Standard asphalt roofing offers durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation, making it a popular choice for many construction projects. Green roofing systems provide environmental benefits such as improved insulation, reduced urban heat island effect, and enhanced stormwater management. Choosing between these roofing options depends on project goals, budget constraints, and sustainability considerations.
Table of Comparison
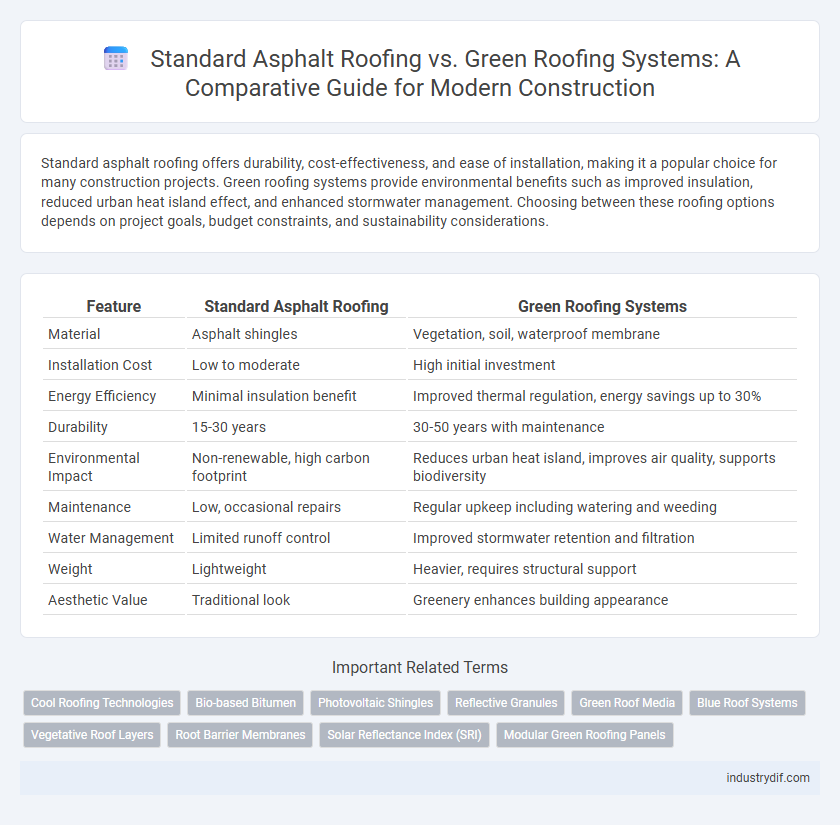
| Feature | Standard Asphalt Roofing | Green Roofing Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Asphalt shingles | Vegetation, soil, waterproof membrane |
| Installation Cost | Low to moderate | High initial investment |
| Energy Efficiency | Minimal insulation benefit | Improved thermal regulation, energy savings up to 30% |
| Durability | 15-30 years | 30-50 years with maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Non-renewable, high carbon footprint | Reduces urban heat island, improves air quality, supports biodiversity |
| Maintenance | Low, occasional repairs | Regular upkeep including watering and weeding |
| Water Management | Limited runoff control | Improved stormwater retention and filtration |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier, requires structural support |
| Aesthetic Value | Traditional look | Greenery enhances building appearance |
Overview of Standard Asphalt Roofing
Standard asphalt roofing, also known as asphalt shingle roofing, dominates the residential construction market due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Composed of fiberglass or organic mat infused with asphalt and topped with mineral granules, these shingles offer durability and weather resistance with an average lifespan of 15 to 30 years. This roofing system provides efficient water runoff, fire resistance, and compatibility with various architectural styles, making it a reliable choice for many construction projects.
Introduction to Green Roofing Systems
Green roofing systems incorporate vegetation layers that enhance energy efficiency and stormwater management in construction projects. Unlike standard asphalt roofing, green roofs provide natural insulation, reduce urban heat island effects, and promote biodiversity. These sustainable roofing solutions contribute to improved air quality and extend the lifespan of roofing materials.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Standard asphalt roofing primarily consists of petroleum-based materials such as fiberglass mats coated with asphalt and mineral granules, offering durability but limited environmental benefits. Green roofing systems integrate layers of waterproofing, root barriers, drainage, and vegetation, significantly enhancing urban biodiversity, reducing heat island effects, and improving air quality. Sustainable material choices in green roofs, including recycled substrates and native plant species, contribute to energy efficiency and long-term ecological balance.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Standard asphalt roofing systems typically have lower energy efficiency due to their dark surfaces absorbing more heat, leading to higher cooling costs. Green roofing systems enhance energy efficiency by providing natural insulation, reducing heat absorption, and lowering indoor temperatures. Studies show green roofs can decrease energy demands for cooling by up to 75%, significantly outperforming asphalt in energy savings.
Installation Processes and Techniques
Standard asphalt roofing installation involves layering sheets of asphalt-saturated organic or fiberglass mats, secured with nails or adhesive, followed by applying granules to protect from UV rays and extend durability. Green roofing systems require a multi-layered approach that includes waterproof membranes, root barriers, drainage layers, growing medium, and vegetation, demanding specialized knowledge for proper layering to ensure plant health and structural integrity. Both systems necessitate precise installation techniques, but green roofing requires more complex preparation and maintenance planning due to living components and additional load considerations.
Durability and Lifespan
Standard asphalt roofing offers a typical lifespan of 15 to 30 years, with durability affected by weather, UV exposure, and maintenance frequency. Green roofing systems, comprised of vegetation layers and waterproof membranes, extend roof life up to 40 years by protecting underlying materials from temperature extremes and physical damage. The natural insulation and moisture retention of green roofs reduce thermal stress and slow membrane degradation, resulting in enhanced durability compared to traditional asphalt options.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Standard asphalt roofing generates significant carbon emissions during production and contributes to urban heat islands due to its high heat absorption. In contrast, green roofing systems provide natural insulation, reduce stormwater runoff, and enhance urban biodiversity, leading to a lower environmental footprint. Life cycle assessments show that green roofs sequester carbon and improve air quality, making them a more sustainable option for environmentally conscious construction projects.
Maintenance Requirements
Standard asphalt roofing requires regular inspections for cracks, granule loss, and sealing to prevent water infiltration, with maintenance typically every 3-5 years. Green roofing systems demand frequent upkeep involving irrigation, vegetation care, and drainage monitoring to ensure plant health and structural integrity. Both roofing types necessitate tailored maintenance schedules, but green roofs often entail higher labor intensity due to biological components.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Standard asphalt roofing systems generally require lower upfront costs, ranging from $3 to $5 per square foot, making them cost-effective for initial installation. Green roofing systems typically incur higher initial investments, often between $10 and $25 per square foot, due to materials and structural requirements. However, green roofs offer long-term savings through reduced energy costs, extended roof lifespan, and stormwater management benefits, potentially offsetting the initial expense over 20 to 40 years.
Suitability for Different Building Types
Standard asphalt roofing excels in residential and commercial buildings requiring cost-effective, durable, and quick-to-install solutions, offering strong waterproofing and UV resistance. Green roofing systems are ideal for urban buildings seeking environmental benefits, such as improved insulation, stormwater management, and enhanced biodiversity, making them suitable for offices, schools, and eco-friendly residential projects. Choosing between the two depends on building design, load capacity, budget, and sustainability goals, with green roofs often requiring structural reinforcement for support.
Related Important Terms
Cool Roofing Technologies
Standard asphalt roofing absorbs heat, leading to higher energy consumption for cooling, whereas green roofing systems incorporate cool roofing technologies like reflective coatings and vegetation layers that reduce surface temperatures by up to 30%, enhancing urban heat island mitigation and improving building energy efficiency. Cool roofing materials, including solar-reflective shingles and green roofs with evapotranspiration effects, lower roof surface temperatures significantly, contributing to reduced air conditioning costs and increased roof lifespan.
Bio-based Bitumen
Standard asphalt roofing primarily utilizes petroleum-based bitumen, which offers durability and waterproofing but has significant environmental impacts due to fossil fuel extraction. Green roofing systems incorporating bio-based bitumen, derived from renewable organic materials such as vegetable oils or lignin, provide eco-friendly alternatives that enhance sustainability while maintaining comparable performance in weather resistance and longevity.
Photovoltaic Shingles
Standard asphalt roofing remains a cost-effective and widely-used option for durability and weather resistance, while green roofing systems incorporating photovoltaic (PV) shingles offer innovative energy generation and sustainable benefits by converting sunlight into electricity directly on the roof surface. PV shingles seamlessly blend with traditional roofing materials, enhancing a building's energy efficiency and reducing carbon footprint without compromising aesthetic appeal or structural integrity.
Reflective Granules
Standard asphalt roofing utilizes reflective granules designed to reduce heat absorption by reflecting sunlight, improving energy efficiency and extending roof lifespan. Green roofing systems incorporate reflective granules alongside vegetation layers, enhancing thermal performance and reducing urban heat island effects by combining natural insulation with solar reflectivity.
Green Roof Media
Green roof media consists of lightweight, engineered soil mixtures designed to support vegetation while providing excellent drainage, thermal insulation, and stormwater management. Unlike standard asphalt roofing, green roof systems enhance building sustainability by reducing heat island effect and improving energy efficiency through natural plant layers.
Blue Roof Systems
Blue roof systems, a specialized standard asphalt roofing solution, efficiently manage stormwater by temporarily storing rainwater on flat or low-slope roofs, reducing runoff and mitigating urban flooding risks. Unlike traditional green roofing systems that prioritize vegetation and ecosystem benefits, blue roofs emphasize hydraulic performance and integrate seamlessly with existing asphalt roofing materials for enhanced durability and cost-effectiveness.
Vegetative Roof Layers
Standard asphalt roofing primarily relies on layers of asphalt felt and shingles designed for waterproofing and durability, whereas green roofing systems incorporate multiple vegetative roof layers including a root barrier, drainage layer, growing medium, and living plants that enhance insulation, reduce stormwater runoff, and improve urban air quality. These vegetative layers not only extend the lifespan of the roofing membrane by shielding it from UV rays and extreme temperatures but also contribute to energy savings and biodiversity in urban construction projects.
Root Barrier Membranes
Standard asphalt roofing systems rely on durable asphaltic membranes known for waterproofing and weather resistance, but often lack protection against root penetration, which can damage roof integrity. Green roofing systems integrate specialized root barrier membranes composed of high-density polyethylene or polypropylene to prevent root infiltration, ensuring longevity and structural stability while supporting vegetation growth.
Solar Reflectance Index (SRI)
Standard asphalt roofing typically has a low Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) of around 0 to 20, absorbing significant heat and increasing cooling costs. In contrast, green roofing systems often feature high SRI values exceeding 50, reflecting more solar radiation and reducing urban heat island effects while enhancing energy efficiency.
Modular Green Roofing Panels
Standard asphalt roofing offers cost-effective, durable protection against weather elements, while modular green roofing panels provide enhanced insulation, stormwater management, and urban heat island mitigation through sustainable vegetation layers. Modular green roofing systems also contribute to improved air quality and biodiversity, making them a superior choice for eco-friendly building designs in urban construction projects.
Standard Asphalt Roofing vs Green Roofing Systems Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com