On-site construction allows customization and immediate problem-solving directly at the building location, accommodating complex designs that require hands-on adjustments. Off-site manufacturing streamlines production by assembling components in controlled environments, improving quality control and reducing construction timelines. Integrating both methods optimizes project efficiency, balancing flexibility with precision and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
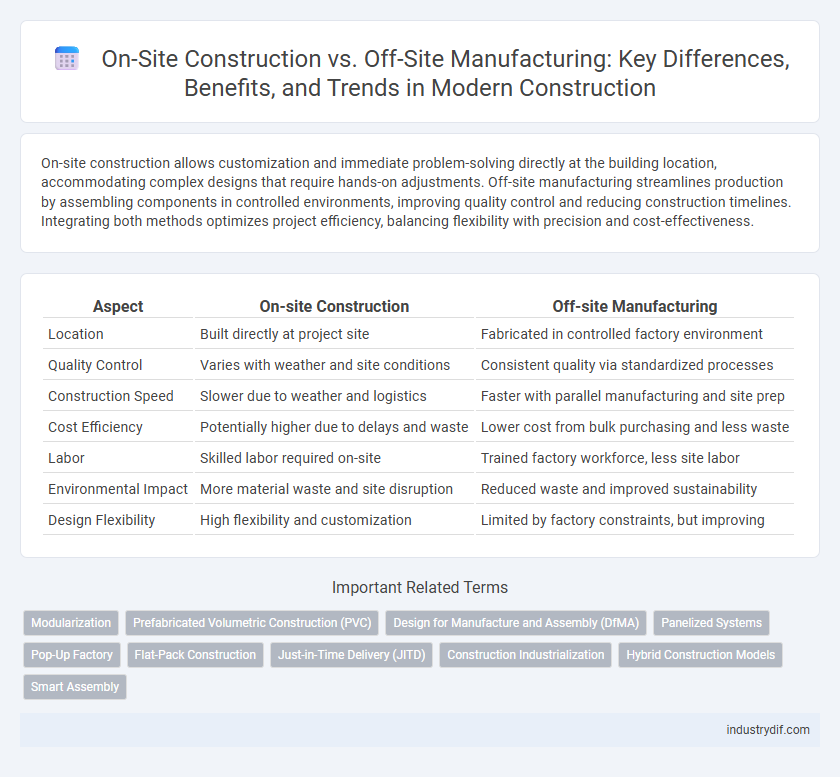
| Aspect | On-site Construction | Off-site Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Built directly at project site | Fabricated in controlled factory environment |
| Quality Control | Varies with weather and site conditions | Consistent quality via standardized processes |
| Construction Speed | Slower due to weather and logistics | Faster with parallel manufacturing and site prep |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher due to delays and waste | Lower cost from bulk purchasing and less waste |
| Labor | Skilled labor required on-site | Trained factory workforce, less site labor |
| Environmental Impact | More material waste and site disruption | Reduced waste and improved sustainability |
| Design Flexibility | High flexibility and customization | Limited by factory constraints, but improving |
Introduction to On-site Construction and Off-site Manufacturing
On-site construction involves building structures directly at the project location, allowing for customization and adaptation to site-specific conditions. Off-site manufacturing, also known as modular or prefabricated construction, entails producing building components in controlled factory settings before transporting them to the site for assembly. Both methods impact project timelines, cost efficiency, and quality control differently, shaping modern construction strategies.
Key Definitions and Industry Terminology
On-site construction involves assembling building components directly at the final location, utilizing traditional methods such as masonry, carpentry, and concrete pouring. Off-site manufacturing, also known as modular or prefabricated construction, refers to the production of building modules or panels in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the site for assembly. Key industry terms include "modular units," "panelized systems," "site work," and "factory fabrication," highlighting differences in workflow, quality control, and project timelines.
Comparative Construction Processes
On-site construction involves assembling structures directly at the project location, enabling real-time adjustments but often causing longer build times due to weather and logistical constraints. Off-site manufacturing, also known as modular construction, fabricates components in a controlled factory environment which enhances precision, reduces waste, and accelerates overall project timelines. The comparison highlights that off-site manufacturing significantly improves quality control and efficiency, while on-site construction offers greater flexibility for custom design changes during the build.
Speed and Project Timelines
On-site construction often faces delays due to weather, labor availability, and material delivery issues, impacting overall project timelines. Off-site manufacturing accelerates construction speed by enabling simultaneous site preparation and module fabrication in controlled factory environments. This parallel workflow significantly reduces on-site labor time and minimizes project duration, ensuring faster completion and earlier occupancy.
Cost Implications and Budget Efficiency
On-site construction often incurs higher labor costs and extended project timelines due to weather delays and material handling inefficiencies, impacting overall budget efficiency. Off-site manufacturing streamlines production through controlled environments, reducing waste and labor expenses, leading to significant cost savings and improved budget predictability. Companies leveraging modular construction report up to 20% reduction in total project costs and 30% faster completion times compared to traditional on-site methods.
Quality Control and Assurance
On-site construction often faces challenges in maintaining consistent quality control due to variable weather conditions and site constraints, leading to potential delays and defects. Off-site manufacturing enables stringent quality assurance through controlled factory environments, standardized processes, and advanced inspection technologies, resulting in higher precision and reduced rework. This shift enhances overall project reliability, minimizes material waste, and supports compliance with industry standards such as ISO 9001.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
On-site construction typically generates higher carbon emissions and construction waste due to inefficient material usage and extended project timelines. Off-site manufacturing reduces environmental impact by optimizing resource consumption, minimizing waste through precise fabrication, and lowering transportation emissions with modular assembly. Sustainable construction increasingly favors off-site methods to meet green building standards and reduce overall project carbon footprints.
Labor Requirements and Workforce Dynamics
On-site construction demands a diverse workforce skilled in various trades to handle dynamic, real-time challenges and complex site conditions, often leading to extended labor hours and higher labor costs. Off-site manufacturing centralizes labor in controlled factory environments, enabling streamlined workflows, consistent quality, and reduced dependency on weather, which optimizes workforce productivity and scheduling. The shift toward off-site production leverages automation and specialized labor, reducing onsite labor requirements and mitigating risks associated with fluctuating labor availability.
Flexibility in Design and Customization
On-site construction offers greater flexibility in design and customization by allowing real-time adjustments and adaptations to unique site conditions and client preferences. Off-site manufacturing provides efficiency and consistency but may limit design modifications once production begins due to standardized processes. Combining both methods can optimize customization while maintaining streamlined production timelines.
Future Trends in Construction Methods
On-site construction is increasingly integrating advanced digital tools such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and drone surveying to enhance precision and efficiency. Off-site manufacturing, including modular and prefabrication methods, is expanding rapidly due to its ability to reduce waste, shorten project timelines, and improve quality control in controlled factory environments. Future construction trends emphasize hybrid approaches combining on-site adaptability with off-site standardization, supported by automation, robotics, and sustainable material innovations.
Related Important Terms
Modularization
Modularization in construction enhances efficiency by fabricating building components off-site under controlled conditions, reducing time, waste, and weather-related delays compared to traditional on-site construction. This method allows for precise quality control, faster assembly on-site, and improved cost predictability, driving innovation in modern building projects.
Prefabricated Volumetric Construction (PVC)
Prefabricated Volumetric Construction (PVC) accelerates building timelines by assembling fully finished modules off-site under controlled factory conditions, ensuring higher quality and reducing on-site labor demands. This method contrasts with traditional on-site construction by minimizing weather-related delays and material waste while enhancing precision and safety standards.
Design for Manufacture and Assembly (DfMA)
Design for Manufacture and Assembly (DfMA) enhances efficiency by streamlining both on-site construction and off-site manufacturing processes, reducing complexity and minimizing waste through standardized components and modular design. Incorporating DfMA principles accelerates project timelines and improves quality control by enabling precise prefabrication in controlled environments before on-site assembly.
Panelized Systems
Panelized systems enhance construction efficiency by prefabricating wall panels off-site in controlled environments, reducing on-site labor and minimizing weather-related delays. This method improves quality control, accelerates project timelines, and lowers overall costs compared to traditional on-site construction techniques.
Pop-Up Factory
Pop-Up Factory revolutionizes the construction landscape by shifting off-site manufacturing directly to the building site, significantly reducing transportation costs and enabling real-time customization. This hybrid approach enhances quality control and accelerates project timelines by integrating precise module fabrication with immediate assembly in dynamic urban environments.
Flat-Pack Construction
Flat-pack construction streamlines on-site assembly by delivering pre-fabricated, modular components manufactured off-site, reducing labor costs and construction timelines. This method enhances quality control and minimizes material waste compared to traditional on-site construction techniques.
Just-in-Time Delivery (JITD)
Just-in-Time Delivery (JITD) in construction minimizes material waste and storage costs by synchronizing off-site manufacturing with on-site assembly schedules, enhancing project efficiency and reducing downtime. Off-site manufacturing enables precise inventory control and timely resource allocation, while on-site construction requires flexible JITD strategies to adapt to variable site conditions and labor availability.
Construction Industrialization
Construction industrialization enhances efficiency by integrating off-site manufacturing processes with traditional on-site construction, reducing project timelines and improving quality control. Prefabricated components produced in controlled factory environments lower labor costs and minimize on-site disruptions, accelerating overall building delivery.
Hybrid Construction Models
Hybrid construction models combine on-site construction and off-site manufacturing to optimize efficiency, reduce construction timelines, and improve quality control by prefabricating components in controlled factory environments. This approach leverages the precision of modular manufacturing with the flexibility of traditional site assembly, leading to cost savings and enhanced sustainability through waste reduction and better resource management.
Smart Assembly
Smart assembly in on-site construction integrates digital technologies to enhance precision and reduce labor inefficiencies, enabling real-time adjustments and project tracking. Off-site manufacturing leverages controlled factory environments and automation, producing modular components that streamline installation and improve quality consistency.
On-site Construction vs Off-site Manufacturing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com