Stick-built construction offers greater flexibility and customization on-site, allowing builders to adapt designs as needed during the build process. Panelized construction speeds up the building timeline by using factory-made wall panels that are quickly assembled on-site, reducing labor costs and minimizing material waste. Choosing between stick-built and panelized construction depends on project complexity, budget constraints, and desired construction speed.
Table of Comparison
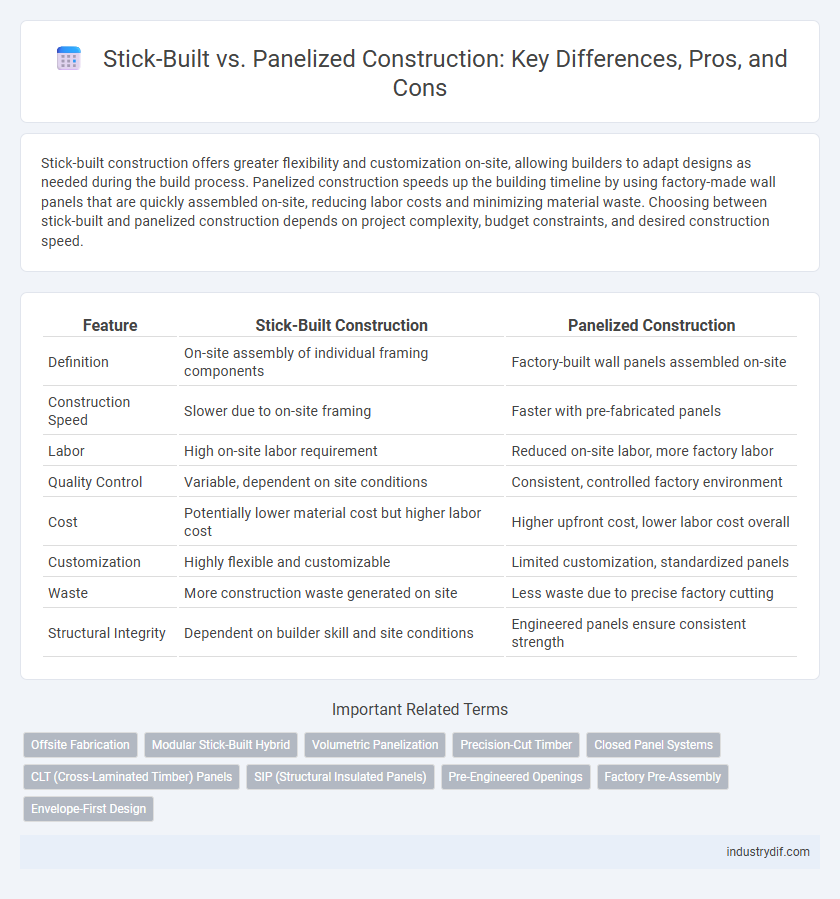
| Feature | Stick-Built Construction | Panelized Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-site assembly of individual framing components | Factory-built wall panels assembled on-site |
| Construction Speed | Slower due to on-site framing | Faster with pre-fabricated panels |
| Labor | High on-site labor requirement | Reduced on-site labor, more factory labor |
| Quality Control | Variable, dependent on site conditions | Consistent, controlled factory environment |
| Cost | Potentially lower material cost but higher labor cost | Higher upfront cost, lower labor cost overall |
| Customization | Highly flexible and customizable | Limited customization, standardized panels |
| Waste | More construction waste generated on site | Less waste due to precise factory cutting |
| Structural Integrity | Dependent on builder skill and site conditions | Engineered panels ensure consistent strength |
Introduction to Stick-Built and Panelized Construction
Stick-built construction involves assembling a building on-site using individual lumber pieces, offering high customization and flexibility in design modifications during the build. Panelized construction uses factory-manufactured wall panels and floor sections, enabling faster assembly and improved quality control through precise pre-fabrication. Both methods impact project timelines, labor requirements, and cost-effectiveness, making the choice crucial based on project scale and design complexity.
Core Definitions: Stick-Built vs Panelized
Stick-built construction involves assembling a structure entirely on-site using individual pieces of lumber, allowing flexibility in design adjustments during the building process. Panelized construction uses factory-built wall panels that are transported to the site and assembled, accelerating build times and improving quality control through standardized manufacturing. Both methods serve distinct project needs, with stick-built offering customization and panelized providing efficiency and consistency.
Historical Evolution of Construction Methods
Stick-built construction, characterized by on-site framing with individual studs and joists, has been the predominant method in North America since the 19th century due to its flexibility and local material use. Panelized construction emerged in the mid-20th century as an industrialized approach, utilizing factory-built wall panels to enhance speed and precision while reducing labor costs. The historical evolution from stick-built to panelized methods reflects advancements in manufacturing technology and the growing demand for sustainable, energy-efficient building practices.
Material Procurement and Handling
Material procurement for stick-built construction involves ordering individual components such as lumber, nails, and drywall, which requires precise timing to prevent onsite storage issues and reduce waste. Panelized construction streamlines handling by delivering pre-assembled wall panels, reducing labor costs and minimizing material damage during transportation. Efficient supply chain coordination in panelized methods enhances project timelines and ensures higher quality control compared to the fragmented deliveries typical in stick-built projects.
Construction Speed and Project Timelines
Stick-built construction requires more on-site labor and time due to individual framing of each component, often extending project timelines by several weeks. Panelized construction offers faster assembly as walls and floors are pre-fabricated in a factory, reducing on-site construction time by up to 50%. Accelerated timelines with panelized methods improve overall project efficiency and enable quicker occupancy dates.
Labor Requirements and Skillsets
Stick-built construction demands highly skilled carpenters capable of on-site framing, requiring precise measurements and adjustments throughout the build, which often extends project timelines. Panelized construction leverages factory-built wall panels, reducing on-site labor intensity and the need for advanced framing skills, accelerating assembly and enhancing consistency. Labor costs decrease with panelized methods due to streamlined workflows, while stick-built projects necessitate a broader range of expertise to manage variable site conditions and custom framing.
Quality Control and Precision
Stick-built construction allows for greater on-site customization but can suffer from inconsistencies due to variable craftsmanship and weather conditions. Panelized construction benefits from factory-controlled environments, ensuring higher precision and uniform quality in components. This controlled setting reduces errors and accelerates assembly, resulting in improved overall structural integrity.
Cost Implications and Budget Considerations
Stick-built construction typically incurs higher labor costs due to on-site assembly and longer build times, impacting overall budget flexibility. Panelized construction reduces labor expenses and project timelines by fabricating wall sections off-site, leading to more predictable budget management and potential cost savings. Material waste is minimized in panelized systems, offering economic efficiency compared to stick-built methods where on-site adjustments often increase expenses.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Stick-built construction typically generates more on-site waste and consumes greater energy during the building process, increasing its environmental footprint. Panelized construction utilizes factory-controlled settings to optimize material use, reduce waste, and improve energy efficiency, resulting in a more sustainable building method. The precision in panel fabrication also enhances thermal performance, lowering long-term energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Stick-built construction offers unparalleled customization and flexibility, making it ideal for unique architectural designs and on-site adjustments. Panelized construction excels in speed and efficiency by utilizing factory-built components, reducing labor costs and minimizing weather-related delays. Selecting the right method depends on project size, budget, timeline, and desired level of customization.
Related Important Terms
Offsite Fabrication
Offsite fabrication in panelized construction enhances precision and reduces onsite labor by assembling wall, floor, and roof panels in controlled factory environments, leading to faster project completion and less material waste compared to traditional stick-built methods. Stick-built construction relies heavily on onsite assembly, increasing susceptibility to weather delays and variability in craftsmanship, whereas panelized systems offer improved quality control and streamlined installation processes.
Modular Stick-Built Hybrid
Modular Stick-Built Hybrid construction combines the flexibility of traditional stick-built methods with the efficiency of panelized systems, enabling faster assembly on-site while maintaining customization options. This approach reduces labor costs and construction time by prefabricating wall panels and modules off-site, ensuring high quality control and minimizing weather-related delays.
Volumetric Panelization
Volumetric panelization in construction involves prefabricating entire 3D modules off-site, allowing for faster assembly and reduced on-site labor compared to traditional stick-built methods. This approach enhances quality control, minimizes material waste, and accelerates project timelines by delivering factory-built volumetric units ready for installation.
Precision-Cut Timber
Precision-cut timber enhances panelized construction by allowing factory-made wall and floor panels to fit together with exact measurements, reducing on-site labor and waste. Stick-built construction relies on individually cut pieces, which can lead to greater material variability and extended assembly times.
Closed Panel Systems
Closed panel systems in stick-built versus panelized construction offer enhanced precision and faster installation by assembling wall panels in a controlled factory environment before on-site delivery. These factory-built closed panels improve energy efficiency, reduce on-site labor costs, and minimize material waste compared to traditional stick-built framing methods.
CLT (Cross-Laminated Timber) Panels
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) panels in panelized construction offer enhanced precision, faster assembly, and superior structural strength compared to traditional stick-built methods. Utilizing prefabricated CLT panels reduces on-site labor costs and construction waste while improving energy efficiency through airtight building envelopes.
SIP (Structural Insulated Panels)
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) in panelized construction offer superior thermal insulation and faster assembly compared to traditional stick-built methods, reducing labor costs and construction time substantially. SIPs consist of rigid foam cores sandwiched between oriented strand boards (OSB), providing enhanced energy efficiency and airtightness crucial for sustainable building performance.
Pre-Engineered Openings
Pre-engineered openings in stick-built construction allow for custom adjustments on-site, providing flexibility but potentially increasing labor time and costs. In panelized construction, these openings are precisely manufactured in a controlled environment, enhancing installation speed and accuracy while reducing onsite modifications.
Factory Pre-Assembly
Factory pre-assembly in panelized construction significantly reduces on-site labor time and improves quality control by assembling wall panels, floors, and roof trusses under controlled factory conditions. Stick-built construction requires most framing to be completed entirely on-site, which can increase exposure to weather delays and inconsistencies in assembly precision.
Envelope-First Design
Envelope-first design in stick-built construction allows precise customization of air and moisture barriers, optimizing thermal performance and reducing energy loss through tailored wall assemblies. Panelized construction benefits from envelope-first planning by integrating pre-fabricated, high-performance panels that ensure consistent insulation and airtightness, accelerating build times while maintaining superior envelope integrity.
Stick-Built vs Panelized Construction Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com