
Narrow vein mining is a specialized extraction method targeting mineral deposits with widths typically less than 1.5 meters, characterized by high-grade ore confined within thin, irregular veins. This technique requires precise drilling and blasting to minimize dilution and maximize ore recovery, often involving cut-and-fill or shrinkage stoping methods. It contrasts with hard rock mining, which generally involves more extensive excavation of broader ore bodies, emphasizing efficiency over precision.
Geological Formations: Hard Rock vs Narrow Vein
Hard rock mining targets large, consolidated geological formations rich in metals such as gold, copper, and iron, often found in igneous or metamorphic rock masses. Narrow vein mining focuses on extracting minerals from thin, discontinuous ore bodies embedded within host rocks, commonly requiring precise mapping and selective excavation to minimize waste. These contrasting geological settings dictate mining techniques, equipment selection, and operational efficiency in mineral extraction.
Equipment and Technology Used
Hard rock mining utilizes heavy-duty equipment such as drills, blasting tools, and large-scale loaders designed to extract ore from solid rock formations, often employing advanced technologies like remote-controlled machinery and geospatial mapping for precision. Narrow vein mining requires specialized, compact equipment including selective drills, micro-blast methods, and narrow-frame loaders to efficiently access thin mineral deposits with minimal waste. Both methods leverage modern automation and real-time data analytics to maximize safety, productivity, and resource recovery in challenging underground environments.
Extraction Methods Compared
Hard rock mining involves extracting ore from solid rock formations using drilling, blasting, and hauling techniques, which enables access to large, low-grade deposits. Narrow vein mining targets thin, high-grade mineral veins through precise methods such as cut-and-fill or shrinkage stoping, optimizing ore recovery while minimizing dilution. Extraction efficiency in hard rock mining hinges on large-scale operations, whereas narrow vein mining prioritizes selective extraction to preserve ore quality.
Safety Considerations in Both Mining Types
Hard rock mining involves extracting ore from solid rock masses, requiring extensive drilling and blasting, which elevates risks related to rock falls and seismic events, necessitating rigorous ground control measures. Narrow vein mining targets thin ore bodies with precise excavation techniques, presenting challenges in ventilation and exposure to confined spaces, demanding strict monitoring of air quality and miner safety protocols. Both methods require comprehensive risk assessments and adherence to safety regulations to mitigate hazards inherent in underground mining environments.
Economic Efficiency and Cost Analysis
Hard rock mining involves extracting large volumes of ore from massive rock formations, generally yielding higher upfront operational costs but benefiting from economies of scale and greater overall output. Narrow vein mining targets thin, high-grade mineral deposits, leading to increased precision and lower waste but often incurring higher per-ton extraction and processing costs. Economic efficiency in mining projects depends on balancing ore grade, volume, and extraction complexity, with narrow vein mining favored for premium mineral concentrations and hard rock mining preferred for bulk commodity deposits.
Environmental Impacts and Management
Hard rock mining generates significant environmental impacts including habitat destruction, groundwater contamination, and extensive waste rock production, necessitating robust tailings management and reclamation strategies. Narrow vein mining minimizes surface disturbance by targeting specific ore bodies with precision, reducing over-excavation and preserving adjacent ecosystems, but requires advanced ventilation and dust control systems to manage underground environmental health. Effective environmental management in both methods involves strict monitoring of water quality, implementation of erosion controls, and adherence to regulatory frameworks to mitigate long-term ecological damage.
Workforce Skills and Training Requirements
Hard rock mining demands a workforce skilled in operating heavy machinery, rock drilling, and blasting techniques, requiring comprehensive technical training and safety certification. Narrow vein mining emphasizes precision and expertise in selective extraction methods, necessitating specialized training in careful rock handling and detailed geological assessment. Both mining types require continuous professional development to adapt to evolving technologies and maintain operational efficiency.
Future Trends in Hard Rock and Narrow Vein Mining
Future trends in hard rock mining emphasize automation and advanced robotics to enhance safety and efficiency in extracting valuable minerals from complex ore bodies. Narrow vein mining is also evolving with precision drilling technologies and real-time data analytics, allowing miners to target high-grade mineral veins with minimal environmental impact. Integration of artificial intelligence and sustainable practices promises to optimize resource recovery while reducing operational costs in both mining methods.
Related Important Terms
Sublevel Stoping Automation
Sublevel stoping automation in hard rock mining enhances safety and productivity by utilizing remote-controlled drilling and blasting equipment, while narrow vein mining benefits from precision automation tools tailored for accessing thin, irregular ore bodies with minimal dilution. Advanced sensor integration and real-time data analytics optimize ore extraction in both methods, reducing operational costs and improving resource recovery rates.
Orebody Dilution Control
Hard rock mining uses broad ore extraction techniques that often lead to higher orebody dilution due to the inclusion of surrounding waste rock. Narrow vein mining prioritizes precision and selective extraction, significantly reducing orebody dilution and maximizing ore grade recovery.
Selective Longhole Drilling
Selective longhole drilling in hard rock mining enables precise extraction of ore by targeting high-grade zones within large, disseminated deposits, maximizing resource recovery and minimizing dilution. In comparison, narrow vein mining employs more selective longhole drilling techniques adapted to confined, vertical veins, prioritizing ore grade control and structural stability in restricted spaces.
Vein Mapping AI
Vein Mapping AI enhances precision in narrow vein mining by accurately identifying mineral-rich zones within complex hard rock formations, reducing waste and operational costs. This technology leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze geological data, optimizing extraction strategies and increasing overall yield in both hard rock and narrow vein mining operations.
Mechanized Narrow Reef Mining
Mechanized Narrow Reef Mining in hard rock mining offers precise extraction of narrow veins, minimizing ore dilution and maximizing recovery compared to traditional broad excavation methods. This technique employs specialized equipment designed to navigate tight reef structures, enhancing operational efficiency and safety while reducing material waste.
Micro-Seismic Monitoring
Micro-seismic monitoring in hard rock mining enables real-time detection of fractures and stress changes within large ore bodies, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. In narrow vein mining, micro-seismic data is crucial for mapping subtle seismic events in confined spaces to prevent collapses and optimize extraction in complex vein structures.
Remote Stope Access
Remote stope access in hard rock mining enables efficient extraction in large, open stopes with high mechanization, while narrow vein mining demands precise, manual or semi-automated access techniques due to limited stope dimensions and complex geology. Advanced remote access technologies like automated drilling and remote-controlled loaders optimize safety and productivity in both mining methods, but challenges in narrow vein operations require tailored solutions for confined space maneuverability.
Digital Drift Profiling
Digital Drift Profiling enhances precision in both hard rock mining and narrow vein mining by enabling detailed, real-time subsurface mapping of ore veins and geological structures. This technology optimizes excavation strategies, reduces ore loss, and improves safety by providing accurate, continuous data streams that support targeted extraction in complex underground environments.
Split-Face Blasting
Split-face blasting in hard rock mining enables efficient fragmentation along predetermined planes, optimizing ore recovery and reducing dilution from surrounding waste rock. In contrast, narrow vein mining demands precise split-face blasting techniques to minimize wall damage and preserve vein integrity, ensuring maximum extraction of high-grade ore within tight geological structures.
Slot-Raise Design Optimization
Slot-raise design optimization in hard rock mining enhances ventilation efficiency and ore extraction by creating precise vertical openings that connect the orebody to access drifts, minimizing dilution and ground control issues. In narrow vein mining, optimized slot-raise designs focus on maintaining vein integrity and reducing waste by tailoring raise dimensions to the vein's geometry, improving safety and productivity in confined spaces.
Hard Rock Mining vs Narrow Vein Mining Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com