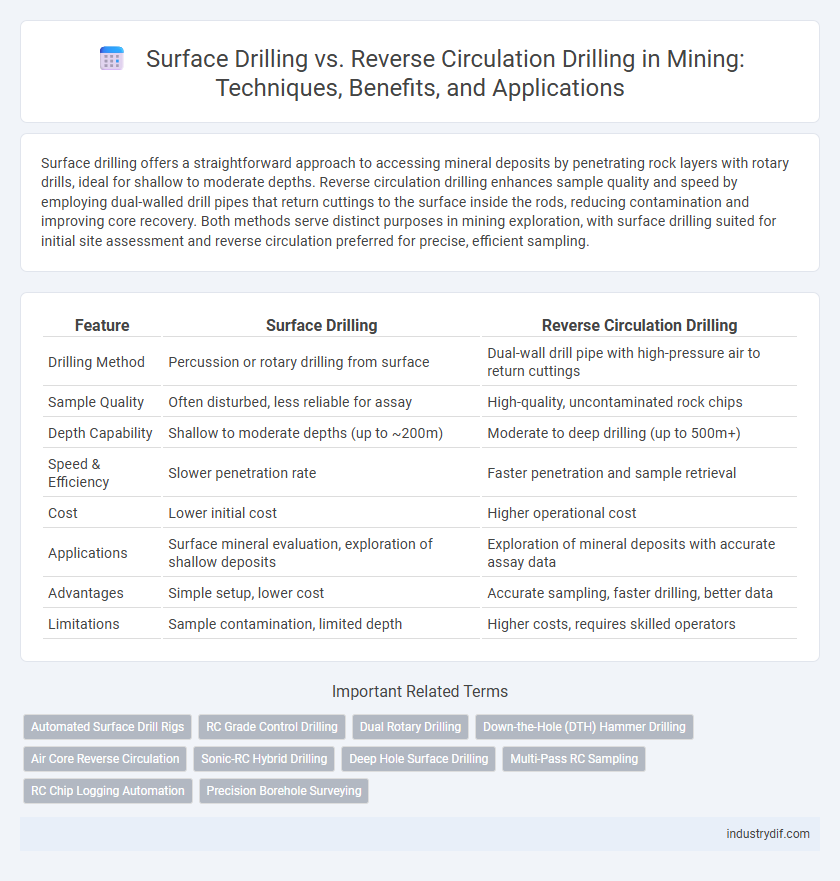
Surface drilling offers a straightforward approach to accessing mineral deposits by penetrating rock layers with rotary drills, ideal for shallow to moderate depths. Reverse circulation drilling enhances sample quality and speed by employing dual-walled drill pipes that return cuttings to the surface inside the rods, reducing contamination and improving core recovery. Both methods serve distinct purposes in mining exploration, with surface drilling suited for initial site assessment and reverse circulation preferred for precise, efficient sampling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Surface Drilling | Reverse Circulation Drilling |
|---|---|---|
| Drilling Method | Percussion or rotary drilling from surface | Dual-wall drill pipe with high-pressure air to return cuttings |
| Sample Quality | Often disturbed, less reliable for assay | High-quality, uncontaminated rock chips |
| Depth Capability | Shallow to moderate depths (up to ~200m) | Moderate to deep drilling (up to 500m+) |
| Speed & Efficiency | Slower penetration rate | Faster penetration and sample retrieval |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher operational cost |
| Applications | Surface mineral evaluation, exploration of shallow deposits | Exploration of mineral deposits with accurate assay data |
| Advantages | Simple setup, lower cost | Accurate sampling, faster drilling, better data |
| Limitations | Sample contamination, limited depth | Higher costs, requires skilled operators |
Overview of Surface Drilling and Reverse Circulation Drilling
Surface drilling involves creating boreholes using rotary or percussion methods to access mineral deposits near the earth's surface, commonly employed for exploration and open-pit mining. Reverse Circulation (RC) drilling utilizes dual-walled drill pipes to return rock cuttings to the surface, offering faster sample retrieval and reduced contamination compared to traditional surface drilling. Both techniques are essential for resource evaluation, with RC drilling providing higher-quality samples and improved efficiency in mineral assay processes.
Key Differences Between Surface Drilling and RC Drilling
Surface drilling involves using large rotary drills to bore into the earth's surface for exploration and extraction, often producing large diameter holes ideal for mining infrastructure. Reverse circulation (RC) drilling uses dual-walled drill rods to simultaneously drill and retrieve rock samples, offering faster sample recovery with reduced contamination compared to surface drilling. RC drilling is preferred for precise mineral exploration due to its efficiency in collecting high-quality, uncontaminated samples, while surface drilling is suited for creating access or large-scale excavation.
Applications and Suitability in Mining Operations
Surface drilling excels in large-scale open-pit mining for extracting bulk samples and creating blast holes, especially in hard rock environments, while reverse circulation drilling is highly suitable for mineral exploration and geotechnical investigations due to its efficiency in retrieving uncontaminated samples from unconsolidated or mixed ground conditions. Reverse circulation drilling reduces sample contamination and improves depth accuracy, making it ideal for exploration targeting precious metals and base metals, whereas surface drilling's adaptability supports a wide range of operational scales and terrain types. Both methods complement mining operations by addressing distinct geological challenges and project phases, optimizing resource evaluation and extraction efficiency.
Equipment and Technology Comparison
Surface drilling utilizes large-diameter drill bits and rotary drill rigs designed for deep-hole drilling on open-pit operations, enabling efficient extraction of ore bodies near the surface. Reverse Circulation (RC) drilling employs dual-walled drill pipes and a specialized hammer bit, facilitating high-pressure air circulation that rapidly returns rock cuttings to the surface for immediate sampling and reduced contamination. The advanced cyclone and sample collection technology integrated into RC rigs significantly improves sample quality and drilling speed compared to traditional surface rotary drilling equipment.
Accuracy and Sample Quality Considerations
Surface drilling offers high accuracy in depth and location control, ideal for precise geological mapping. Reverse circulation drilling provides superior sample quality by minimizing contamination and delivering uncontaminated, representative rock cuttings. The choice depends on balancing accuracy needs with sample integrity for effective mineral exploration.
Cost Implications and Operational Efficiency
Surface drilling typically incurs higher operational costs due to slower penetration rates and increased maintenance requirements, while reverse circulation drilling offers significant cost savings through faster drilling speeds and reduced sample contamination. Reverse circulation drilling enhances operational efficiency by delivering continuous, high-quality samples, minimizing downtime, and lowering fuel consumption. The choice between the two methods impacts overall project economics, with reverse circulation drilling often favored for its balance of cost-effectiveness and productivity in exploration and resource evaluation.
Environmental and Safety Aspects
Surface drilling techniques minimize ground disturbance and reduce dust emissions, enhancing environmental protection measures in mining operations. Reverse circulation drilling significantly lowers the risk of sample contamination and improves occupational safety by reducing exposure to airborne particulates. Both methods contribute to sustainable mining practices, with reverse circulation drilling offering better control over material handling and waste containment.
Depth Penetration and Geological Adaptability
Surface drilling typically achieves greater depth penetration in hard rock formations, making it suitable for deep exploration targets, while reverse circulation drilling excels in geological adaptability by efficiently handling unconsolidated or mixed materials due to its dual-tube system that minimizes sample contamination. Reverse circulation drilling offers faster sample retrieval and improved accuracy in varied geological conditions, whereas surface drilling methods provide more precise control in stable, homogeneous rock masses. Choosing between the two methods depends on the specific depth requirements and geological complexity of the mining site, optimizing resource evaluation and operational efficiency.
Maintenance and Downtime Factors
Surface drilling requires frequent maintenance of drill bits and rig components due to high wear from continuous exposure to abrasive rock surfaces, directly impacting operational downtime. Reverse circulation drilling experiences reduced maintenance intervals because its dual-wall drill rods minimize contamination and wear, leading to higher efficiency and less downtime. Choosing reverse circulation drilling can enhance productivity by decreasing equipment failures and maintenance-related interruptions in mining operations.
Choosing the Right Drilling Method for Your Mining Project
Surface drilling offers versatility for varied terrain and is ideal for initial exploration and bulk sampling due to its ability to penetrate deep and extract large core samples. Reverse circulation drilling provides faster sample retrieval and improved sample quality by minimizing contamination, making it suitable for resource definition and grade control in mineral deposits. Selection depends on project goals, budget constraints, and the specific geology of the mining site to optimize operational efficiency and data accuracy.
Related Important Terms
Automated Surface Drill Rigs
Automated surface drill rigs enhance efficiency and safety in surface drilling by integrating advanced robotics and real-time data analytics, minimizing human error and operational downtime. Compared to reverse circulation drilling, these rigs offer faster setup times and improved precision in extracting bulk samples while reducing environmental impact through optimized resource use.
RC Grade Control Drilling
RC grade control drilling offers precise and rapid sampling by using dual-walled drill pipes to recover uncontaminated rock chips, enabling accurate ore body delineation and efficient resource estimation, which is essential in mining operations. Surface drilling methods, while versatile for exploration and large-scale excavation, often lack the targeted sampling accuracy and speed that RC drilling provides for grade control purposes.
Dual Rotary Drilling
Dual rotary drilling combines surface drilling and reverse circulation methods to enhance efficiency in mining operations by simultaneously employing rotary drilling to penetrate hard rock and reverse circulation to extract cuttings rapidly. This technique improves sample quality and increases drilling speed, making it ideal for mineral exploration and ore evaluation in diverse geological conditions.
Down-the-Hole (DTH) Hammer Drilling
Down-the-hole (DTH) hammer drilling excels in both surface and reverse circulation drilling by delivering high penetration rates and optimal drilling accuracy through its percussion and rotary action applied directly at the bottom of the hole. This technology outperforms traditional surface methods by minimizing drill string wear and enabling efficient cuttings removal, making it ideal for hard rock formations and large-diameter boreholes in mining operations.
Air Core Reverse Circulation
Air core reverse circulation drilling offers greater efficiency in surface drilling by using dual-wall drill rods to extract rock samples with minimal contamination, enhancing mineral exploration accuracy. This method reduces sample dilution compared to traditional surface drilling, improving the detection of ore boundaries and geological structures.
Sonic-RC Hybrid Drilling
Sonic-RC Hybrid Drilling combines the high penetration rates of sonic drilling with the sample integrity and depth capacity of reverse circulation (RC) drilling, optimizing mineral exploration efficiency. This technique improves core recovery, reduces contamination, and enables precise geological data collection in challenging surface mining conditions.
Deep Hole Surface Drilling
Deep hole surface drilling uses large-diameter rotary drill rigs to create deep vertical or inclined boreholes essential for mineral exploration and blasting operations in mining, enabling precise extraction of subsurface resources. Reverse circulation drilling, while efficient for material retrieval and sampling, typically handles shallower depths and smaller diameters, making deep hole surface drilling the preferred method for high-depth, large-volume mining projects requiring detailed geological data.
Multi-Pass RC Sampling
Multi-Pass Reverse Circulation (RC) sampling offers enhanced sample recovery and reduced contamination compared to traditional surface drilling methods by utilizing multiple passes to ensure representative ore sampling. This technique improves grade control accuracy and operational efficiency in open-pit mining by delivering higher quality samples with minimized sample bias.
RC Chip Logging Automation
Reverse Circulation (RC) drilling offers significant advantages over surface drilling by producing clean, uncontaminated rock chips that enable more precise geological analysis. Automation in RC chip logging accelerates sample processing, improves data accuracy, and enhances decision-making efficiency in mineral exploration projects.
Precision Borehole Surveying
Surface drilling offers accurate borehole positioning but can suffer from deviations due to uneven terrain, whereas Reverse Circulation Drilling enables more precise borehole surveying by directly sampling geological strata and minimizing contamination. The RC method improves data quality and spatial resolution, optimizing mineral resource modeling and reducing exploration costs.
Surface Drilling vs Reverse Circulation Drilling Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com