Distribution centers typically handle large volumes of inventory with extensive storage capacity, allowing for efficient bulk shipping and longer-term stock management. Urban nano-warehouses, in contrast, are smaller facilities strategically located within city limits to enable rapid last-mile delivery and minimize transportation costs. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the need for scale versus speed and proximity to the end customer in supply chain operations.
Table of Comparison
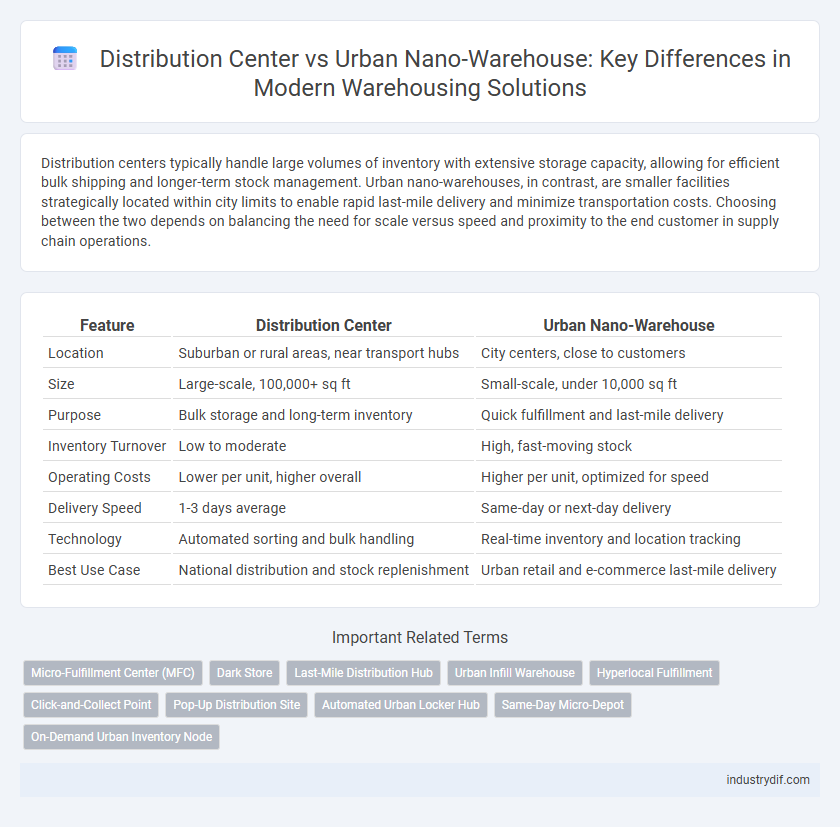
| Feature | Distribution Center | Urban Nano-Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Suburban or rural areas, near transport hubs | City centers, close to customers |
| Size | Large-scale, 100,000+ sq ft | Small-scale, under 10,000 sq ft |
| Purpose | Bulk storage and long-term inventory | Quick fulfillment and last-mile delivery |
| Inventory Turnover | Low to moderate | High, fast-moving stock |
| Operating Costs | Lower per unit, higher overall | Higher per unit, optimized for speed |
| Delivery Speed | 1-3 days average | Same-day or next-day delivery |
| Technology | Automated sorting and bulk handling | Real-time inventory and location tracking |
| Best Use Case | National distribution and stock replenishment | Urban retail and e-commerce last-mile delivery |
Introduction to Distribution Centers and Urban Nano-warehouses
Distribution centers are large-scale facilities designed to store and manage inventory for efficient bulk distribution to retail locations or customers, optimizing supply chain operations through advanced logistics and automation. Urban nano-warehouses, typically small footprint facilities located within city limits, focus on last-mile delivery by storing limited inventory close to consumers, enabling faster order fulfillment and reduced transportation costs. Both facility types play crucial roles in modern warehousing by balancing volume handling at centralized hubs and responsiveness in dense urban areas.
Core Functions: Distribution Centers vs Urban Nano-warehouses
Distribution centers primarily handle bulk storage, inventory management, and large-scale order fulfillment, optimizing supply chain efficiency across wide geographic areas. Urban nano-warehouses focus on last-mile delivery support, offering rapid access to inventory within dense city environments to meet high-demand, time-sensitive orders. These core functions differentiate distribution centers by volume and reach, while urban nano-warehouses emphasize speed and proximity in urban logistics.
Location Strategy: Suburban vs Urban Warehousing
Distribution centers are typically located in suburban areas to capitalize on larger spaces and lower land costs, enabling high-volume storage and efficient transportation links to highways. Urban nano-warehouses prioritize proximity to densely populated city centers, facilitating rapid delivery and last-mile logistics in limited spaces. The location strategy balances cost-efficiency in suburban hubs against speed and accessibility in urban micro-fulfillment facilities.
Facility Size and Storage Capabilities
Distribution centers typically span hundreds of thousands to over a million square feet, offering extensive storage capabilities suited for bulk inventory and large-scale order fulfillment. Urban nano-warehouses are significantly smaller, often under 10,000 square feet, optimized for high-density storage of fast-moving goods and last-mile delivery efficiency. The compact size of nano-warehouses limits storage capacity but enhances proximity to end consumers, reducing delivery times in urban environments.
Technology Adoption in Modern Warehousing
Distribution centers leverage advanced warehouse management systems (WMS), robotics, and automated sorting technologies to optimize large-scale inventory handling and order fulfillment. Urban nano-warehouses prioritize IoT integration, real-time inventory tracking, and AI-driven demand forecasting to enable rapid, localized delivery in dense metropolitan areas. Both warehouse types increasingly adopt automation and data analytics to enhance operational efficiency and speed in modern supply chains.
Order Fulfillment Speed and Efficiency
Distribution centers handle large-scale inventory storage and bulk order processing, enabling efficient fulfillment for wide geographic regions but often with longer delivery times. Urban nano-warehouses are compact facilities located close to end consumers, significantly reducing last-mile delivery time and increasing order fulfillment speed for small, frequent orders. Leveraging urban nano-warehouses enhances efficiency in densely populated areas by minimizing transportation costs and enabling same-day or next-day delivery options.
Cost Structures and Operational Expenses
Distribution centers typically incur higher fixed costs due to larger facility sizes, extensive inventory storage, and complex logistics infrastructure, whereas urban nano-warehouses operate with lower fixed costs by utilizing smaller spaces closer to end consumers. Operational expenses for distribution centers include staffing, utilities, and transportation costs associated with bulk shipments, while nano-warehouses emphasize last-mile delivery expenses and rapid inventory turnover, leading to reduced warehousing fees but increased delivery frequency. Cost structures in distribution centers lean towards economies of scale, contrasting with the agile, cost-effective, and customer-centric model of urban nano-warehouses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Distribution centers typically have a larger carbon footprint due to extensive transportation requirements and higher energy consumption for climate control and lighting. Urban nano-warehouses, smaller facilities located closer to end consumers, reduce last-mile delivery distances, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and decreased traffic congestion. The implementation of nano-warehouses supports sustainability by enabling efficient inventory management and promoting the use of electric delivery vehicles in dense urban areas.
Industry Use Cases: Distribution Center vs Urban Nano-warehouse
Distribution centers are designed for large-scale inventory storage and bulk order fulfillment, supporting industries like e-commerce, retail, and manufacturing with widespread delivery networks. Urban nano-warehouses cater to last-mile delivery needs in densely populated areas, ideal for industries requiring rapid order turnaround such as food delivery, pharmaceuticals, and local retail. The strategic deployment of nano-warehouses enhances speed and reduces transportation costs, complementing traditional distribution center operations.
Future Trends in Warehousing: From Large-scale to Micro-fulfillment
Distribution centers are evolving with the rise of urban nano-warehouses, signaling a significant shift towards micro-fulfillment strategies that optimize last-mile delivery. Urban nano-warehouses, typically under 5,000 square feet, leverage automation and AI to rapidly process smaller, localized orders in high-density markets, reducing delivery times and costs. This trend drives warehousing from large-scale, centralized facilities towards decentralized, tech-driven micro-hubs strategically positioned near consumers, shaping the future logistics landscape.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Fulfillment Center (MFC)
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) serve as compact, technology-driven hubs designed to accelerate order processing and delivery within dense urban areas, contrasting with traditional Distribution Centers (DCs) that operate on a larger scale with extensive storage capacity. MFCs optimize last-mile logistics through automation and proximity to consumers, significantly reducing delivery times and supporting e-commerce growth in urban nano-warehouses.
Dark Store
A distribution center typically serves as a large-scale facility for bulk storage and regional product distribution, while an urban nano-warehouse, often functioning as a dark store, operates as a smaller, strategically located fulfillment hub designed for rapid last-mile delivery in dense metropolitan areas. Dark stores optimize inventory management and order processing by being closed to the public, enabling faster e-commerce fulfillment and reduced delivery times compared to traditional retail or larger distribution centers.
Last-Mile Distribution Hub
Distribution centers handle large-scale inventory storage and bulk shipments, optimizing regional supply chains with extensive sorting and cross-docking capabilities. Urban nano-warehouses serve as compact last-mile distribution hubs, strategically located to expedite delivery times and reduce urban transportation costs in densely populated areas.
Urban Infill Warehouse
Urban infill warehouses maximize space in densely populated areas by offering smaller, strategically located facilities that reduce last-mile delivery times and transportation costs compared to traditional distribution centers. These nano-warehouses support faster inventory turnover and improved customer satisfaction by enabling retailers to respond swiftly to urban demand fluctuations.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Distribution centers are large-scale facilities designed for bulk storage and regional distribution, optimizing inventory management and transportation efficiency, while urban nano-warehouses operate as compact storage units strategically placed within city limits to enable rapid hyperlocal fulfillment and reduce last-mile delivery times. By leveraging urban nano-warehouses, retailers can enhance customer satisfaction through same-day or even hour-long delivery options in densely populated areas, meeting the increasing demand for instant gratification in e-commerce.
Click-and-Collect Point
Distribution centers serve as large-scale storage hubs designed for bulk inventory management, optimizing supply chain efficiency by facilitating high-volume order fulfillment. Urban nano-warehouses, strategically located in city centers, enhance click-and-collect points by enabling faster last-mile delivery and convenient customer pickup, significantly reducing transit times and improving urban logistics.
Pop-Up Distribution Site
Pop-up distribution sites operate as temporary urban nano-warehouses strategically placed to enhance last-mile delivery speed and reduce transportation costs in densely populated areas. Unlike traditional distribution centers with large-scale storage and inflexible locations, these agile nano-warehouses enable rapid inventory deployment and scalable order fulfillment close to end consumers.
Automated Urban Locker Hub
Automated urban locker hubs in urban nano-warehouses optimize last-mile delivery by enabling contactless, secure, and rapid parcel collection within densely populated city centers, reducing delivery time and traffic congestion compared to traditional large-scale distribution centers. These compact, technology-driven facilities integrate IoT and AI for real-time inventory management and seamless customer access, supporting efficient same-day and next-day deliveries in urban logistics.
Same-Day Micro-Depot
Same-day micro-depots, often set up within urban nano-warehouses, enable rapid last-mile delivery by storing limited inventory closer to high-demand areas, contrasting with large-scale distribution centers that focus on bulk storage and regional shipment. This proximity reduces transit times and shipping costs, optimizing urban logistics and meeting the growing consumer expectation for immediate delivery.
On-Demand Urban Inventory Node
Distribution centers serve as large-scale hubs designed for bulk storage and regional order fulfillment, while urban nano-warehouses function as compact, strategically located on-demand urban inventory nodes that enable rapid last-mile delivery and enhanced responsiveness to fluctuating consumer demands. These nano-warehouses optimize inventory proximity within dense metropolitan areas, significantly reducing delivery times and transportation costs for e-commerce and retail sectors.
Distribution Center vs Urban Nano-warehouse Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com