Stick-built construction offers greater flexibility for custom designs and on-site adjustments, making it ideal for unique or complex projects. Modular construction significantly reduces build time and waste by manufacturing components off-site in controlled environments before assembly. Both methods can deliver high-quality structures, but choosing between them depends on factors like budget, timeline, and project scope.
Table of Comparison
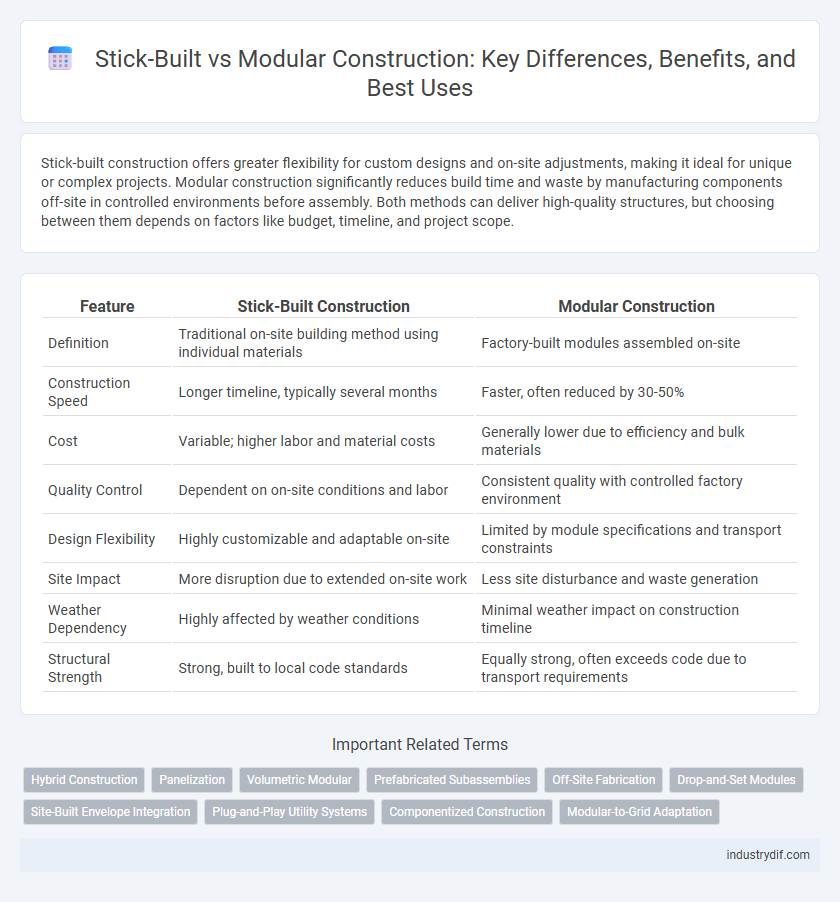
| Feature | Stick-Built Construction | Modular Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional on-site building method using individual materials | Factory-built modules assembled on-site |
| Construction Speed | Longer timeline, typically several months | Faster, often reduced by 30-50% |
| Cost | Variable; higher labor and material costs | Generally lower due to efficiency and bulk materials |
| Quality Control | Dependent on on-site conditions and labor | Consistent quality with controlled factory environment |
| Design Flexibility | Highly customizable and adaptable on-site | Limited by module specifications and transport constraints |
| Site Impact | More disruption due to extended on-site work | Less site disturbance and waste generation |
| Weather Dependency | Highly affected by weather conditions | Minimal weather impact on construction timeline |
| Structural Strength | Strong, built to local code standards | Equally strong, often exceeds code due to transport requirements |
Overview of Stick-Built and Modular Construction
Stick-built construction involves assembling a building piece by piece on-site using traditional materials like wood and steel, offering flexibility in design and customization. Modular construction fabricates building components in a controlled factory environment, enhancing quality control and reducing construction time through prefabrication. Both methods impact project timelines, labor costs, and site logistics differently, influencing the choice based on project scope and budget.
Key Differences Between Stick-Built and Modular Construction
Stick-built construction involves on-site building using traditional framing methods, allowing for greater customization and flexibility during the building process. Modular construction consists of factory-produced sections assembled on-site, significantly reducing construction time and minimizing weather-related delays. Cost efficiency, quality control, and faster project completion are primary advantages distinguishing modular from stick-built methods.
Cost Comparison: Stick-Built vs Modular Construction
Stick-built construction typically incurs higher labor costs due to extended build times on-site, with expenses averaging 10-25% more than modular construction. Modular construction reduces costs by streamlining production in controlled factory environments, often cutting total project expenses by 15-20%. Material waste and weather delays are minimized in modular methods, further decreasing overall costs compared to traditional stick-built projects.
Construction Timeline and Efficiency
Stick-built construction typically involves longer timelines due to on-site assembly of individual components, exposing projects to weather delays and labor variability. Modular construction significantly shortens timelines by fabricating sections off-site in controlled environments, allowing simultaneous site preparation and module fabrication. This method enhances overall project efficiency by reducing on-site labor needs and minimizing disruptions, leading to faster project completion and cost savings.
Material Quality and Sustainability
Stick-built construction often allows for more precise material selection and onsite quality control, ensuring durable and customized structures. Modular construction promotes sustainability by minimizing waste through factory-controlled production processes and enabling efficient use of recycled materials. Both methods contribute to environmentally responsible building practices, with modular construction typically offering faster implementation of green technologies.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
Stick-built construction offers superior design flexibility with customizable floor plans, materials, and finishes tailored to specific site conditions and client preferences. Modular construction, while faster and cost-effective, typically involves standardized design options limited by factory production constraints. Clients seeking unique architectural features and extensive customization usually prefer stick-built methods for their adaptability.
Building Codes and Regulatory Considerations
Stick-built construction must comply with local building codes throughout the entire site, requiring onsite inspections to ensure adherence to zoning, fire safety, and structural standards. Modular construction involves pre-fabricated modules built in a factory setting that must meet both factory and local building codes before transportation and final assembly on site. Regulatory considerations often favor modular construction for its controlled environment quality assurance but require careful coordination with local authorities to meet all final inspection and permitting requirements.
Labor Requirements and Skilled Workforce
Stick-built construction demands a larger, highly skilled workforce due to on-site framing, custom adjustments, and sequential labor-intensive tasks. Modular construction significantly reduces on-site labor by assembling pre-fabricated units in controlled factory environments, requiring fewer specialized trades and shorter project timelines. Labor cost savings and workforce efficiency make modular methods advantageous in urban areas with skilled labor shortages.
Site Preparation and Logistics
Stick-built construction requires extensive on-site preparation, including grading, foundation work, and material staging, which can extend project timelines and increase labor costs. Modular construction minimizes site disruption by delivering pre-fabricated sections assembled off-site, reducing on-site construction time and improving logistics efficiency. Efficient site preparation and streamlined logistics in modular projects lead to faster project completion and lower overall site management expenses.
Long-Term Performance and Resale Value
Stick-built construction offers superior long-term durability due to customizable materials and techniques tailored to local environmental conditions. Modular construction provides consistent quality control and faster build times, but potential limitations in customization may affect long-term adaptation and market appeal. Resale value tends to favor stick-built homes because buyers often perceive them as having higher craftsmanship and greater flexibility for future modifications.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Construction
Hybrid construction combines the precision and speed of modular construction with the flexibility and customization of stick-built methods, resulting in reduced on-site labor and shortened project timelines. This approach optimizes material usage and enhances quality control by prefabricating standardized components off-site while allowing for on-site adjustments to meet specific architectural requirements.
Panelization
Panelization in stick-built construction involves assembling wall and floor panels onsite, allowing for customization but often increasing labor costs and construction time. Modular construction leverages factory-built panels that are transported and assembled onsite, enhancing quality control, reducing waste, and accelerating project timelines significantly.
Volumetric Modular
Volumetric modular construction accelerates project timelines by assembling fully finished three-dimensional building sections off-site, reducing on-site labor and minimizing weather-related delays. Stick-built methods offer design flexibility and customization but typically extend construction schedules and increase labor costs compared to volumetric modular systems.
Prefabricated Subassemblies
Prefabricated subassemblies in stick-built construction involve on-site assembly of components like wall panels and trusses, allowing customization but extending build time. Modular construction uses factory-made modules with integrated systems, enhancing quality control and reducing on-site labor and overall project duration.
Off-Site Fabrication
Off-site fabrication in modular construction enables precise factory-controlled assembly, resulting in reduced construction time and minimized on-site disruptions compared to traditional stick-built methods. Stick-built construction relies heavily on on-site labor and materials handling, leading to variable weather impacts and extended project schedules.
Drop-and-Set Modules
Drop-and-set modules in modular construction significantly reduce on-site labor and construction time by delivering pre-fabricated, fully finished sections directly to the site, compared to traditional stick-built methods that require extensive on-site assembly. This approach enhances precision and consistency while minimizing weather-related delays and material waste, optimizing project timelines and cost-efficiency.
Site-Built Envelope Integration
Site-built envelope integration in stick-built construction allows for precise customization and seamless adaptation to complex site conditions, enhancing thermal performance and structural integrity. Modular construction often faces challenges with envelope continuity and on-site adjustments, potentially impacting energy efficiency and weather resistance.
Plug-and-Play Utility Systems
Plug-and-play utility systems in modular construction allow for pre-installed electrical, plumbing, and HVAC components that significantly reduce on-site labor and construction time compared to traditional stick-built methods. These systems enhance precision and minimize errors by integrating standardized modules assembled off-site, leading to faster project completion and lower overall costs.
Componentized Construction
Componentized construction involves assembling standardized building components off-site, enhancing quality control and reducing on-site labor compared to traditional stick-built methods. This approach accelerates project timelines, improves material efficiency, and minimizes waste, making it a sustainable alternative within modular construction practices.
Modular-to-Grid Adaptation
Modular-to-grid adaptation streamlines construction by enabling prefabricated modules to be precisely aligned with on-site structural grids, significantly reducing assembly time and labor costs. This integration enhances design flexibility and ensures faster project completion compared to traditional stick-built methods.
Stick-Built vs Modular Construction Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com