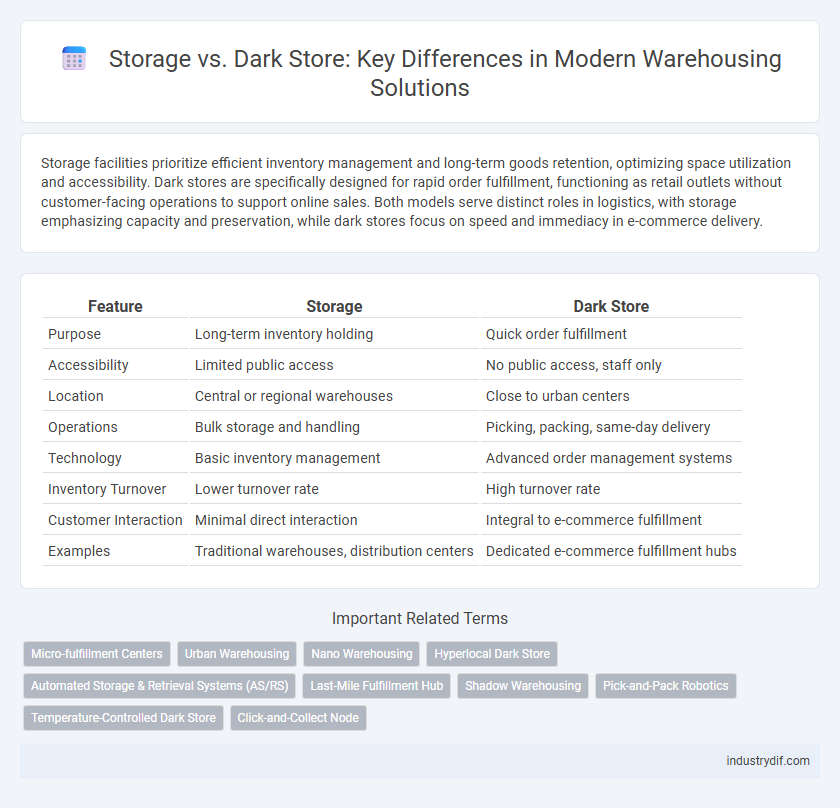
Storage facilities prioritize efficient inventory management and long-term goods retention, optimizing space utilization and accessibility. Dark stores are specifically designed for rapid order fulfillment, functioning as retail outlets without customer-facing operations to support online sales. Both models serve distinct roles in logistics, with storage emphasizing capacity and preservation, while dark stores focus on speed and immediacy in e-commerce delivery.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Storage | Dark Store |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Long-term inventory holding | Quick order fulfillment |
| Accessibility | Limited public access | No public access, staff only |
| Location | Central or regional warehouses | Close to urban centers |
| Operations | Bulk storage and handling | Picking, packing, same-day delivery |
| Technology | Basic inventory management | Advanced order management systems |
| Inventory Turnover | Lower turnover rate | High turnover rate |
| Customer Interaction | Minimal direct interaction | Integral to e-commerce fulfillment |
| Examples | Traditional warehouses, distribution centers | Dedicated e-commerce fulfillment hubs |
Introduction to Storage and Dark Store Concepts
Storage in warehousing refers to the organized placement and preservation of goods within a facility, enabling efficient inventory management and order fulfillment. Dark stores are specialized retail distribution centers that operate without customer-facing storefronts, designed exclusively for online order processing and rapid last-mile delivery. Understanding the distinction between traditional storage and dark store models is crucial for optimizing supply chain logistics and meeting evolving e-commerce demands.
Key Differences Between Traditional Storage and Dark Stores
Traditional storage facilities primarily function as inventory hubs supporting wholesale distribution, emphasizing long-term stock management and bulk item organization. Dark stores are retail-optimized warehouses designed for rapid order fulfillment, integrating advanced technology and proximity to urban centers for same-day delivery. The key differences lie in operational purpose, layout efficiency, and customer accessibility, with dark stores focusing on speed and direct-to-consumer service while traditional storage prioritizes volume and supply chain continuity.
Inventory Management: Storage Facilities vs. Dark Stores
Storage facilities primarily manage inventory through traditional warehousing techniques, focusing on bulk stock organization and long-term holding to support supply chain stability. Dark stores operate as localized fulfillment centers with real-time inventory tracking optimized for rapid order processing and same-day delivery. Efficient inventory management in dark stores leverages advanced software for dynamic stock allocation, minimizing delays and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Order Fulfillment Efficiency: A Comparative Analysis
Storage facilities optimize space for bulk inventory, enhancing long-term stock management, while dark stores prioritize rapid order picking and dispatch, significantly improving last-mile delivery speed. Dark stores utilize real-time inventory tracking and zone picking to streamline order fulfillment, reducing errors and processing time compared to traditional warehouses. Integrating dark store strategies within warehousing improves efficiency metrics such as order accuracy rate and fulfillment cycle time, directly impacting customer satisfaction and operational cost reduction.
Technological Integration in Storage and Dark Stores
Storage facilities increasingly leverage automated inventory management systems, IoT sensors, and AI-driven analytics to optimize space utilization and enhance real-time stock tracking. Dark stores, designed explicitly for rapid e-commerce fulfillment, integrate cutting-edge robotics, advanced warehouse management systems (WMS), and seamless last-mile delivery coordination software to accelerate order processing and reduce errors. Both models benefit from cloud computing platforms that enable scalable data management and remote monitoring, improving operational efficiency and responsiveness.
Cost Implications of Storage versus Dark Store Models
Storage facilities typically incur lower operational costs due to standardized inventory management and bulk handling efficiencies, whereas dark stores require higher expenses for customized layouts and rapid fulfillment technologies tailored for e-commerce demand. Dark stores often generate increased labor costs and specialized infrastructure investments, driving up overall expenditure compared to traditional warehousing. Evaluating cost implications necessitates balancing the lower fixed costs of storage against the higher variable costs but faster turnaround capabilities of dark store models.
Scalability and Flexibility: Which Model Wins?
Storage facilities excel in scalability by accommodating diverse inventory volumes across multiple product categories, offering flexible spatial arrangements that adapt to fluctuating demand. Dark stores provide hyper-efficient, last-mile fulfillment tailored for e-commerce, optimizing order picking and delivery speed but with limited scalability due to their specialized layout and confined geographic coverage. For businesses prioritizing expansive inventory management and flexible handling, traditional warehousing stands out, while dark stores dominate in rapid, localized fulfillment for specific markets.
Impact on Supply Chain and Distribution Networks
Storage facilities serve as traditional warehouses holding inventory for bulk supply, optimizing space and minimizing stockouts through centralized management. Dark stores function as localized fulfillment centers designed exclusively for online order processing, accelerating last-mile delivery and enhancing customer satisfaction by reducing delivery times. Integrating dark stores into distribution networks reshapes supply chain dynamics by enabling faster order fulfillment while necessitating more sophisticated inventory tracking and demand forecasting systems.
Customer Experience: Dark Store vs. Traditional Storage
Dark stores enhance customer experience by enabling faster order fulfillment and reducing delivery times compared to traditional storage warehouses that prioritize bulk inventory management. These strategically located dark stores facilitate real-time inventory updates and seamless last-mile delivery, improving accuracy and convenience for online shoppers. Traditional storage facilities, while optimized for large-scale stockholding, often lack the agility required for immediate consumer-oriented services, impacting the overall satisfaction of e-commerce customers.
Future Trends in Warehousing: Storage and Dark Stores
Future trends in warehousing highlight the growing importance of dark stores, which serve as localized fulfillment centers for rapid e-commerce deliveries, optimizing last-mile logistics. Traditional storage warehouses continue to evolve with advanced automation, AI-driven inventory management, and robotics to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. Integration of both dark stores and smart storage solutions is expected to maximize supply chain responsiveness and meet increasing consumer demand for fast, flexible order fulfillment.
Related Important Terms
Micro-fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers optimize urban warehousing by combining storage efficiency with rapid fulfillment, unlike traditional dark stores that primarily serve as large inventory holding locations without integrated automation. These centers leverage advanced robotics and AI-driven inventory management to enhance order accuracy and speed, addressing the last-mile delivery challenges in densely populated areas.
Urban Warehousing
Urban warehousing leverages storage facilities strategically located within city centers to enhance rapid order fulfillment and last-mile delivery efficiency. Dark stores function as urban warehouses optimized exclusively for online retail, minimizing customer foot traffic to maximize inventory management and speed in densely populated areas.
Nano Warehousing
Nano warehousing revolutionizes urban logistics by integrating compact storage units directly within city centers, contrasting with dark stores that serve solely as online order fulfillment hubs without customer access. This micro-scale approach enhances inventory proximity and delivery speed, optimizing last-mile distribution in densely populated areas.
Hyperlocal Dark Store
Hyperlocal dark stores function as specialized storage facilities optimized for rapid order fulfillment within a localized area, reducing delivery times significantly compared to traditional warehousing. These dark stores leverage real-time inventory management and strategic urban placement to support e-commerce and grocery delivery services, enhancing efficiency in the hyperlocal supply chain.
Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) enhance both traditional storage warehouses and dark stores by increasing inventory accuracy and reducing retrieval times through robotic automation. While warehouses focus on bulk inventory management, dark stores utilize AS/RS to expedite e-commerce order fulfillment with optimized space utilization and real-time inventory tracking.
Last-Mile Fulfillment Hub
Storage facilities primarily focus on inventory management and long-term product holding, whereas dark stores function as localized fulfillment hubs optimized for rapid last-mile delivery, enhancing speed and efficiency in urban areas. Dark stores leverage strategic urban locations and streamlined picking processes to reduce delivery times and meet increasing consumer demand for same-day or rapid shipping.
Shadow Warehousing
Shadow warehousing enhances traditional storage by utilizing underused retail spaces as dark stores, enabling faster fulfillment and reducing last-mile delivery costs. This strategic approach leverages real-time inventory visibility and proximity to urban customers, optimizing supply chain efficiency and boosting e-commerce performance.
Pick-and-Pack Robotics
Pick-and-pack robotics streamline efficiency in both traditional warehousing storage and dark stores by automating item retrieval and order assembly, significantly reducing labor costs and fulfillment times. These advanced robotic systems optimize space utilization and inventory management, enabling faster, more accurate order processing in high-demand e-commerce and grocery delivery environments.
Temperature-Controlled Dark Store
Temperature-controlled dark stores optimize inventory management by maintaining precise climate conditions for perishable goods, ensuring freshness and reducing spoilage compared to traditional storage facilities. These specialized dark stores support rapid order fulfillment in urban areas, enhancing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction in the grocery and pharmaceutical sectors.
Click-and-Collect Node
Dark stores operate as dedicated fulfillment centers optimized for online orders, enhancing the speed and efficiency of click-and-collect services by storing inventory close to high-demand urban areas. Traditional warehousing focuses on bulk storage and long-term inventory management, whereas dark stores emphasize rapid processing and immediate availability to support same-day pickup.
Storage vs Dark Store Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com