Zone picking divides a warehouse into specific areas where workers pick items within their assigned zones, optimizing human labor and minimizing travel time. Robotic swarm picking employs multiple coordinated robots to navigate the warehouse, efficiently retrieving items and enhancing speed and accuracy. While zone picking leverages human expertise and flexibility, robotic swarm picking offers scalability and improved efficiency through automation.
Table of Comparison
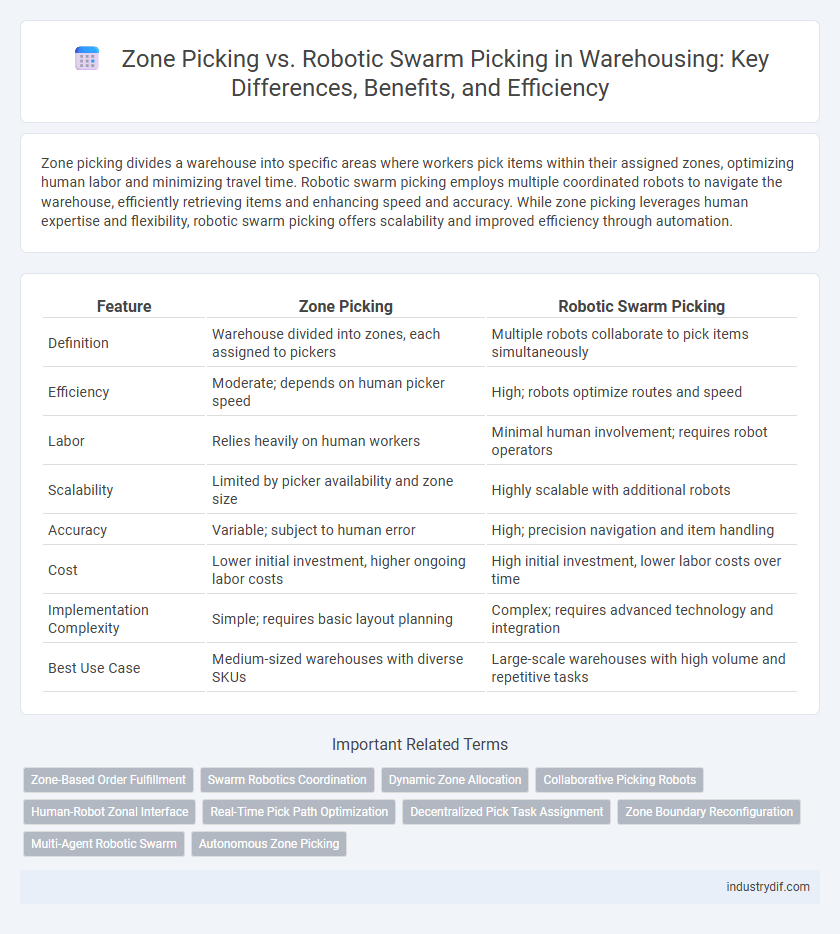
| Feature | Zone Picking | Robotic Swarm Picking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Warehouse divided into zones, each assigned to pickers | Multiple robots collaborate to pick items simultaneously |
| Efficiency | Moderate; depends on human picker speed | High; robots optimize routes and speed |
| Labor | Relies heavily on human workers | Minimal human involvement; requires robot operators |
| Scalability | Limited by picker availability and zone size | Highly scalable with additional robots |
| Accuracy | Variable; subject to human error | High; precision navigation and item handling |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, higher ongoing labor costs | High initial investment, lower labor costs over time |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple; requires basic layout planning | Complex; requires advanced technology and integration |
| Best Use Case | Medium-sized warehouses with diverse SKUs | Large-scale warehouses with high volume and repetitive tasks |
Introduction to Zone Picking and Robotic Swarm Picking
Zone Picking divides a warehouse into specific areas with workers assigned to each zone, optimizing efficiency by minimizing travel time and improving order accuracy. Robotic Swarm Picking employs multiple autonomous robots that collaborate to retrieve items simultaneously, enhancing speed and scalability in high-demand environments. Both methods aim to streamline order fulfillment but differ significantly in technology use and operational approach.
Core Principles of Zone Picking
Zone picking divides a warehouse into specific sections where workers are assigned to pick items within their designated area, optimizing order fulfillment by reducing picker travel distance and increasing efficiency. This method relies on clear zone boundaries, accurate inventory placement, and synchronized coordination among workers to minimize picking errors and improve throughput. Emphasizing human roles within fixed zones, zone picking contrasts with automated systems by leveraging spatial organization and manual execution for scalability in varying warehouse sizes.
How Robotic Swarm Picking Operates
Robotic Swarm Picking operates through a coordinated group of autonomous robots that navigate warehouse aisles to retrieve items simultaneously, optimizing speed and accuracy. Each robot uses advanced sensors and AI algorithms to communicate and avoid collisions, enabling efficient distribution of picking tasks without human intervention. This system reduces bottlenecks common in zone picking by dynamically allocating resources based on real-time demand and item location.
Key Differences Between Zone Picking and Robotic Swarm Picking
Zone picking divides a warehouse into distinct areas where workers pick items assigned to their specific zones, optimizing human labor through task specialization. Robotic swarm picking deploys multiple autonomous robots that collaboratively navigate and retrieve items across the entire warehouse, enhancing flexibility and reducing dependency on manual labor. Unlike zone picking's fixed human-operated structure, robotic swarm picking leverages dynamic coordination algorithms and real-time data to increase efficiency and scalability in complex order fulfillment environments.
Efficiency and Throughput Comparison
Zone Picking segments the warehouse into designated areas where workers pick items simultaneously, enhancing order accuracy but potentially slowing throughput due to human movement and handoffs. Robotic Swarm Picking employs multiple autonomous robots working collaboratively to retrieve items, significantly increasing picking speed and operational efficiency by minimizing travel time and reducing labor costs. Comparative studies show robotic swarm systems can boost throughput by up to 40% while maintaining high accuracy, making them ideal for high-volume warehouses aiming to optimize efficiency.
Technology Integration Requirements
Zone picking requires seamless integration of warehouse management systems (WMS) with real-time inventory tracking to coordinate human pickers efficiently within designated areas. Robotic swarm picking depends heavily on advanced robotics software, AI-driven navigation algorithms, and IoT connectivity to enable autonomous robots to collaborate and optimize picking routes dynamically. Both methods demand robust technology frameworks, but robotic swarm picking necessitates higher investments in sensor networks and machine learning infrastructure for effective operation.
Labor Implications and Workforce Adaptation
Zone picking requires workforce segmentation into skilled teams managing specific warehouse sections, increasing the need for targeted training and coordination. Robotic swarm picking reduces manual labor by leveraging autonomous robots, shifting human roles towards robot supervision, maintenance, and exception handling. Transitioning to robotic systems demands workforce adaptability, emphasizing technical skills development and continuous learning to manage advanced automation technologies effectively.
Scalability in Modern Warehousing
Zone picking optimizes scalability by dividing warehouses into distinct areas, enabling parallel processing and reducing worker travel time, which enhances overall efficiency in high-volume operations. Robotic swarm picking leverages multiple autonomous robots that collaboratively navigate and retrieve items, offering dynamic scalability to adapt quickly to fluctuating order volumes and complex inventory layouts. Integrating these solutions supports modern warehousing demands by balancing human oversight with robotic precision, ensuring scalable throughput and operational flexibility.
Suitability for Various Product Profiles
Zone picking excels in warehouses with varied product sizes and fragile items, allowing human pickers to handle complex sorting and delicate goods with accuracy. Robotic swarm picking is highly suitable for uniform, high-density, and small-to-medium-sized items, offering speed and efficiency in repetitive picking tasks. Choosing between these methods depends on product diversity, fragility, and order complexity to optimize warehouse throughput and accuracy.
Future Trends in Automated Picking Systems
Zone picking integrates human decision-making within designated warehouse areas, enhancing flexibility and accuracy, while robotic swarm picking leverages autonomous robots working collaboratively for scalable, high-speed item retrieval. Emerging trends indicate a shift towards hybrid systems combining zone picking's adaptability with robotic swarms' efficiency, driven by advances in AI, machine learning, and real-time data analytics. Future automated picking solutions will emphasize increased interoperability, predictive maintenance, and energy-efficient robotics to optimize throughput and reduce operational costs.
Related Important Terms
Zone-Based Order Fulfillment
Zone-based order fulfillment enhances efficiency by dividing the warehouse into specific zones where workers or robots pick items simultaneously, reducing travel time and increasing throughput. Compared to robotic swarm picking, zone picking offers more controlled and predictable workflows, facilitating better inventory management and quicker order accuracy in high-demand fulfillment centers.
Swarm Robotics Coordination
Swarm robotics coordination in warehousing leverages multiple autonomous robots working collaboratively to optimize zone picking efficiency, reducing navigation time and increasing order accuracy. This decentralized system dynamically allocates tasks based on real-time data, enhancing flexibility and scalability compared to traditional zone picking methods.
Dynamic Zone Allocation
Dynamic Zone Allocation in zone picking enhances labor efficiency by assigning workers to specific, adaptable zones based on real-time order volume and SKU demand, reducing travel time and increasing throughput. In contrast, robotic swarm picking leverages autonomous robots dynamically coordinating across zones to optimize path planning and workload distribution, enabling scalable and flexible fulfillment without manual zone reassignment.
Collaborative Picking Robots
Collaborative picking robots in zone picking systems enhance efficiency by dividing warehouse areas into specific zones where robots work simultaneously to retrieve items, minimizing human error and reducing picking time. Robotic swarm picking leverages multiple autonomous robots coordinating in real-time to dynamically allocate tasks and optimize pathways, increasing throughput and operational flexibility in complex warehousing environments.
Human-Robot Zonal Interface
Human-robot zonal interfaces in warehousing enable efficient coordination by assigning specific zones to both workers and robotic swarms, optimizing task allocation and reducing travel time. This hybrid approach enhances order accuracy and throughput by leveraging human flexibility alongside robotic precision within designated operational zones.
Real-Time Pick Path Optimization
Zone picking organizes workers into designated areas to streamline order fulfillment, but real-time pick path optimization is limited by manual coordination and static zone boundaries. Robotic swarm picking leverages autonomous robots with advanced algorithms to dynamically optimize pick paths in real time, enhancing efficiency, reducing travel distance, and increasing throughput in complex warehouse environments.
Decentralized Pick Task Assignment
Zone picking divides the warehouse into specific areas where workers independently fulfill orders, optimizing task efficiency through decentralized pick task assignment by minimizing cross-zone travel. Robotic swarm picking employs multiple autonomous robots coordinating in real time, utilizing decentralized algorithms to dynamically assign pick tasks based on proximity and workload, enhancing speed and flexibility in order fulfillment.
Zone Boundary Reconfiguration
Zone boundary reconfiguration in zone picking requires manual adjustments to optimize labor allocation and workflow efficiency, often causing downtime during the process. In contrast, robotic swarm picking utilizes autonomous systems that dynamically reconfigure zones in real-time, enhancing adaptability and reducing operational interruptions in warehousing environments.
Multi-Agent Robotic Swarm
Multi-agent robotic swarm picking leverages a coordinated group of autonomous robots working simultaneously to optimize order fulfillment speed and accuracy in warehousing environments. This dynamic system enhances scalability, reduces human labor dependency, and improves space utilization compared to traditional zone picking methods.
Autonomous Zone Picking
Autonomous Zone Picking utilizes robotic systems to navigate designated warehouse zones, optimizing order accuracy and reducing labor costs compared to traditional zone picking methods. This technology enhances real-time inventory management and accelerates fulfillment by coordinating multiple robots to work collaboratively within specific areas.
Zone Picking vs Robotic Swarm Picking Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com