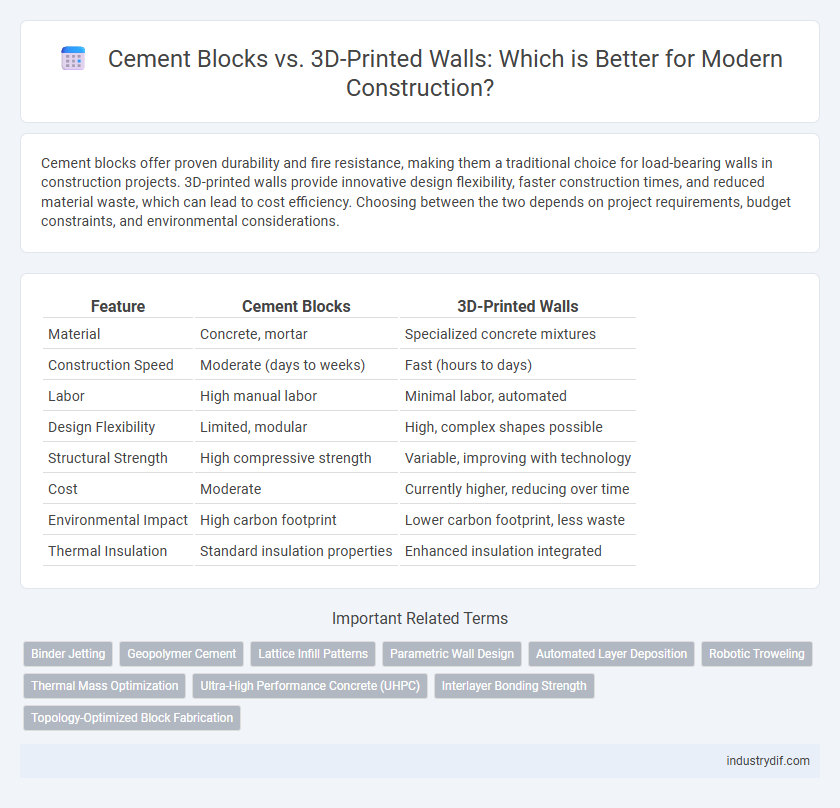
Cement blocks offer proven durability and fire resistance, making them a traditional choice for load-bearing walls in construction projects. 3D-printed walls provide innovative design flexibility, faster construction times, and reduced material waste, which can lead to cost efficiency. Choosing between the two depends on project requirements, budget constraints, and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cement Blocks | 3D-Printed Walls |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Concrete, mortar | Specialized concrete mixtures |
| Construction Speed | Moderate (days to weeks) | Fast (hours to days) |
| Labor | High manual labor | Minimal labor, automated |
| Design Flexibility | Limited, modular | High, complex shapes possible |
| Structural Strength | High compressive strength | Variable, improving with technology |
| Cost | Moderate | Currently higher, reducing over time |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint | Lower carbon footprint, less waste |
| Thermal Insulation | Standard insulation properties | Enhanced insulation integrated |
Introduction to Cement Blocks and 3D-Printed Walls
Cement blocks, composed mainly of cement, sand, and aggregate, have been a foundational building material due to their durability, fire resistance, and thermal insulation properties. In contrast, 3D-printed walls utilize advanced additive manufacturing technology to layer concrete or composite materials, allowing for highly customizable designs and reduced construction waste. Both methods offer unique structural advantages, with cement blocks excelling in traditional load-bearing applications and 3D-printed walls enabling rapid, precise building processes.
Material Composition and Properties
Cement blocks are composed primarily of Portland cement, aggregates, and water, offering high compressive strength and durability, making them ideal for load-bearing walls. In contrast, 3D-printed walls utilize a specially formulated concrete mixture often reinforced with additives like fibers or polymers to enhance flexibility and adhesion during the layer-by-layer printing process. The distinct material properties impact construction speed, thermal insulation, and structural performance, with 3D-printed walls promoting customization and reduced waste compared to traditional cement blocks.
Construction Speed and Efficiency
3D-printed walls significantly accelerate construction speed by automating the layering process, reducing build time by up to 50% compared to traditional cement block methods. The precision of 3D printing minimizes material waste and labor costs, enhancing overall efficiency on-site. Cement blocks require manual stacking and curing time, which prolongs project timelines and increases the likelihood of human error.
Structural Strength and Durability
Cement blocks offer proven structural strength and long-term durability in construction, with high resistance to compression and weathering. 3D-printed walls, made from layered concrete mixtures, provide consistent material density and enhanced design flexibility but require ongoing evaluation for load-bearing capacity and resilience under harsh environmental conditions. Advances in additive manufacturing aim to match or surpass traditional masonry performance by optimizing mix formulations and printing techniques to improve wall integrity and longevity.
Cost Comparison and Budget Impact
Cement blocks typically offer lower upfront costs due to widespread availability and established manufacturing processes, making them a budget-friendly choice for many construction projects. 3D-printed walls, while having higher initial investment in technology and equipment, can reduce labor expenses and material waste, potentially lowering overall project costs in larger scale developments. Evaluating cost efficiency requires analyzing project size, labor rates, and material savings to determine the most budget-effective option between traditional cement blocks and innovative 3D printing methods.
Environmental Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Cement blocks traditionally contribute to significant carbon emissions during production, whereas 3D-printed walls use precise layering techniques that drastically reduce material waste and lower environmental impact. The 3D printing process enables the use of sustainable, recyclable materials, improving energy efficiency and minimizing construction debris on-site. This emerging technology supports circular economy principles by optimizing resource use and decreasing landfill contributions compared to conventional cement block construction.
Flexibility in Design and Customization
Cement blocks offer standardized shapes and sizes, limiting design flexibility and customization in construction projects. In contrast, 3D-printed walls enable complex geometries and tailored architectural features, allowing for innovative, site-specific designs. This capability reduces material waste and accelerates project timelines while meeting unique aesthetic and structural requirements.
Labor Requirements and Skillsets
Cement blocks demand skilled masonry labor capable of precise handling, alignment, and mortar application to ensure structural integrity, often resulting in longer project timelines. In contrast, 3D-printed walls reduce manual labor needs by automating the layering process through advanced robotics, requiring operators with expertise in digital design, machine programming, and equipment maintenance. The shift from traditional craftsmanship to technology-driven construction alters labor dynamics, emphasizing digital proficiency over manual masonry skills.
Regulatory Approvals and Building Codes
Cement blocks benefit from well-established regulatory approvals and compliance with global building codes, ensuring their widespread acceptance in construction projects. In contrast, 3D-printed walls face evolving regulatory frameworks due to the novel nature of additive manufacturing technologies, requiring rigorous testing and certification processes. Builders must navigate these regulatory landscapes to guarantee structural safety, durability, and legal certification for both materials in accordance with local and international standards.
Future Trends in Wall Construction Technologies
Future trends in wall construction technologies reveal a shift from traditional cement blocks toward advanced 3D-printed walls, offering enhanced design flexibility and reduced material waste. Innovations in additive manufacturing enable precise layering of concrete mixtures, accelerating build times and improving structural integrity. Integration of smart sensors within 3D-printed walls further advances monitoring capabilities for durability and energy efficiency in modern construction projects.
Related Important Terms
Binder Jetting
Binder jetting in 3D-printed walls enables precise layering of cementitious material, reducing waste and accelerating construction compared to traditional cement blocks. This technology enhances structural uniformity and allows for complex geometries that conventional masonry methods struggle to achieve efficiently.
Geopolymer Cement
Geopolymer cement used in 3D-printed walls offers superior sustainability and durability compared to traditional cement blocks, reducing carbon emissions by up to 80% while enhancing structural integrity. Integrating geopolymer technology in construction optimizes material efficiency and accelerates project timelines through automated layering, outpacing manual block assembly in precision and strength.
Lattice Infill Patterns
Lattice infill patterns in 3D-printed walls optimize structural integrity and material efficiency by distributing loads evenly and reducing waste compared to traditional cement blocks. This innovative design enhances thermal insulation and accelerates construction time while maintaining strength and durability in building applications.
Parametric Wall Design
Parametric wall design in 3D-printed walls allows for highly customizable shapes and optimized material usage, enabling intricate geometries that traditional cement blocks cannot achieve. This technology enhances structural efficiency and reduces waste, making it a superior choice for innovative construction projects focused on sustainability and precision.
Automated Layer Deposition
Automated layer deposition in 3D-printed walls enables precise material placement, reducing waste and enhancing structural consistency compared to traditional cement blocks. This technology accelerates construction timelines while allowing complex, customizable designs that are difficult to achieve with conventional block masonry.
Robotic Troweling
Robotic troweling in 3D-printed walls ensures precision and consistency by automating the smoothing and finishing process, significantly reducing labor costs compared to traditional cement block construction. This technology enhances structural integrity and accelerates project timelines while minimizing human error and material waste in modern building methods.
Thermal Mass Optimization
Cement blocks provide high thermal mass, absorbing and slowly releasing heat, which stabilizes indoor temperatures and reduces energy consumption for heating and cooling. Compared to 3D-printed walls, traditional cement blocks often have superior thermal inertia, but advances in 3D printing materials and techniques are improving the thermal mass characteristics of printed structures.
Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC)
Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) used in 3D-printed walls offers superior strength, durability, and design flexibility compared to traditional cement blocks, enabling faster construction with reduced material waste. The enhanced mechanical properties of UHPC, including high compressive strength and improved durability, make it an ideal choice for innovative, sustainable building techniques in modern construction.
Interlayer Bonding Strength
Cement blocks exhibit strong interlayer bonding due to mortar adhesion that enhances overall wall stability, while 3D-printed walls rely on precise extrusion parameters and material composition to achieve optimal interlayer bonding strength crucial for structural integrity. Studies indicate that advancements in 3D printing technology can match or exceed the bonding strength of traditional cement block walls by improving layer consolidation and minimizing weak interfaces.
Topology-Optimized Block Fabrication
Topology-optimized block fabrication enhances cement block designs by minimizing material usage while maximizing structural strength and durability, leading to cost-effective and sustainable construction solutions. In contrast, 3D-printed walls offer precise geometric complexity and rapid onsite assembly but currently face limitations in material variability and long-term performance consistency compared to optimized cement blocks.
Cement Blocks vs 3D-Printed Walls Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com