Source reduction minimizes waste at its origin by designing products and processes that use fewer materials and generate less pollution. Ecodesign incorporates sustainability principles into product development, emphasizing energy efficiency, recyclability, and minimal environmental impact throughout the lifecycle. Both strategies aim to reduce waste but differ in approach: source reduction targets waste prevention at the production stage, while ecodesign optimizes the entire product lifecycle for environmental benefits.
Table of Comparison
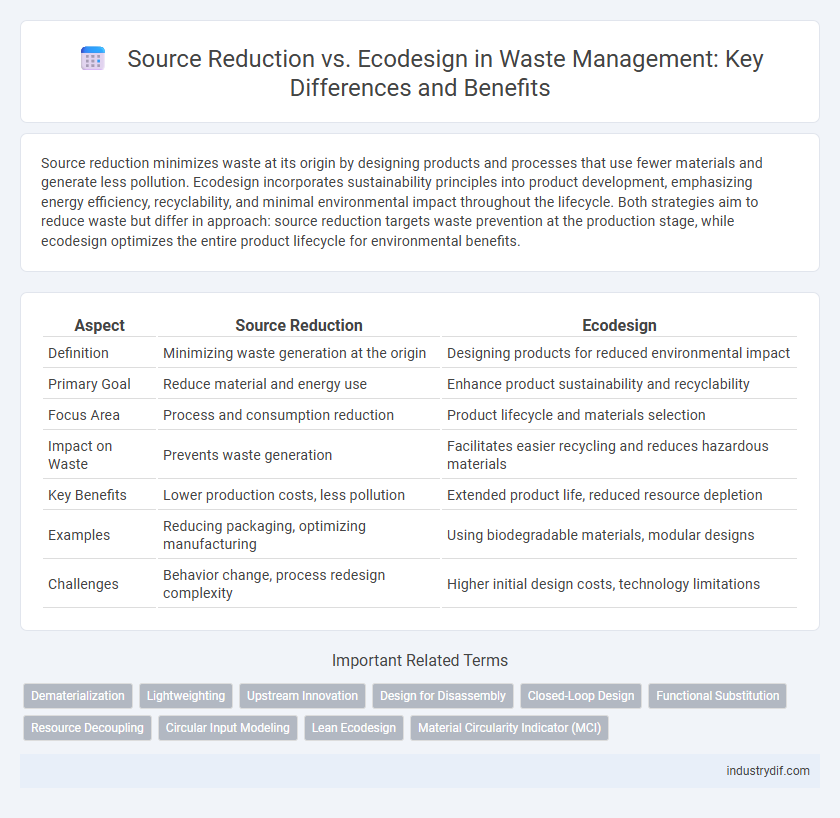
| Aspect | Source Reduction | Ecodesign |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimizing waste generation at the origin | Designing products for reduced environmental impact |
| Primary Goal | Reduce material and energy use | Enhance product sustainability and recyclability |
| Focus Area | Process and consumption reduction | Product lifecycle and materials selection |
| Impact on Waste | Prevents waste generation | Facilitates easier recycling and reduces hazardous materials |
| Key Benefits | Lower production costs, less pollution | Extended product life, reduced resource depletion |
| Examples | Reducing packaging, optimizing manufacturing | Using biodegradable materials, modular designs |
| Challenges | Behavior change, process redesign complexity | Higher initial design costs, technology limitations |
Defining Source Reduction in Waste Management
Source reduction in waste management refers to strategies aimed at minimizing the amount of waste generated at its origin by altering production processes, material selection, and product design. This approach reduces the need for waste treatment and disposal, conserving resources and lowering environmental impact. Source reduction contrasts with ecodesign by focusing specifically on decreasing waste volume before it enters the consumption cycle.
Understanding Ecodesign Principles
Ecodesign principles prioritize minimizing environmental impact by integrating sustainable materials, energy efficiency, and product longevity from the initial design phase. Source reduction targets waste minimization at the origin by altering production processes and material usage to reduce resource consumption and pollution. Understanding ecodesign enables manufacturers to create products that inherently generate less waste and facilitate easier recycling, complementing source reduction strategies for comprehensive waste management.
Key Differences Between Source Reduction and Ecodesign
Source reduction focuses on minimizing waste generation at the origin by using fewer materials or adopting efficient manufacturing processes, thereby preventing waste before it is created. Ecodesign emphasizes designing products with environmental impacts in mind, integrating aspects like recyclability, durability, and energy efficiency throughout the product lifecycle. Key differences lie in source reduction targeting waste volume reduction during production, while ecodesign addresses the entire lifecycle to enhance sustainability and reduce environmental footprint.
Environmental Impact of Source Reduction
Source reduction minimizes waste generation at the origin, significantly decreasing environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, and pollution compared to conventional waste management. It reduces the need for raw material extraction and lowers energy consumption throughout the product life cycle. Implementing source reduction strategies leads to substantial conservation of natural resources and mitigates landfill overflow, directly benefiting ecosystems and reducing carbon footprints.
Ecodesign’s Role in Product Lifecycle
Ecodesign plays a critical role in the product lifecycle by integrating environmental considerations at the earliest stages of product development, reducing waste generation and resource consumption. By optimizing materials, enhancing durability, and facilitating disassembly and recycling, ecodesign minimizes the environmental impact from production to disposal. Source reduction targets waste prevention by limiting materials used, but ecodesign achieves greater sustainability by embedding circular economy principles throughout the entire lifecycle.
Benefits of Integrating Source Reduction Strategies
Integrating source reduction strategies with ecodesign enhances material efficiency by minimizing waste generation during production and product lifecycle stages. This approach leads to significant cost savings and resource conservation, while reducing environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions and landfill dependency. Combining these methods supports sustainable manufacturing practices and promotes circular economy principles by extending product durability and facilitating easier recycling.
Ecodesign Standards and Regulations
Ecodesign standards and regulations prioritize minimizing environmental impact by integrating sustainability into product development, encouraging manufacturers to use eco-friendly materials and improve energy efficiency. These regulations often mandate lifecycle assessments and compliance with specific environmental criteria, driving innovation towards reduced waste generation at the source. Compared to source reduction, which targets waste prevention through consumption changes, ecodesign focuses on systemic product improvements aligned with regulatory frameworks to achieve sustainable resource management.
Case Studies: Source Reduction vs Ecodesign
Case studies on source reduction versus ecodesign reveal significant environmental and economic benefits tailored to product lifecycle management. Source reduction emphasizes minimizing waste generation at the origin by optimizing material use, exemplified by companies redesigning packaging to use fewer resources. Ecodesign incorporates sustainable materials and energy-efficient processes, proven to lower carbon footprints in industries like electronics and apparel, demonstrating complementary strategies for effective waste management.
Challenges in Implementing Source Reduction and Ecodesign
Implementing source reduction faces challenges including accurately measuring waste avoidance and overcoming resistance from manufacturers reliant on established production processes. Ecodesign implementation struggles with balancing eco-friendly materials and functionality while managing increased costs and limited consumer awareness. Both strategies require systemic changes in supply chains and strong regulatory support to achieve meaningful waste minimization.
Future Trends in Sustainable Waste Management Practices
Source reduction targets minimizing waste generation at its origin through material efficiency and process optimization, significantly reducing environmental impact. Ecodesign integrates sustainability into product development by emphasizing recyclability, resource conservation, and lifecycle analysis to prevent waste creation. Emerging trends highlight the convergence of digital technologies and circular economy principles to enhance both source reduction and ecodesign, driving innovative sustainable waste management solutions.
Related Important Terms
Dematerialization
Source reduction minimizes waste generation by designing products with fewer materials and simpler components, directly reducing resource consumption and environmental impact. Ecodesign incorporates dematerialization principles by optimizing product functionality and lifespan while using lightweight, recyclable materials to achieve sustainability goals.
Lightweighting
Source reduction minimizes waste generation by reducing material use at the origin, while ecodesign integrates environmental considerations into product development to enhance sustainability. Lightweighting, a key strategy in ecodesign, reduces material input and transportation emissions by creating lighter products without compromising functionality.
Upstream Innovation
Source reduction minimizes waste generation by redesigning products and processes to use fewer materials and create less pollution, while ecodesign incorporates environmental considerations into product development to enhance sustainability. Upstream innovation targets waste prevention at the design phase, emphasizing material efficiency, durability, and recyclability to reduce environmental impact before products reach consumers.
Design for Disassembly
Design for Disassembly prioritizes creating products that can be easily taken apart at the end of their lifecycle, significantly supporting source reduction by enabling efficient material recovery and reuse. This approach contrasts with traditional ecodesign by emphasizing modular components and standardized fasteners to minimize waste and facilitate circular economy practices.
Closed-Loop Design
Source reduction minimizes waste generation by designing products that use fewer materials and create less pollution throughout their lifecycle. Closed-loop design, a key aspect of ecodesign, emphasizes creating products that can be easily disassembled and recycled, enabling continuous material reuse and minimizing environmental impact.
Functional Substitution
Source reduction minimizes waste generation at its origin by altering production processes or materials, whereas ecodesign emphasizes functional substitution by redesigning products to use alternative materials or technologies that fulfill the same purpose with less environmental impact. Functional substitution in ecodesign enhances sustainability by replacing hazardous components with eco-friendly alternatives, reducing resource consumption and improving product lifecycle management.
Resource Decoupling
Source reduction minimizes waste generation by optimizing material use during production, directly contributing to resource decoupling by lowering raw material consumption per output unit. Ecodesign enhances product lifecycle efficiency through sustainable design and material selection, enabling long-term resource decoupling by facilitating reuse, recycling, and reducing environmental impact.
Circular Input Modeling
Source Reduction minimizes waste generation at its origin by optimizing resource use, while Ecodesign integrates sustainable materials and modularity to enhance product lifespan and recyclability; Circular Input Modeling supports both strategies by quantifying input flows to maximize material recirculation and reduce virgin resource dependency in circular economy systems.
Lean Ecodesign
Lean Ecodesign emphasizes minimizing waste and resource use at every stage of product development, enhancing sustainability more effectively than traditional source reduction methods. By integrating lean principles with ecodesign, companies achieve optimized material efficiency, reduced emissions, and cost savings while maintaining product quality and innovation.
Material Circularity Indicator (MCI)
Source reduction minimizes waste generation at its origin by using fewer materials, while ecodesign enhances product sustainability through innovative design strategies promoting reuse and recyclability. The Material Circularity Indicator (MCI) quantifies the circularity of materials in products, facilitating evaluation of both approaches by measuring how effectively materials are preserved within the lifecycle.
Source Reduction vs Ecodesign Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com