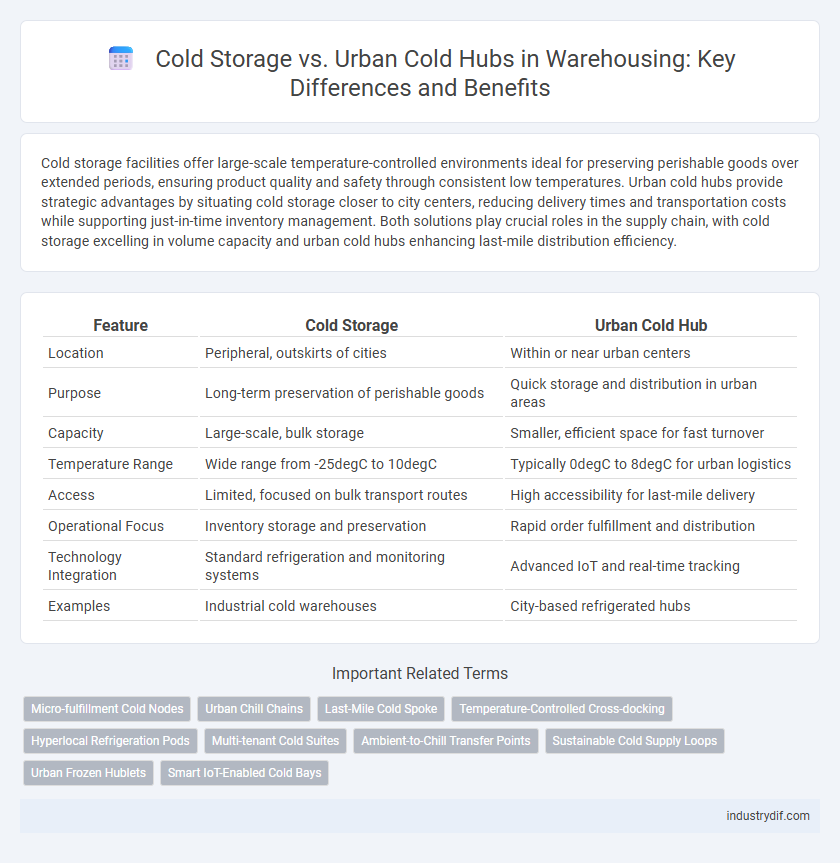
Cold storage facilities offer large-scale temperature-controlled environments ideal for preserving perishable goods over extended periods, ensuring product quality and safety through consistent low temperatures. Urban cold hubs provide strategic advantages by situating cold storage closer to city centers, reducing delivery times and transportation costs while supporting just-in-time inventory management. Both solutions play crucial roles in the supply chain, with cold storage excelling in volume capacity and urban cold hubs enhancing last-mile distribution efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cold Storage | Urban Cold Hub |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Peripheral, outskirts of cities | Within or near urban centers |
| Purpose | Long-term preservation of perishable goods | Quick storage and distribution in urban areas |
| Capacity | Large-scale, bulk storage | Smaller, efficient space for fast turnover |
| Temperature Range | Wide range from -25degC to 10degC | Typically 0degC to 8degC for urban logistics |
| Access | Limited, focused on bulk transport routes | High accessibility for last-mile delivery |
| Operational Focus | Inventory storage and preservation | Rapid order fulfillment and distribution |
| Technology Integration | Standard refrigeration and monitoring systems | Advanced IoT and real-time tracking |
| Examples | Industrial cold warehouses | City-based refrigerated hubs |
Introduction to Cold Storage and Urban Cold Hubs
Cold storage facilities are specialized warehouses designed to preserve perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, dairy, and pharmaceuticals at controlled low temperatures, extending shelf life and reducing spoilage. Urban cold hubs operate as strategically located mini cold storage units within cities, enabling efficient last-mile distribution and minimizing transit time for fresh produce. Both innovations address supply chain challenges by maintaining quality from farm to consumer while optimizing storage capacity and reducing wastage.
Defining Cold Storage Facilities
Cold storage facilities are specialized warehouses designed to preserve perishable goods such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals by maintaining controlled low temperatures. Urban cold hubs are compact, strategically located cold storage units within city centers that reduce last-mile delivery time and enhance supply chain efficiency. While traditional cold storage focuses on large-scale, bulk storage, urban cold hubs emphasize proximity to consumers and faster distribution.
Understanding Urban Cold Hubs
Urban Cold Hubs are strategically located cold storage facilities designed to minimize the distance between perishable goods and urban consumers, reducing transit time and spoilage risks. These hubs leverage advanced refrigeration technology and real-time temperature monitoring to maintain optimal conditions for fruits, vegetables, dairy, and pharmaceuticals. Unlike traditional cold storage warehouses, Urban Cold Hubs support last-mile delivery efficiency, lower carbon footprints, and enhanced supply chain responsiveness in densely populated areas.
Key Differences: Cold Storage vs Urban Cold Hub
Cold storage facilities are large-scale warehouses designed for long-term preservation of perishable goods at consistently low temperatures, typically located on the outskirts of cities to accommodate bulk storage and transportation logistics. Urban cold hubs, by contrast, offer smaller, strategically placed cold storage solutions within city limits, emphasizing rapid access and last-mile distribution efficiency for fresh produce and temperature-sensitive products. The key differences lie in their scale, proximity to urban markets, and operational focus--cold storage prioritizes volume and duration, while urban cold hubs optimize speed and accessibility.
Temperature Control and Monitoring Systems
Cold storage facilities maintain stable low temperatures using advanced refrigeration units and insulated structures to prevent spoilage of perishable goods. Urban cold hubs integrate IoT-enabled temperature control and real-time monitoring systems, ensuring precise climate regulation with immediate alerts for deviations. These systems enhance inventory safety by minimizing temperature fluctuations and optimizing energy efficiency in densely populated areas.
Location and Accessibility Factors
Cold storage facilities are typically situated on the outskirts of cities where land is more affordable and space is ample for large-scale refrigeration units and inventory management. Urban cold hubs, however, are strategically located within city centers to ensure faster access to retail markets and reduce last-mile delivery times, enhancing freshness and reducing transportation costs. The accessibility of urban cold hubs supports just-in-time inventory systems and minimizes logistical inefficiencies common in traditional cold storage warehouses.
Storage Capacity and Scalability
Cold storage facilities typically offer larger storage capacities suited for bulk inventory, ensuring consistent temperature control for perishable goods. Urban cold hubs, while smaller in scale, provide enhanced scalability by allowing flexible storage adjustments closer to high-demand urban centers. This proximity reduces transit times and supports just-in-time inventory models, making urban cold hubs ideal for dynamic supply chains.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Cold storage facilities traditionally consume high energy due to extensive refrigeration needs, resulting in significant carbon footprints. Urban cold hubs leverage strategic city locations with advanced insulation and renewable energy integration to enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Implementing smart climate control systems in urban cold hubs further optimizes sustainability by minimizing energy waste and supporting cold chain integrity.
Cost Implications and ROI Comparison
Cold storage facilities typically entail higher operational costs due to large energy consumption and extensive space requirements, impacting overall cost-efficiency. Urban cold hubs leverage proximity to demand centers, reducing last-mile delivery expenses and increasing inventory turnover rates, which enhances return on investment (ROI). Evaluating ROI involves balancing upfront infrastructure investment with ongoing savings in logistics and energy, where urban cold hubs often demonstrate superior financial performance in dense metropolitan areas.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Cold storage facilities are evolving with the rise of urban cold hubs, which offer strategic proximity to high-demand markets and reduce last-mile delivery times. Industry trends indicate a shift towards automated, energy-efficient cold storage solutions equipped with IoT sensors for real-time temperature monitoring and inventory management. The future outlook highlights increased investment in urban cold hubs driven by expanding e-commerce in perishable goods and the growing need for sustainable logistics in the cold chain sector.
Related Important Terms
Micro-fulfillment Cold Nodes
Micro-fulfillment cold nodes in urban cold hubs offer enhanced proximity to consumers compared to traditional cold storage, enabling faster last-mile delivery and reduced spoilage for perishable goods. These decentralized facilities leverage advanced refrigeration technology and real-time inventory management to optimize supply chain efficiency in densely populated areas.
Urban Chill Chains
Urban chill chains enhance cold storage solutions by integrating strategically located urban cold hubs that reduce transportation time and maintain product freshness for perishable goods. These systems leverage advanced temperature control technologies and real-time monitoring to ensure optimal cold chain integrity in densely populated areas.
Last-Mile Cold Spoke
Cold storage facilities are crucial for preserving perishable goods, but urban cold hubs enhance efficiency by positioning last-mile cold spoke centers closer to end consumers, reducing transit times and maintaining optimal temperature control. This strategic placement minimizes spoilage risks and lowers delivery costs in densely populated areas, offering a competitive advantage for cold chain logistics.
Temperature-Controlled Cross-docking
Temperature-controlled cross-docking in cold storage facilities ensures precise preservation of perishable goods by maintaining consistent low temperatures during transfer, minimizing spoilage and handling time. Urban cold hubs enhance this process by strategically situating temperature-controlled environments closer to end consumers, reducing transit times and optimizing last-mile delivery efficiency.
Hyperlocal Refrigeration Pods
Hyperlocal refrigeration pods in urban cold hubs offer scalable, energy-efficient cold storage solutions designed to meet the fast-paced demands of city-based businesses by enabling near-instant access to perishable goods. These pods reduce transit time and spoilage compared to traditional cold storage warehouses, enhancing supply chain responsiveness and minimizing carbon footprint through localized inventory management.
Multi-tenant Cold Suites
Multi-tenant cold suites in cold storage facilities offer scalable temperature-controlled environments designed for diverse businesses, optimizing space utilization and reducing operational costs. Urban cold hubs integrate multi-tenant cold suites within city centers, enhancing last-mile delivery efficiency and improving supply chain responsiveness for perishable goods.
Ambient-to-Chill Transfer Points
Ambient-to-chill transfer points in warehousing play a critical role in cold storage by maintaining product integrity during temperature transitions, while urban cold hubs optimize these transfers with shorter transit times and proximity to end consumers, reducing spoilage and enhancing freshness. Cold storage facilities focus on large-scale, stable temperature environments, whereas urban cold hubs specialize in rapid ambient-to-chill conversions for last-mile distribution efficiency.
Sustainable Cold Supply Loops
Cold storage facilities optimize energy use through advanced insulation and renewable energy integration, minimizing carbon footprints in the supply chain. Urban cold hubs reduce last-mile transportation emissions by decentralizing storage closer to consumers, enhancing sustainable cold supply loops with lower waste and improved freshness retention.
Urban Frozen Hublets
Urban frozen hublets offer localized cold storage solutions designed to maintain optimal sub-zero temperatures for perishable goods within city environments, enhancing supply chain efficiency by reducing transit times and spoilage compared to traditional cold storage facilities located in remote areas. These compact, strategically placed hublets integrate advanced refrigeration technology and real-time monitoring systems, ensuring consistent frozen conditions that support rapid distribution to retail and foodservice sectors in densely populated urban centers.
Smart IoT-Enabled Cold Bays
Smart IoT-enabled cold bays optimize temperature and humidity control in cold storage, enhancing energy efficiency and product quality through real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Urban cold hubs leverage these advanced technologies to provide scalable, last-mile cold storage solutions that reduce food spoilage and logistics costs in densely populated areas.
Cold Storage vs Urban Cold Hub Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com