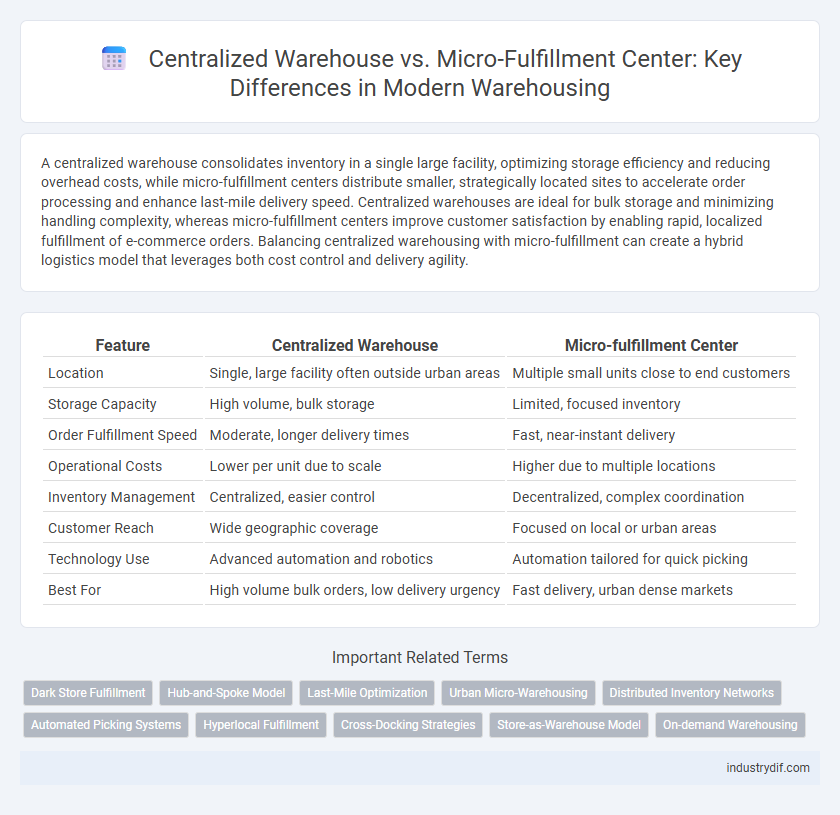
A centralized warehouse consolidates inventory in a single large facility, optimizing storage efficiency and reducing overhead costs, while micro-fulfillment centers distribute smaller, strategically located sites to accelerate order processing and enhance last-mile delivery speed. Centralized warehouses are ideal for bulk storage and minimizing handling complexity, whereas micro-fulfillment centers improve customer satisfaction by enabling rapid, localized fulfillment of e-commerce orders. Balancing centralized warehousing with micro-fulfillment can create a hybrid logistics model that leverages both cost control and delivery agility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Centralized Warehouse | Micro-fulfillment Center |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Single, large facility often outside urban areas | Multiple small units close to end customers |
| Storage Capacity | High volume, bulk storage | Limited, focused inventory |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Moderate, longer delivery times | Fast, near-instant delivery |
| Operational Costs | Lower per unit due to scale | Higher due to multiple locations |
| Inventory Management | Centralized, easier control | Decentralized, complex coordination |
| Customer Reach | Wide geographic coverage | Focused on local or urban areas |
| Technology Use | Advanced automation and robotics | Automation tailored for quick picking |
| Best For | High volume bulk orders, low delivery urgency | Fast delivery, urban dense markets |
Introduction to Centralized Warehousing and Micro-fulfillment
Centralized warehousing consolidates inventory in a single, large facility to streamline management and reduce overall storage costs, supporting bulk storage and long-term inventory. Micro-fulfillment centers operate within urban areas or retail locations, enabling faster order processing and delivery by utilizing automation and real-time inventory tracking. Both models optimize supply chains, with centralized warehouses prioritizing efficiency in stock management and micro-fulfillment centers enhancing speed and last-mile delivery.
Key Differences Between Centralized and Micro-fulfillment Centers
Centralized warehouses consolidate inventory in a single large facility, optimizing storage capacity and reducing overall inventory holding costs, whereas micro-fulfillment centers are smaller, decentralized units located closer to end customers to expedite order fulfillment and last-mile delivery. Centralized warehouses typically handle bulk shipments and longer lead times, while micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and advanced robotics to process high volumes of small, frequent orders rapidly. The strategic choice between the two depends on trade-offs in scale economies, delivery speed, and service level requirements in supply chain operations.
Benefits of Centralized Warehousing
Centralized warehousing enhances inventory control by consolidating stock in a single location, reducing redundancy and improving order accuracy. It enables significant cost savings through economies of scale in storage, labor, and transportation. Streamlined operations in centralized warehouses also facilitate better demand forecasting and faster replenishment cycles.
Advantages of Micro-fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers offer rapid order processing and reduced last-mile delivery costs by being strategically located near urban areas. Their smaller footprint allows for efficient inventory management and scalability enabling retailers to meet increasing e-commerce demand. Enhanced automation within micro-fulfillment centers improves picking accuracy and operational efficiency compared to traditional centralized warehouses.
Operational Costs: Centralized vs Micro-fulfillment
Centralized warehouses typically incur higher transportation and labor costs due to their large scale and distant locations from end consumers, while micro-fulfillment centers reduce last-mile delivery expenses by situating inventory closer to urban demand hubs. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and smaller footprints, lowering overall operational expenses related to storage and order processing. In contrast, centralized warehouses benefit from economies of scale in inventory management but face increased shipping and handling costs that impact total operational efficiency.
Impact on Delivery Speed and Customer Satisfaction
Centralized warehouses often result in longer delivery times due to the greater distance between the facility and end customers, potentially affecting customer satisfaction negatively. Micro-fulfillment centers, located closer to urban areas or retail stores, significantly reduce delivery speed by enabling faster order processing and last-mile fulfillment. This proximity directly enhances customer satisfaction by meeting increasing demands for rapid shipping and same-day delivery options.
Scalability and Flexibility in Warehousing Solutions
Centralized warehouses offer high scalability by consolidating inventory in a single location, optimizing storage capacity, and streamlining bulk handling processes. Micro-fulfillment centers enhance flexibility with their proximity to end consumers, enabling faster order processing and adaptive inventory management for fluctuating demand. Combining centralized warehousing scalability with micro-fulfillment agility supports dynamic supply chains and responsive distribution strategies.
Technology Integration in Modern Warehousing
Centralized warehouses leverage advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) and automation technologies to streamline large-scale inventory handling and optimize storage capacity. Micro-fulfillment centers integrate robotics and AI-powered order picking systems to enhance speed and accuracy in last-mile delivery within urban areas. Both models depend on IoT sensors and real-time data analytics to improve operational efficiency and inventory visibility across the supply chain.
Industry Use Cases: E-commerce, Retail, Grocery
Centralized warehouses are ideal for large-scale e-commerce and retail operations that require extensive inventory storage and bulk order fulfillment, enhancing cost efficiency through economies of scale. Micro-fulfillment centers serve grocery and fast-retail sectors by enabling rapid, localized order processing and same-day delivery, crucial for fresh produce and consumer convenience. These centers optimize last-mile logistics by integrating automation and real-time inventory management to meet high-volume demand spikes in urban markets.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Supply Chain
Centralized warehouses offer large storage capacity and streamlined inventory management, ideal for businesses with high-volume, less frequent shipments. Micro-fulfillment centers provide faster last-mile delivery and cater to urban markets with limited space, enhancing customer satisfaction through expedited order fulfillment. Selecting the right solution depends on balancing storage needs, delivery speed, and geographic distribution to optimize supply chain efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Dark Store Fulfillment
Centralized warehouses consolidate inventory in large facilities, enabling bulk storage and cost-efficient shipping but often resulting in longer delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers, especially dark stores designed solely for online order fulfillment, optimize last-mile delivery speed by positioning inventory closer to urban customers and leveraging automation for rapid order processing.
Hub-and-Spoke Model
The hub-and-spoke model leverages a centralized warehouse as the hub to store bulk inventory, while micro-fulfillment centers at the spokes enable faster last-mile delivery and higher order accuracy. This hybrid approach optimizes supply chain efficiency by balancing cost-effective centralized storage with the agility of localized inventory distribution.
Last-Mile Optimization
Centralized warehouses offer high storage capacity and inventory consolidation but often face challenges in last-mile delivery speed and cost efficiency. Micro-fulfillment centers, located near urban areas, optimize last-mile delivery by reducing transit times and enabling faster order fulfillment through automation and proximity to customers.
Urban Micro-Warehousing
Urban micro-warehousing optimizes last-mile delivery by strategically placing small-scale fulfillment centers close to dense consumer areas, reducing transit times and transportation costs compared to centralized warehouses. These micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and real-time inventory management to enhance operational efficiency and meet the growing demand for rapid e-commerce fulfillment in urban environments.
Distributed Inventory Networks
Distributed inventory networks leverage micro-fulfillment centers to reduce delivery times and increase responsiveness by positioning stock closer to end customers, contrasting with centralized warehouses that consolidate inventory for cost efficiency but incur longer transit times. Integrating multiple localized micro-fulfillment centers enables flexible inventory allocation across regions, optimizing last-mile delivery and enhancing supply chain agility.
Automated Picking Systems
Centralized warehouses utilize large-scale automated picking systems that maximize throughput efficiency by integrating robotics, conveyor belts, and advanced sorting technologies to manage high-volume inventory. Micro-fulfillment centers rely on compact automated picking solutions designed for rapid order processing and immediate last-mile delivery, optimizing space and reducing labor costs in urban environments.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Centralized warehouses optimize inventory management with large storage capacities but often face challenges in fast delivery for hyperlocal fulfillment compared to micro-fulfillment centers situated near end customers, dramatically reducing last-mile delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and strategic urban locations to enhance speed and efficiency in fulfilling local orders, meeting the growing demand for same-day delivery in densely populated areas.
Cross-Docking Strategies
Centralized warehouses consolidate inventory for bulk storage, enabling efficient cross-docking that minimizes handling and accelerates shipment through direct transfers from inbound to outbound transportation. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage localized, automated cross-docking to rapidly process smaller, high-demand orders, reducing last-mile delivery times and optimizing urban supply chains.
Store-as-Warehouse Model
The Store-as-Warehouse model leverages micro-fulfillment centers within retail locations to enhance last-mile delivery speed and reduce inventory holding costs compared to traditional centralized warehouses. By utilizing existing store space for local order fulfillment, retailers optimize inventory distribution, improve stock turnover rates, and increase customer satisfaction through faster, more flexible delivery options.
On-demand Warehousing
Centralized warehouses offer large-scale storage with high inventory capacity but often face challenges in speed and last-mile delivery efficiency, whereas micro-fulfillment centers leverage on-demand warehousing to enable rapid order processing and localized inventory management. On-demand warehousing optimizes space utilization and flexibility, allowing businesses to scale storage dynamically while reducing transportation costs and improving delivery speed in urban areas.
Centralized Warehouse vs Micro-fulfillment Center Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com